Scrum Process Demystified (PowerPoint PPTX Slide Deck)
PowerPoint (PPTX) 46 Slides
SCRUM PPT DESCRIPTION
Scrum Process Demystified
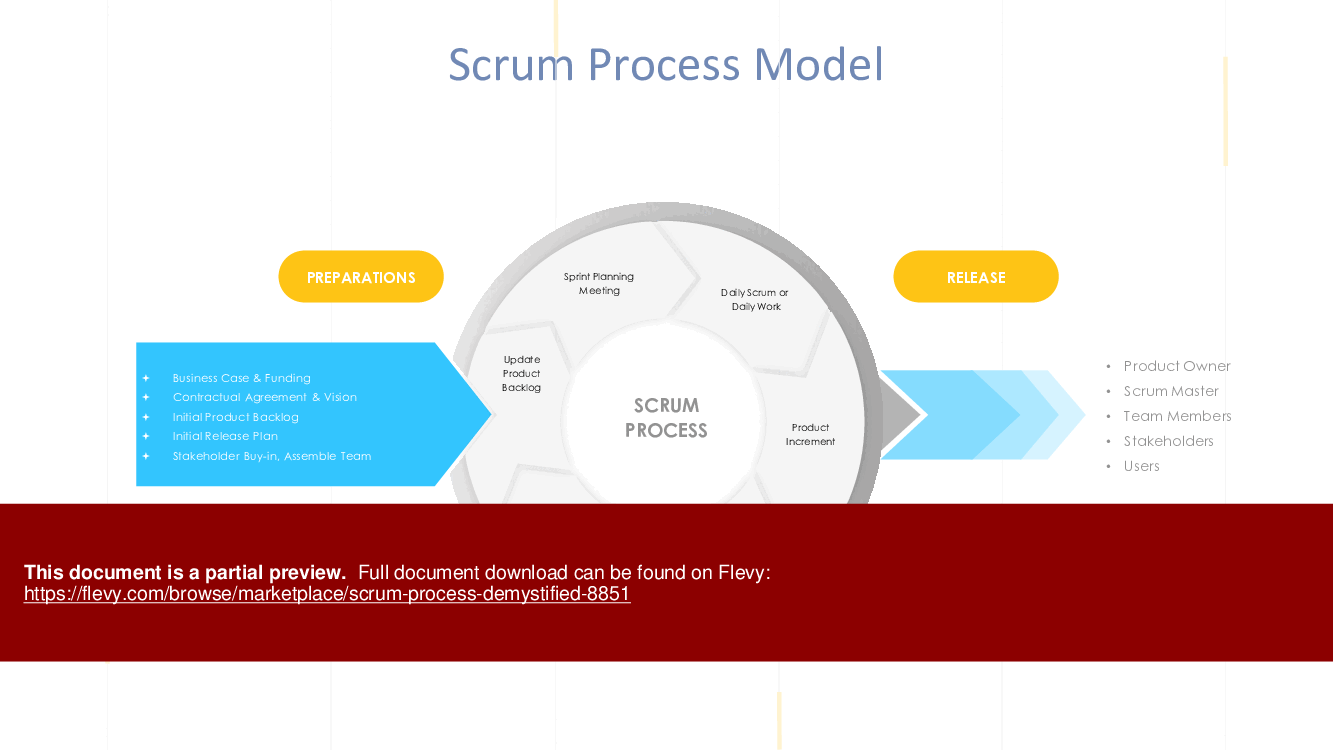
Scrum is an agile framework designed to facilitate efficient and flexible project management, particularly in software development. It emphasizes iterative progress, team collaboration, and continuous improvement to deliver high-quality products. The Scrum process is structured around several key elements: roles, artifacts, and events.
1. Roles
Scrum defines three primary roles:
• Product Owner: Represents the stakeholders and is responsible for defining the product backlog, ensuring it is prioritized according to business value and customer needs.
• Scrum Master: Acts as a facilitator for the team, ensuring Scrum practices are followed, removing impediments, and fostering an environment conducive to productivity.
• Development Team: A cross-functional group of professionals who are responsible for delivering potentially shippable increments of the product at the end of each sprint.
2. Artifacts
Scrum employs three main artifacts to manage work:
• Product Backlog: A dynamic list of features, enhancements, and bug fixes required for the product. It is continuously refined and reprioritized by the Product Owner.
• Sprint Backlog: A subset of the Product Backlog items selected for implementation in the upcoming sprint. It also includes a plan for delivering the increment.
• Increment: The sum of all Product Backlog items completed during a sprint and all previous sprints, representing the latest version of the product.
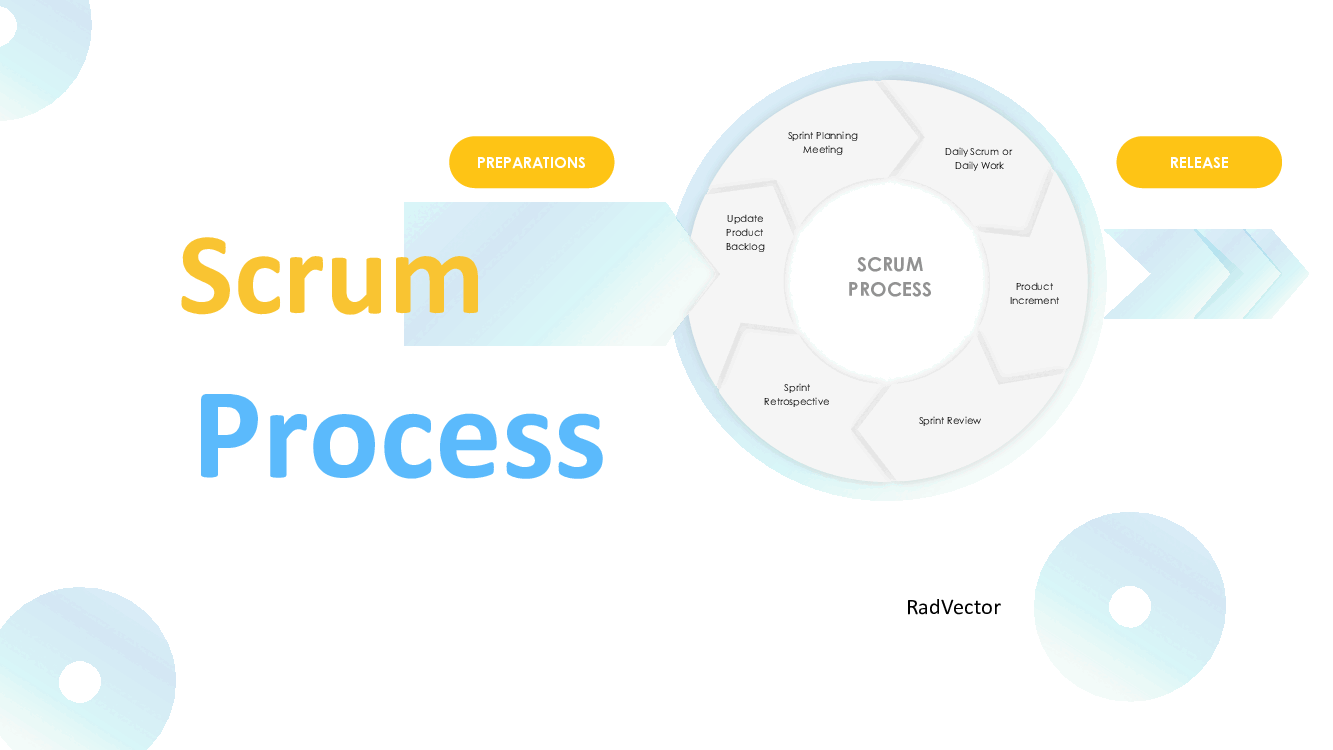
3. Events
Scrum uses a series of events to create regularity and minimize the need for other meetings:
• Sprint: The core of the Scrum process, a time-boxed period (usually 2-4 weeks) during which the team works to complete selected backlog items.
• Sprint Planning: A meeting at the beginning of each sprint where the team decides what work will be done and how it will be accomplished.
• Daily Scrum: A 15-minute daily stand-up meeting for the team to synchronize activities and plan the next 24 hours.
• Sprint Review: Held at the end of the sprint, this meeting allows the team to demonstrate the increment to stakeholders and gather feedback.
• Sprint Retrospective: A reflective meeting where the team discusses what went well, what didn't, and how processes can be improved in the next sprint.
The Scrum process is designed to enhance team collaboration, improve product quality, and ensure that projects are aligned with customer needs and business goals. By fostering an iterative and incremental approach, Scrum allows teams to respond swiftly to changes, continuously refine their work, and ultimately deliver more valuable products.
Got a question about the product? Email us at support@flevy.com or ask the author directly by using the "Ask the Author a Question" form. If you cannot view the preview above this document description, go here to view the large preview instead.
Source: Best Practices in Scrum PowerPoint Slides: Scrum Process Demystified PowerPoint (PPTX) Presentation Slide Deck, RadVector Consulting