Lean Six Sigma - Holistic View (PowerPoint PPTX Slide Deck)
PowerPoint (PPTX) 146 Slides
LEAN PPT DESCRIPTION
We Can Define LEAN :
The methodology of increasing the speed of production by eliminating process steps which do not add value
• those which delay the product or service
• those which deal with the waste and rework of defects along the way
We Can Define Six Sigma :
a highly structured strategy for acquiring, assessing, and applying customer, competitor, and enterprise intelligence for the purposes of product, system or enterprise innovation and design.
We Can Define Lean Six Sigma or Lean Sigma :
A management philosophy and disciplined problem-solving METHODOLOGY backed by powerful tools using a cross-functional team approach to eliminate waste and reduce service errors / process defects to 3.4 ppm opportunities or less ("world-class").
Finally, We Can Define Design For Six Sigma :
Applications of Six Sigma that focus on the design or redesign of products and services and their enabling processes so that from the beginning customer needs and expectations are fulfilled
are known as Design for Six Sigma or DFSS.
The aim of DFSS is to create designs that are resource efficient, capable of exceptionally high yields, and are robust to process variations. This aim produces a recasting of DMAIC that can be
characterized as: Define-Measure-Analyze-Design-Verify (DMADV) or as Invention-Innovation-Design-Optimize-Verify (I2DOV) or as CDOV.
This work gives you the holistic view and the fundamentals of all these interrelated mindsets and approaches.
The pptx document is easily customizable, content can be removed (or skipped over during presentation). Plenty of graphics are included in order to get the holistic vision.
Got a question about the product? Email us at support@flevy.com or ask the author directly by using the "Ask the Author a Question" form. If you cannot view the preview above this document description, go here to view the large preview instead.
MARCUS OVERVIEW
This synopsis was written by Marcus [?] based on the analysis of the full 146-slide presentation.
Executive Summary
The "Lean Six Sigma - Holistic View" presentation provides a comprehensive overview of Lean and Six Sigma methodologies, emphasizing their synergy for process improvement. Developed by experts with experience at leading consulting firms, this deck equips corporate executives and integration leaders with the tools to enhance operational efficiency and quality. By understanding Lean principles and Six Sigma strategies, users can effectively eliminate waste, reduce defects, and foster a culture of continuous improvement within their organizations.
Who This Is For and When to Use
• Corporate executives overseeing operational excellence initiatives
• Integration leaders managing process improvement projects
• Quality assurance teams focused on defect reduction
• Project managers implementing Lean Six Sigma methodologies
• Change management professionals driving organizational transformation
Best-fit moments to use this deck:
• During strategic planning sessions to align on process improvement goals
• In training workshops for teams adopting Lean Six Sigma practices
• When initiating projects aimed at enhancing product quality and operational efficiency
• To facilitate discussions on integrating customer feedback into design processes
Learning Objectives
• Define Lean and Six Sigma principles and their applications in business processes
• Identify and eliminate non-value-added activities in workflows
• Analyze process performance using statistical tools and methodologies
• Develop a culture of continuous improvement through Lean Six Sigma practices
• Implement Design for Six Sigma (DFSS) to enhance product and process design
• Establish metrics to measure process capability and performance
Table of Contents
• Understanding Lean (page 3)
• Understanding Six Sigma (page 10)
• Lean Six Sigma Synergy (page 20)
• Design for Six Sigma (page 30)
• Lessons Learned (page 40)
• The People of Six Sigma (page 50)
Primary Topics Covered
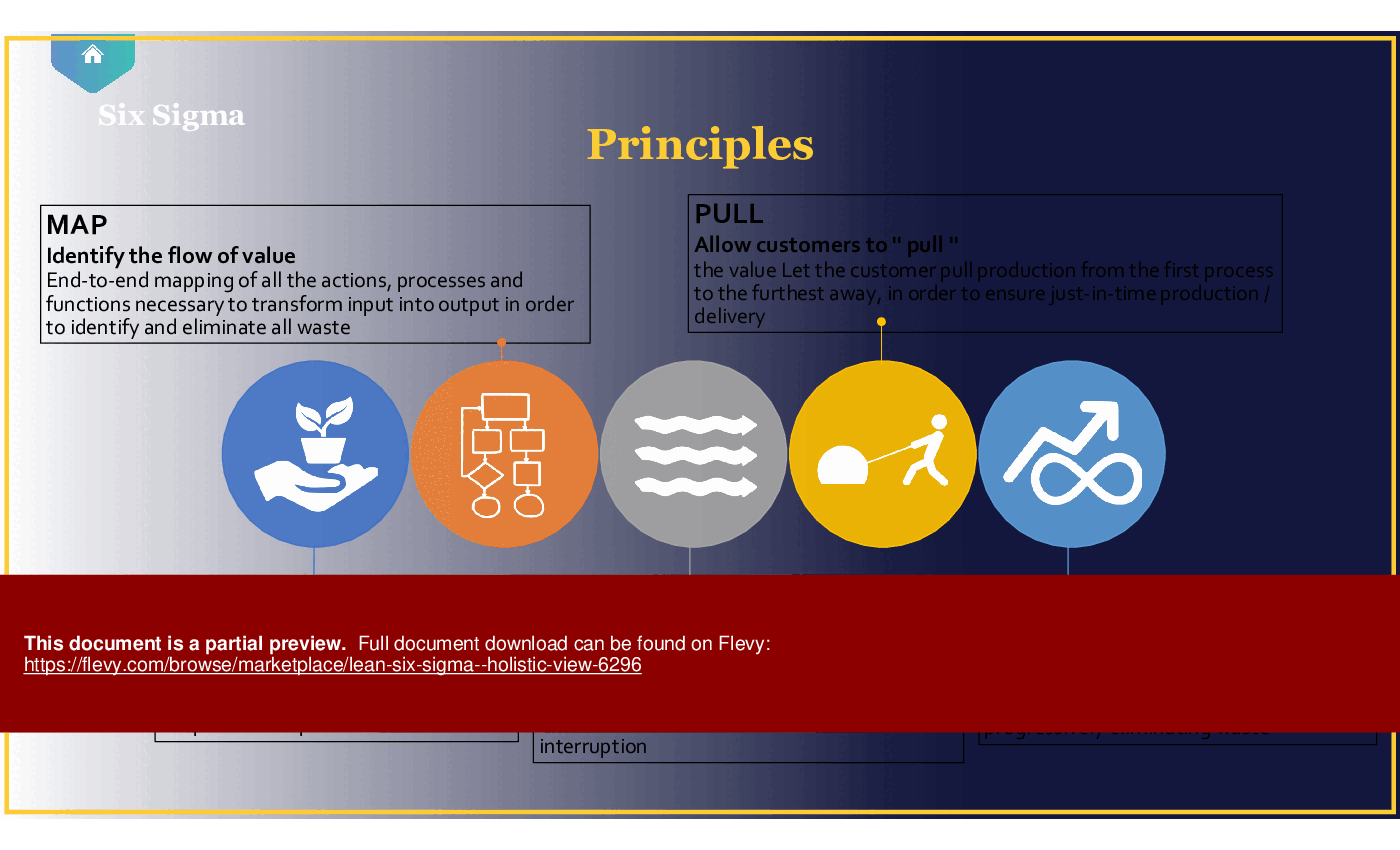
• Understanding Lean - Lean focuses on eliminating waste and enhancing the speed of production by streamlining processes and improving flow.
• Understanding Six Sigma - Six Sigma employs a structured approach to improve quality by reducing process variation and defects, aiming for near-perfect performance.
• Lean Six Sigma Synergy - The integration of Lean and Six Sigma methodologies enhances both efficiency and quality, creating a robust framework for continuous improvement.
• Design for Six Sigma - DFSS emphasizes designing processes and products that meet customer requirements from the outset, ensuring high quality and efficiency.
• Lessons Learned - Insights from implementing Lean Six Sigma initiatives that highlight best practices and common pitfalls.
• The People of Six Sigma - Roles and responsibilities of key stakeholders, including Champions, Black Belts, and Green Belts, in driving Six Sigma projects.
Deliverables, Templates, and Tools
• Lean process mapping templates for visualizing workflows
• Six Sigma DMAIC and DMADV frameworks for structured problem-solving
• Statistical tools for measuring process capability and performance
• Training materials for Lean Six Sigma practitioners
• Project charters and documentation templates for Six Sigma initiatives
• Customer feedback analysis tools for integrating Voice of the Customer (VOC)
Slide Highlights
• Overview of Lean principles and their historical context
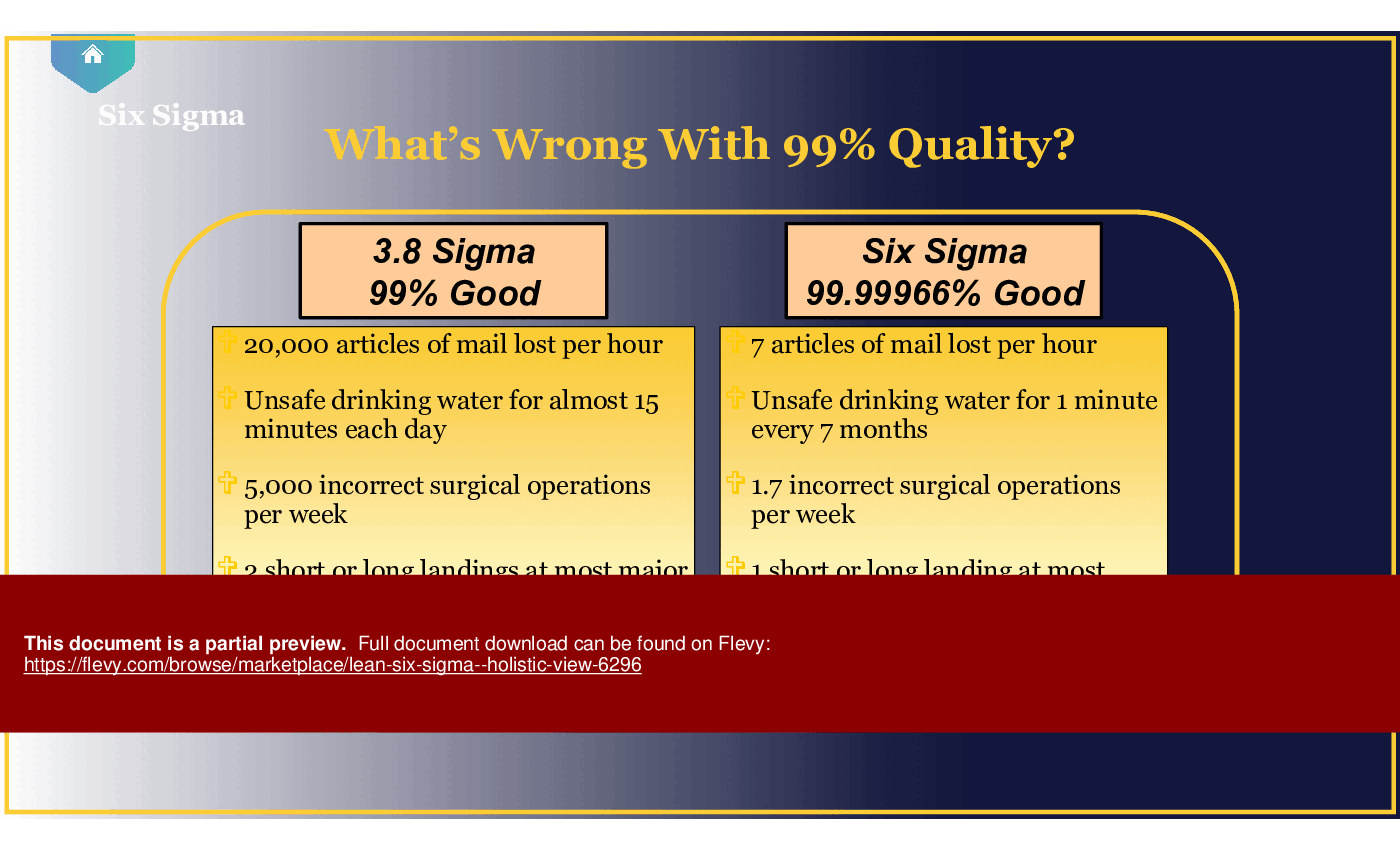
• Key Six Sigma metrics and the significance of achieving 3.4 defects per million opportunities
• Synergy between Lean and Six Sigma methodologies illustrated with practical examples
• Detailed explanation of the Design for Six Sigma process and its phases
• Success stories and lessons learned from organizations implementing Lean Six Sigma
Potential Workshop Agenda
Lean Six Sigma Overview Session (90 minutes)
• Introduction to Lean and Six Sigma principles
• Discussion on the synergy between Lean and Six Sigma
• Case studies of successful Lean Six Sigma implementations
Practical Application Workshop (120 minutes)
• Hands-on exercises in process mapping and identifying waste
• Group activities to apply DMAIC and DMADV methodologies
• Development of action plans for upcoming Lean Six Sigma projects
Customization Guidance
• Tailor the presentation to reflect specific organizational goals and industry context
• Adjust examples and case studies to align with the audience's experience and challenges
• Incorporate company-specific metrics and performance indicators into discussions
Secondary Topics Covered
• The role of leadership in fostering a Lean Six Sigma culture
• Techniques for sustaining improvements over time
• The importance of cross-functional collaboration in Lean Six Sigma projects
• Tools for measuring customer satisfaction and process performance
Topic FAQ
What are the core phases of the DMAIC methodology and what does each phase do?
DMAIC stands for Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control; it is a five-phase Six Sigma roadmap for improving existing processes by defining the problem and CTQs, measuring current performance, analyzing root causes, implementing improvements, and sustaining gains, ending with the Control phase in a 5-phase DMAIC approach.How does Lean complement Six Sigma in process improvement work?
Lean targets waste elimination and flow improvements while Six Sigma focuses on reducing variation and defects; combined, they enhance both speed and quality by using tools like value stream mapping to remove non-value activities and SPC to control variability, with value stream mapping as a common Lean tool.When should an organization use Design for Six Sigma (DFSS) instead of DMAIC?
DFSS is used when designing or redesigning products and processes to meet customer requirements from the outset; it follows DMADV (Define, Measure, Analyze, Design, Verify) or alternative recastings like I2DOV, and is appropriate during new product/process design using DMADV.What should I look for when selecting a Lean Six Sigma slide deck or template for workshops?
Choose materials that explain Lean and Six Sigma concepts, present DMAIC and DMADV frameworks, include process-mapping templates, statistical measurement tools, training modules, and project-charter examples; a useful reference set will explicitly include DMAIC and DMADV frameworks.How can organizations measure the value or ROI of Lean Six Sigma initiatives?
Value is typically tracked via KPIs such as defect rates, cycle time reductions, process capability indices, and customer satisfaction scores; many Six Sigma programs benchmark toward near-zero defects, with the 3.4 defects per million opportunities (DPMO) target cited as a quality benchmark.What practical first steps should a manufacturing team take to reduce defects using Lean Six Sigma?
Begin with Define and Measure activities: map the process with SIPOC and value stream mapping, identify CTQs, collect baseline data with SPC, and perform FMEA to prioritize risks, proceeding into Analyze and Improve after initial measurement in the DMAIC Define and Measure phases.For a post-merger integration, how can Lean Six Sigma help align processes across organizations?
Use process mapping and value stream mapping to compare end-to-end workflows, standardize best practices through 5S and documented SOPs, measure capability differences with SPC, and run DMAIC projects to close gaps, starting with value stream mapping for alignment.What is a practical workshop agenda to introduce teams to Lean Six Sigma concepts and tools?
A compact approach pairs a 90-minute overview on Lean, Six Sigma, and their synergy with a 120-minute practical session for hands-on process mapping, DMAIC/DMADV exercises, and action-plan development; many decks provide sample agendas including a 120-minute practical workshop.Document FAQ
These are questions addressed within this presentation.
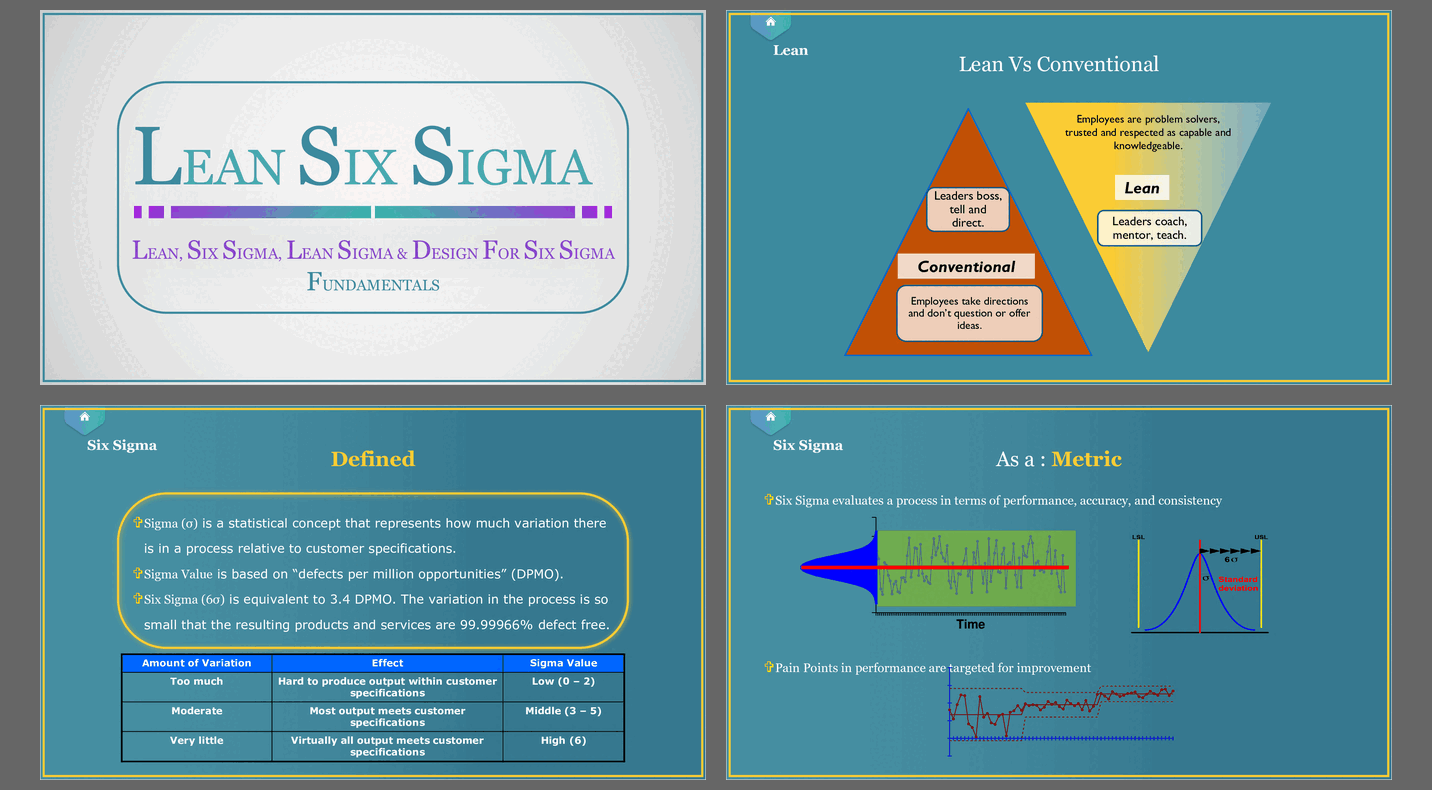
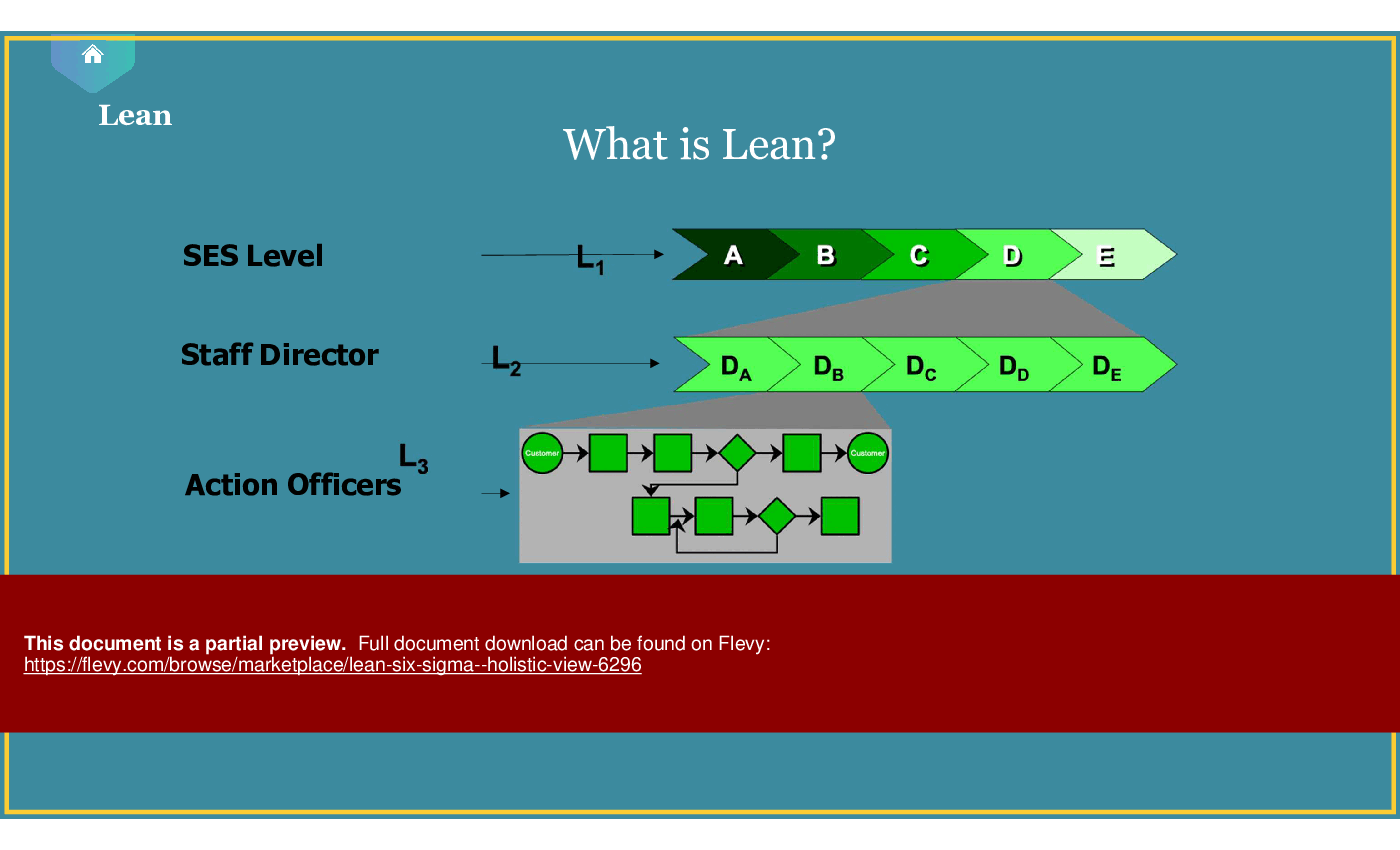
What is Lean?
Lean is a methodology focused on eliminating waste and improving process efficiency by streamlining workflows and enhancing value delivery.
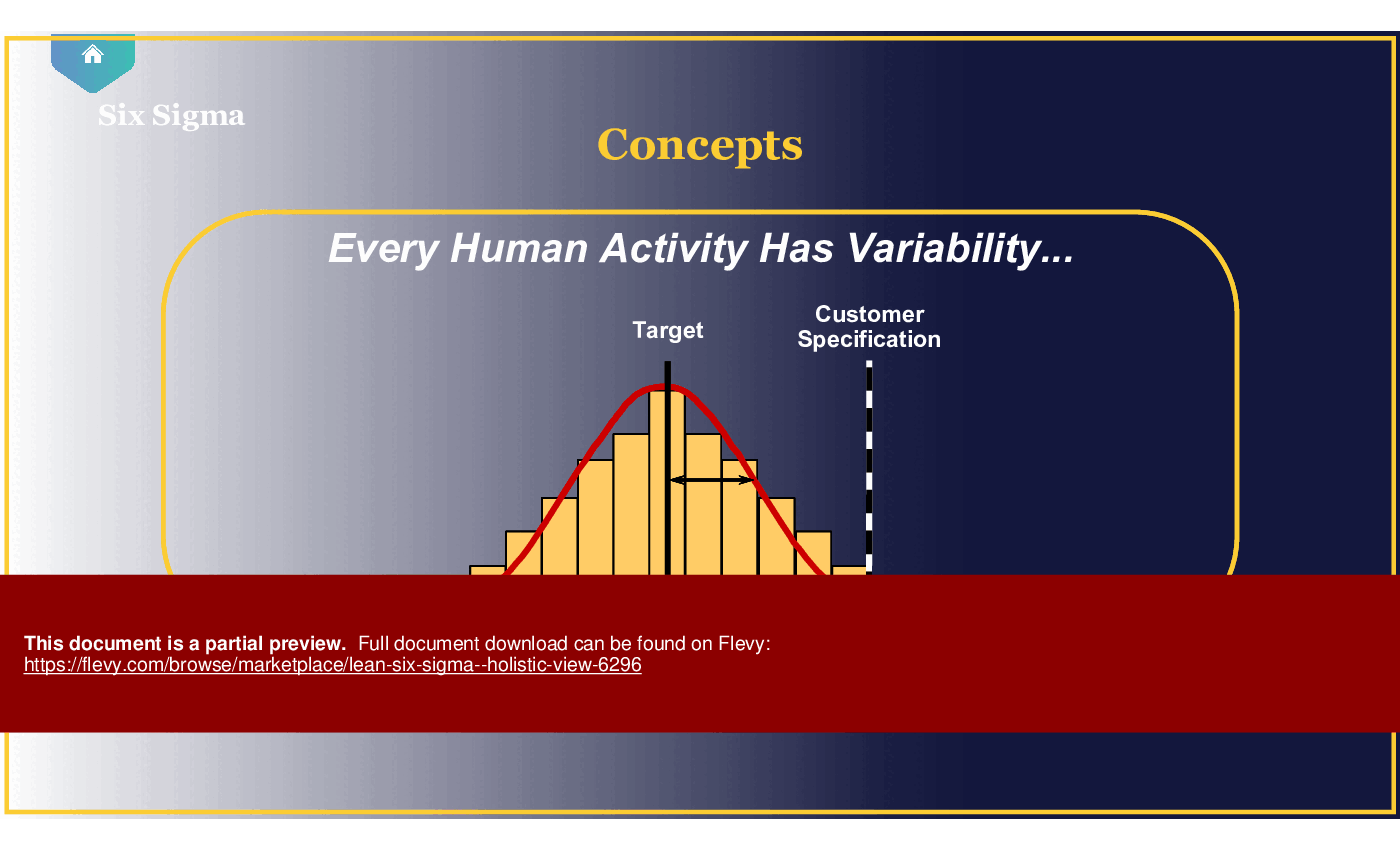
What is Six Sigma?
Six Sigma is a data-driven approach aimed at reducing process variation and defects, striving for near-perfect quality in products and services.
How do Lean and Six Sigma work together?
Lean improves efficiency by eliminating waste, while Six Sigma enhances quality by reducing defects. Together, they create a powerful framework for continuous improvement.
What is Design for Six Sigma (DFSS)?
DFSS is a methodology that focuses on designing processes and products to meet customer needs from the outset, ensuring high quality and efficiency.
Who are the key roles in Six Sigma projects?
Key roles include Champions, who drive the vision; Black Belts, who lead projects; and Green Belts, who support project teams while managing their regular duties.
What tools are commonly used in Lean Six Sigma?
Common tools include process mapping, statistical analysis, root cause analysis, and various quality improvement methodologies.
How can organizations measure the success of Lean Six Sigma initiatives?
Success can be measured through key performance indicators (KPIs), customer satisfaction scores, and reductions in defects and process cycle times.
What are some common challenges in implementing Lean Six Sigma?
Common challenges include resistance to change, lack of leadership support, and insufficient training and resources for team members.
Glossary
• Lean - A methodology focused on eliminating waste and improving process efficiency.
• Six Sigma - A data-driven approach to reducing process variation and defects.
• DMAIC - Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control; a Six Sigma framework for process improvement.
• DMADV - Define, Measure, Analyze, Design, Verify; a framework for designing new processes or products.
• DFSS - Design for Six Sigma; a methodology for designing processes that meet customer requirements from the start.
• VOC - Voice of the Customer; feedback used to inform product and process design.
• Black Belt - A Six Sigma expert who leads projects and trains team members.
• Green Belt - A team member trained in Six Sigma methodologies who supports projects part-time.
• Champion - A leader who advocates for Six Sigma initiatives within the organization.
• Kaizen - A continuous improvement philosophy that emphasizes small, incremental changes.
• 5S - A Lean tool for organizing and standardizing the workplace.
• Value Stream Mapping - A Lean tool used to visualize and analyze the flow of materials and information.
• CTQ - Critical to Quality; key measurable characteristics that are essential for customer satisfaction.
• SPC - Statistical Process Control; a method of monitoring and controlling processes using statistical tools.
• FMEA - Failure Mode and Effects Analysis; a systematic approach for identifying potential failures in a process.
• Poka-Yoke - A mistake-proofing technique used to prevent errors in processes.
• SIPOC - Suppliers, Inputs, Process, Outputs, Customers; a tool for mapping out a process at a high level.
• Root Cause Analysis - A method for identifying the underlying causes of problems or defects.
• Benchmarking - Comparing processes and performance metrics to industry bests or best practices from other organizations.
Source: Best Practices in Lean, Six Sigma Project PowerPoint Slides: Lean Six Sigma - Holistic View PowerPoint (PPTX) Presentation Slide Deck, RadVector Consulting