M&A PPT DESCRIPTION
This is a training document on business valuation. It gives an overview of major valuation concepts and issues, discusses alternative valuation methods and provides practical examples for business valuation.
It is particularly useful to financial analysts, MBA students, and consultants.
Valuation is a huge topic with many key issues to consider. This document dives deep into the cost of capital in DCF or discounted earnings, selection of market multiples, and adjustments. It also covers growth rates in earnings and cash flow projections, terminal value method, and calculation. Using several vantage points and avoiding false precision are emphasized to ensure robust valuation.
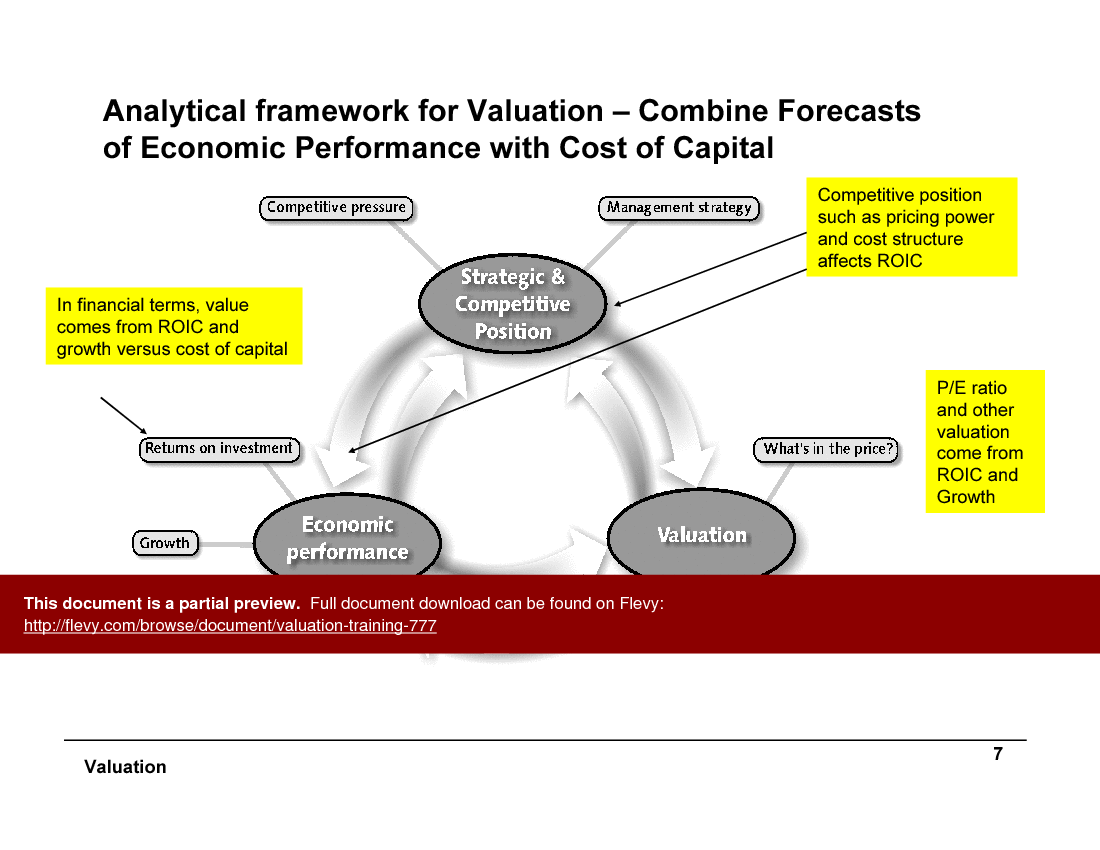
The analytical framework for valuation combines forecasts of economic performance with the cost of capital. Competitive position and management strategy significantly affect ROIC. This framework helps in understanding how strategic and competitive positioning impacts economic performance and valuation. The P/E ratio and other valuation metrics are derived from ROIC and growth.
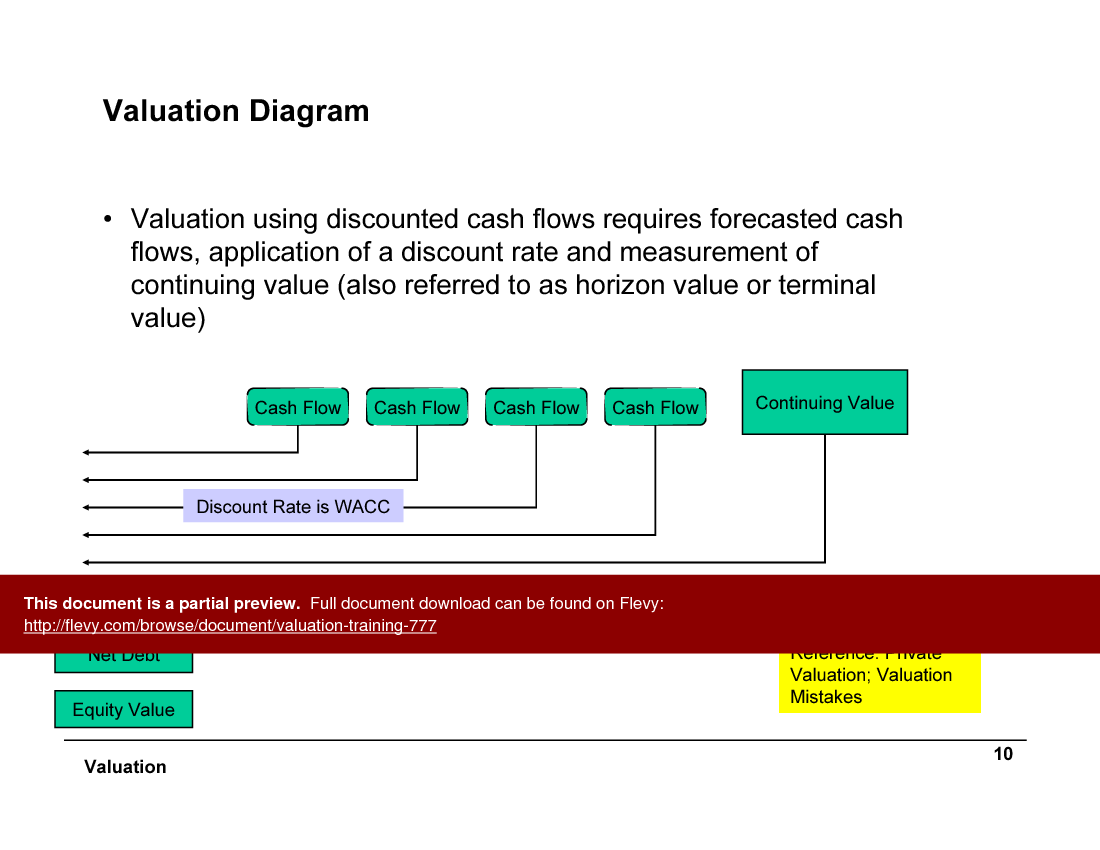
Valuation using discounted cash flows (DCF) involves forecasted cash flows, application of a discount rate, and measurement of continuing value. The discount rate is typically the weighted average cost of capital (WACC). This method provides a clear picture of equity value by considering net debt and other factors.
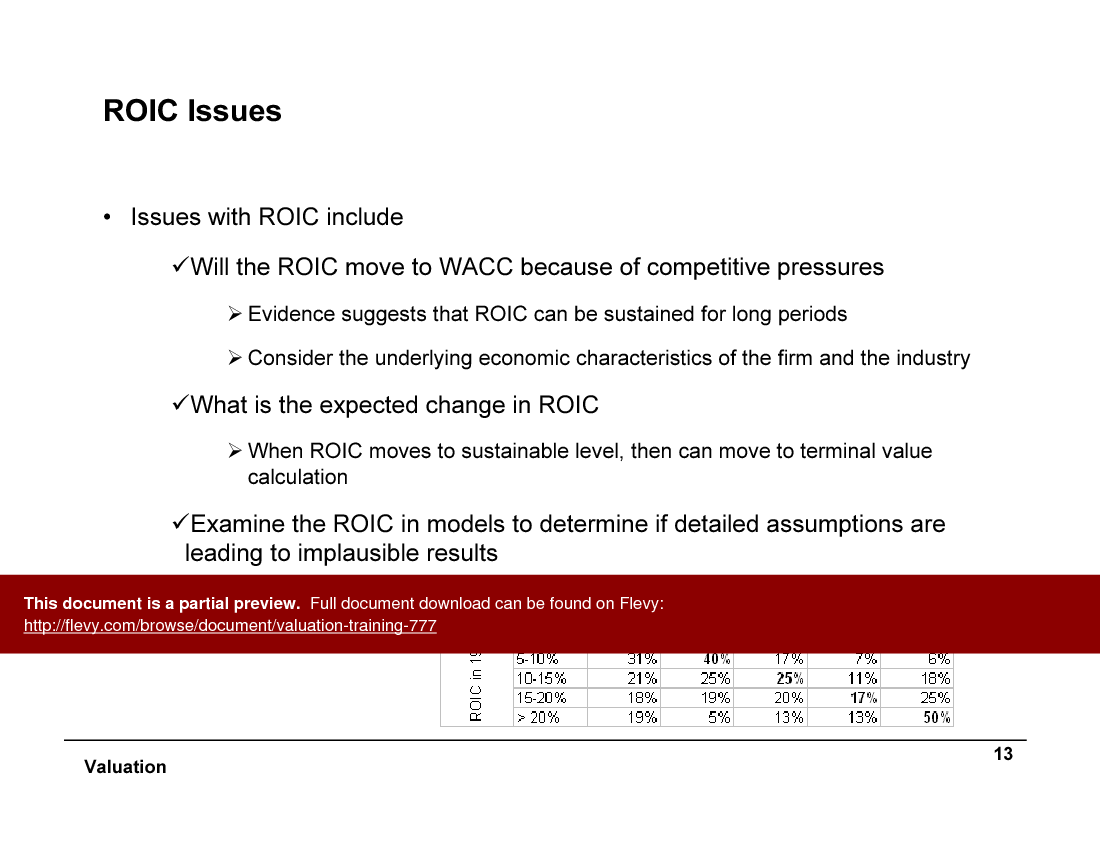
Issues with ROIC include competitive pressures and expected changes in ROIC. The document examines how ROIC might move to WACC and the implications for terminal value calculation. It also looks at the sustainability of ROIC and growth, considering industry norms and competitive pressures over time. This section provides a detailed analysis of how to maintain growth and ROIC above WACC.
Got a question about the product? Email us at support@flevy.com or ask the author directly by using the "Ask the Author a Question" form. If you cannot view the preview above this document description, go here to view the large preview instead.
MARCUS OVERVIEW
This synopsis was written by Marcus [?] based on the analysis of the full 164-slide presentation.
Executive Summary
This Valuation Training presentation provides a robust framework for understanding and applying various valuation techniques, essential for financial analysts and consultants. It is structured in a consulting-grade format, akin to what you would expect from McKinsey, Bain, or BCG-quality presentations (not affiliated). The training covers critical valuation methods such as Discounted Cash Flow (DCF), valuation using multiples, and projected earnings, enabling users to make informed financial decisions based on intrinsic value assessments.
Who This Is For and When to Use
• Financial analysts seeking to enhance their valuation skills
• Corporate finance professionals involved in investment analysis
• Consultants advising clients on mergers and acquisitions
• Business leaders making strategic decisions based on valuation metrics
Best-fit moments to use this deck:
• During financial analysis for mergers and acquisitions
• When preparing investment proposals or business valuations
• In training sessions for finance teams on valuation methodologies
Learning Objectives
• Define intrinsic value and its significance in financial decision-making
• Build a comprehensive valuation model using DCF and multiples
• Establish a clear understanding of risk assessment in valuation
• Analyze case studies to apply valuation techniques in real-world scenarios
• Compare different valuation methods and their applicability
• Identify key drivers of value and how to forecast them
Table of Contents
• Introduction – Where Value Comes From (page 2)
• Discounting Basics (page 33)
• Overview of Alternative Valuation Methods (page 17)
• Valuation Using Multiples (page 41)
• Valuation Using Projected Earnings (page 101)
• Case Studies (page 130)
Primary Topics Covered
• Valuation Fundamentals - Valuation is rooted in understanding future cash flows and the associated risks, crucial for making sound financial decisions.
• Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) - DCF involves forecasting cash flows and applying a discount rate to determine present value, essential for intrinsic value calculations.
• Valuation Using Multiples - This method leverages market comparables to derive value, providing a quick assessment of a company's worth relative to its peers.
• Projected Earnings Valuation - This approach focuses on estimating future earnings and applying a growth rate to determine value, particularly useful for growth companies.
• Risk Assessment in Valuation - Understanding the risks associated with cash flows is vital for accurate valuation and decision-making.
• Case Studies - Real-world examples illustrate the application of various valuation methods, enhancing practical understanding.
Deliverables, Templates, and Tools
• Valuation model template for DCF analysis
• Comparative analysis template for valuation multiples
• Risk assessment framework for evaluating cash flow uncertainties
• Case study examples for practical application of valuation techniques
• Financial forecasting models for projected earnings
• Guidelines for selecting appropriate valuation methods
Slide Highlights
• Overview of valuation fundamentals emphasizing cash flow and risk
• Detailed explanation of DCF methodology with practical examples
• Comparative analysis of valuation multiples with industry benchmarks
• Case studies demonstrating the application of valuation techniques
• Visual aids illustrating the relationship between risk and return in valuation
Potential Workshop Agenda
Valuation Fundamentals Session (90 minutes)
• Introduction to valuation concepts and importance
• Discussion on cash flow forecasting and risk assessment
• Overview of valuation methods and their applications
Practical Valuation Techniques Session (120 minutes)
• Hands-on training on building a DCF model
• Group activity on valuation using multiples
• Case study analysis to apply learned techniques
Customization Guidance
• Tailor the valuation model template to reflect specific industry metrics
• Adjust case studies to align with the audience's sector for relevance
• Incorporate company-specific data into comparative analysis templates
Secondary Topics Covered
• Economic profit and its role in valuation
• The impact of market conditions on valuation multiples
• Adjustments for liquidity and control premiums in valuations
• Challenges in valuing private firms versus public companies
• The importance of normalized earnings in valuation
Topic FAQ
What are the main valuation methods I should know and when is each appropriate?
Core valuation methods include Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) for intrinsic value via future cash-flow forecasts, valuation using multiples for market-comparable quick assessments, and projected earnings valuation for growth companies. Supplementary methods in practice include Dividend Discount Model, Residual Income, and the Venture Capital Method as noted in the glossary. Concrete methods: DCF, multiples, projected earnings.How does a Discounted Cash Flow model work and what components are essential?
A DCF model projects future free cash flows, applies a discount rate to convert to present value, and includes a terminal value to capture value beyond the explicit forecast. The discount rate is typically the Weighted Average Cost of Capital (WACC), and terminal value selection is a critical component in valuation. Key components: projected cash flows, WACC, terminal value.What is the role of WACC and ROIC in valuation analysis?
WACC serves as the discount rate in DCF and helps convert future cash flows into present value, while ROIC influences sustainable returns and growth assumptions. Valuation analysis examines how ROIC may converge toward WACC over time and the implications for terminal value and long-term forecasts. Relevant concepts: WACC and ROIC impact on terminal value.How should I assess and incorporate risk into a valuation?
Risk assessment involves identifying uncertainties in projected cash flows and reflecting them through discount rate selection, scenario analysis, and adjustments to forecasts. The training includes a risk assessment framework to evaluate cash-flow uncertainties and integrate those considerations into valuation outputs. Specific tool: risk assessment framework for cash flow uncertainties.What should I look for when buying a valuation template or training deck?
Buyers should verify inclusion of a DCF valuation model template, comparative analysis template for multiples, guidance on discount-rate selection (WACC), risk assessment approaches, and case studies for practical application. Valuation Training specifically lists a valuation model template and comparative analysis template among its deliverables. Key items: valuation model template and comparative analysis template.How much time should I allocate to train a finance team using a valuation deck?
Training time depends on depth; a suggested agenda in the material allocates a 90-minute Valuation Fundamentals session and a 120-minute Practical Valuation Techniques session that covers hands-on DCF building, multiples exercises, and case-study analysis. Example timings: 90 minutes and 120 minutes.Are there templates available for multiples and comparable company analysis?
Yes—comparable company analysis and multiples are covered, and the materials include a comparative analysis template designed for valuation multiples and industry benchmark comparison. The product Valuation Training explicitly lists a comparative analysis template for valuation multiples. Specific deliverable: comparative analysis template.How should I value a private company with negative earnings or volatile cash flows?
For negative earnings, valuation practice recommends normalizing earnings by adjusting for non-recurring items and using historical performance or industry averages to estimate future potential; private-company valuation also considers liquidity and control adjustments. Concrete approach: normalize earnings using historical performance or industry averages.Document FAQ
These are questions addressed within this presentation.
What are the key components of a DCF model?
A DCF model includes projected cash flows, a discount rate, and a terminal value calculation to determine present value.
How do I select the appropriate valuation multiple?
Choose multiples based on industry standards and the specific financial characteristics of the company being valued.
What is the significance of risk assessment in valuation?
Risk assessment helps in understanding the uncertainties associated with cash flows, which is crucial for accurate valuation.
How can I apply these valuation techniques in real-world scenarios?
Use case studies and practical exercises provided in the training to practice applying valuation methods in various contexts.
What are the common pitfalls in valuation?
Common pitfalls include overestimating growth rates, misapplying multiples, and neglecting to account for risk factors.
How do I normalize earnings for valuation?
Normalize earnings by adjusting for non-recurring items and using industry averages to reflect true earnings potential.
What is the role of terminal value in DCF?
Terminal value represents the value of a company beyond the explicit forecast period and is crucial for capturing long-term growth potential.
How do I handle negative earnings in valuation?
For negative earnings, use normalized earnings based on historical performance or industry averages to estimate future potential.
Glossary
• Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) - A valuation method that estimates the value of an investment based on its expected future cash flows.
• Valuation Multiple - A financial metric used to compare a company's value relative to a financial performance measure.
• Terminal Value - The estimated value of a business at the end of a forecast period, often calculated using a perpetuity growth model.
• Intrinsic Value - The perceived or calculated value of an asset, based on fundamental analysis without reference to its market value.
• Economic Profit - The difference between a company's total revenue and its total costs, including opportunity costs.
• Normalized Earnings - Adjusted earnings that exclude non-recurring items to reflect the true earning potential of a company.
• Risk Assessment - The process of identifying and analyzing potential issues that could negatively impact key business initiatives or projects.
• Weighted Average Cost of Capital (WACC) - The average rate of return a company is expected to pay its security holders to finance its assets.
• Free Cash Flow (FCF) - Cash generated by a company's operations after accounting for capital expenditures.
• Return on Invested Capital (ROIC) - A measure of a company's efficiency at allocating the capital under its control to profitable investments.
• Price-to-Earnings Ratio (P/E) - A valuation ratio calculated by dividing the current share price by its earnings per share (EPS).
• Market-to-Book Ratio - A financial valuation metric used to compare a company's current market price to its book value.
• Growth Rate - The rate at which a company's earnings or revenue is expected to grow over a specific period.
• Control Premium - The amount that an acquirer is willing to pay over the current market price to gain control of a company.
• Liquidity Discount - A reduction in the value of an asset due to the lack of marketability or the difficulty of selling it quickly.
• Comparable Company Analysis - A valuation method that compares a company’s financial metrics to those of similar companies in the industry.
• Dividend Discount Model (DDM) - A method for valuing a stock by using the predicted dividends and discounting them back to present value.
• Residual Income Model - A valuation method that calculates the intrinsic value of a company based on its expected future residual income.
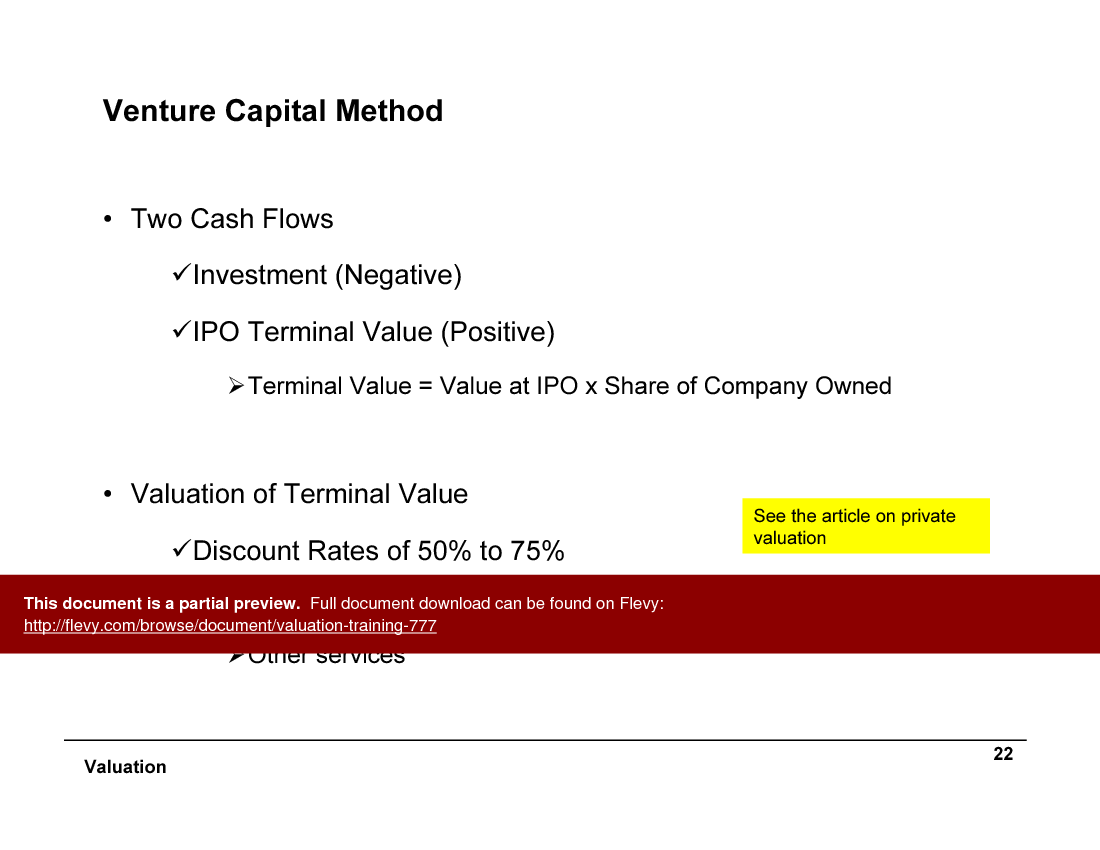
• Venture Capital Method - A valuation technique used primarily for startups, focusing on projected cash flows and exit values.
• Replacement Cost - The cost to replace an asset with a similar one at current market prices.
• Real Options - The application of option pricing theory to real-life business decisions, allowing for flexibility in investment choices.
• Earnings Before Interest and Taxes (EBIT) - A measure of a firm's profit that includes all expenses except interest and income tax expenses.
• Net Present Value (NPV) - The difference between the present value of cash inflows and outflows over a period of time.
M&A PPT SLIDES
Source: Best Practices in M&A, Valuation PowerPoint Slides: Valuation Training PowerPoint (PPT) Presentation Slide Deck, Documents & Files