BCBS 239 - Risk Data Aggregation (PowerPoint PPT Slide Deck)
PowerPoint (PPT) 27 Slides FlevyPro Document
PPT DESCRIPTION
It is a known fact that majority of the banks need to further develop their Risk Data Aggregation and Risk Reporting (RDARR) capabilities. The recent global economic crisis exposed many banks deficiency to efficiently and effectively report the events to the senior management.
BCBS 239 is the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision's standard number 239, which is aimed at improving the RDARR capabilities of Global Systemically Important Banks (G-SIBs), and establish compliance requirements for various risk types. BCBS 239 focuses on enhancing the banks' Risk Data Aggregation and Risk Reporting (RDARR) skills.
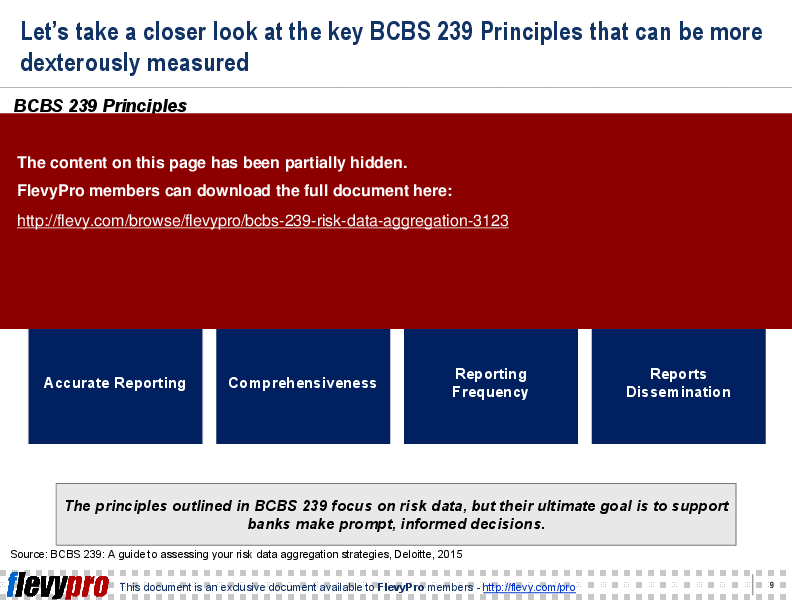
BCBS 239 regulation is presented in the form of 8 key principles that the banks need to comply with:
1. Data Architecture and IT Infrastructure
2. Accuracy and Integrity
3. Completeness
4. Timeliness
5. Accurate Reporting
6. Comprehensiveness
7. Reporting Frequency
8. Reports Dissemination
This presentation also discusses BCBS 239 implementation challenges and approach.
The slide deck also includes some slide templates for you to use in your own business presentations.
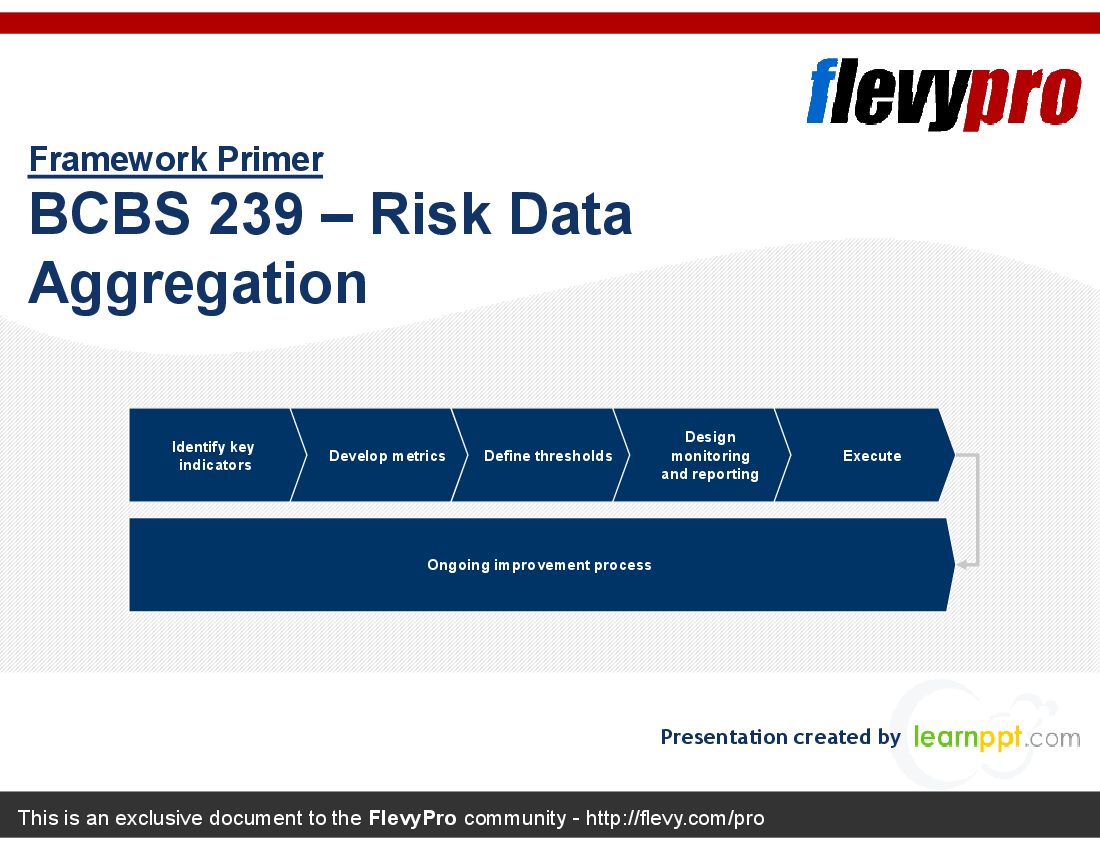
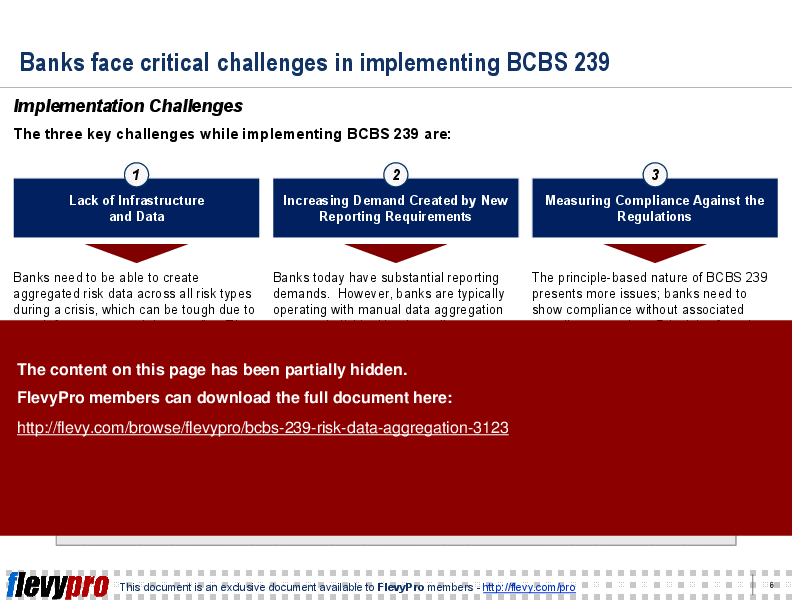
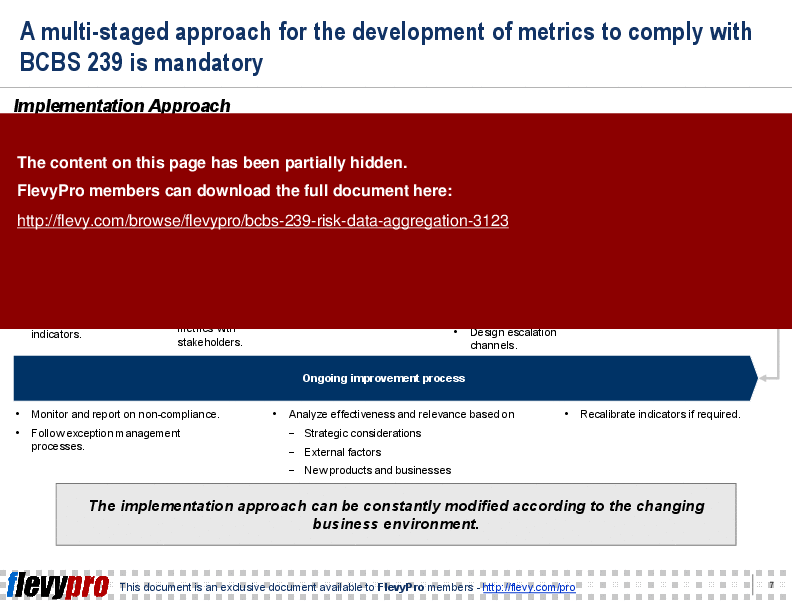
This PPT delves into the critical challenges banks face in implementing BCBS 239. Key obstacles include lack of infrastructure and data, increased reporting demands, and compliance measurement. The presentation outlines a multi-staged approach for developing metrics to comply with BCBS 239, emphasizing the need for ongoing improvement processes and strategic considerations.
The slide deck also provides detailed templates for BCBS 239 implementation and principles, covering data architecture, accuracy, completeness, and timeliness. These templates are designed to help financial institutions streamline their risk data aggregation and reporting processes, ensuring they meet regulatory requirements and enhance decision-making capabilities.
Got a question about this document? Email us at flevypro@flevy.com.
PPT SLIDES
Source: Best Practices in Risk Management, Financial Services Industry, BCBS 239 PowerPoint Slides: BCBS 239 - Risk Data Aggregation PowerPoint (PPT) Presentation Slide Deck, LearnPPT Consulting
Did you need more documents?
Consider a FlevyPro subscription from $39/month. View plans here.
For $10.00 more, you can download this document plus 2 more FlevyPro documents. That's just $13 each.