Risk Management - Comprehensive Guide (PowerPoint PPTX Slide Deck)
PowerPoint (PPTX) 56 Slides
RISK MANAGEMENT PPT DESCRIPTION
Comprehensive Guide to Risk Management
Effective risk management is a cornerstone of organizational success, ensuring uncertainties are systematically identified, assessed, and addressed. This guide delves into essential aspects of risk management, providing a structured approach for managing risks across various domains.
Introduction
Risk management encompasses identifying, analyzing, and mitigating potential threats or opportunities that may impact objectives. A proactive approach fosters resilience and informed decision-making.
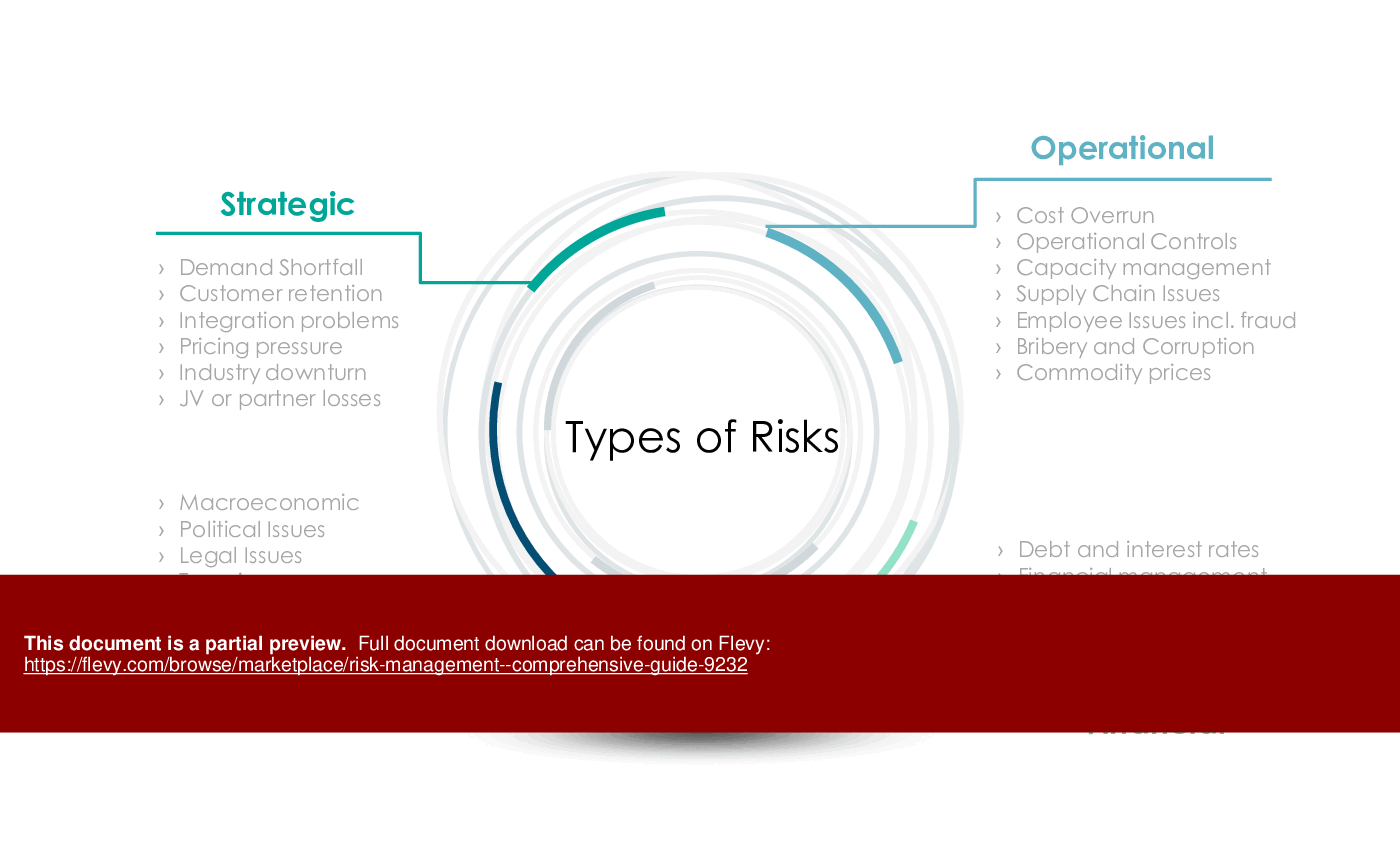
Types of Risk
Risks can be internal or external, categorized into operational, financial, strategic, or compliance risks, among others. Understanding these types helps in tailoring mitigation strategies.
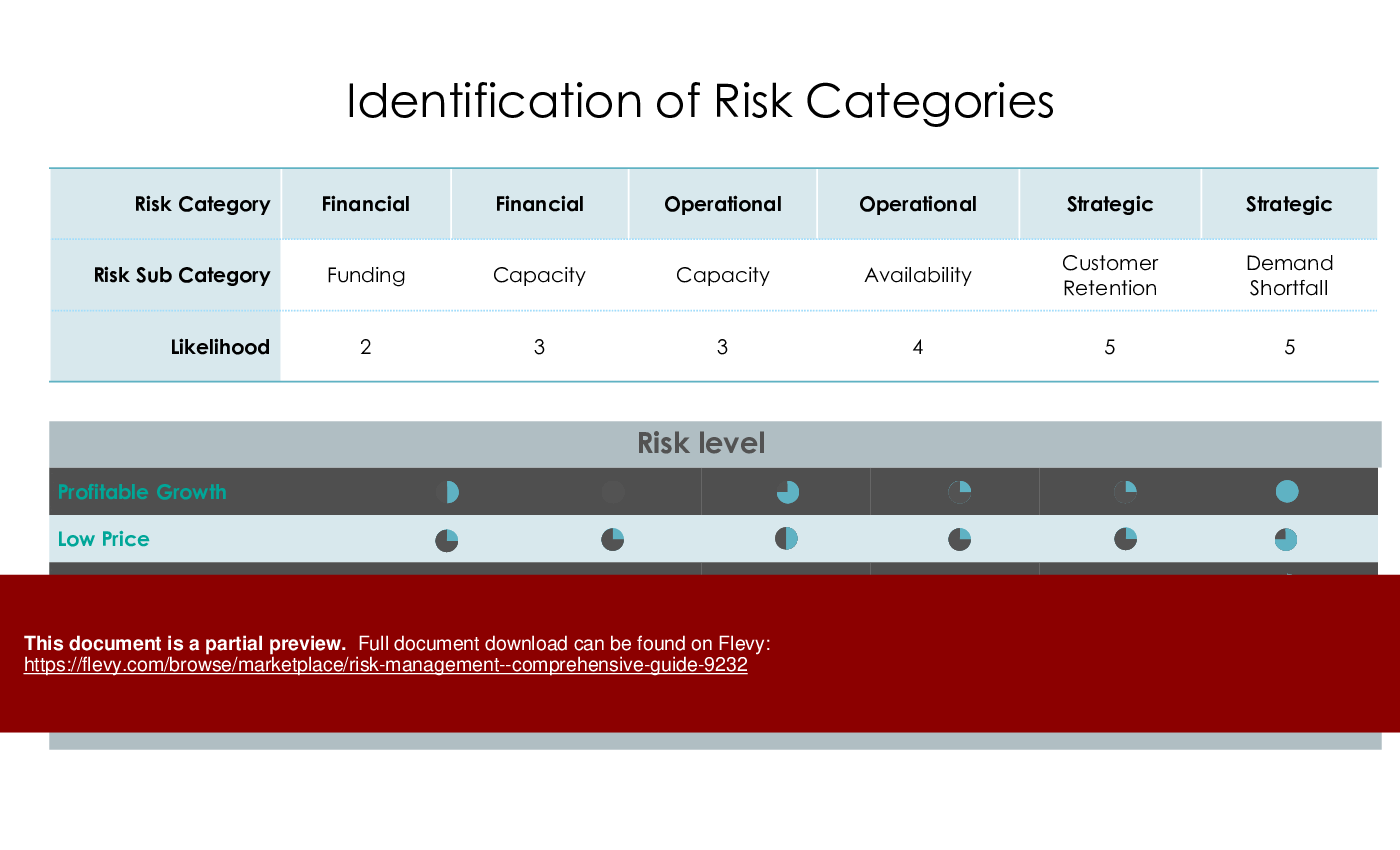
Risk Categories
Categorizing risks simplifies prioritization and management. Examples include market, technical, safety, environmental, and reputational risks.
Risk Identification
Identifying risks involves brainstorming, historical data analysis, and consultation with subject matter experts. Early detection is crucial for timely action.
Stakeholder Engagement
Engaging stakeholders ensures a comprehensive understanding of risk impacts and fosters a collaborative approach to mitigation.
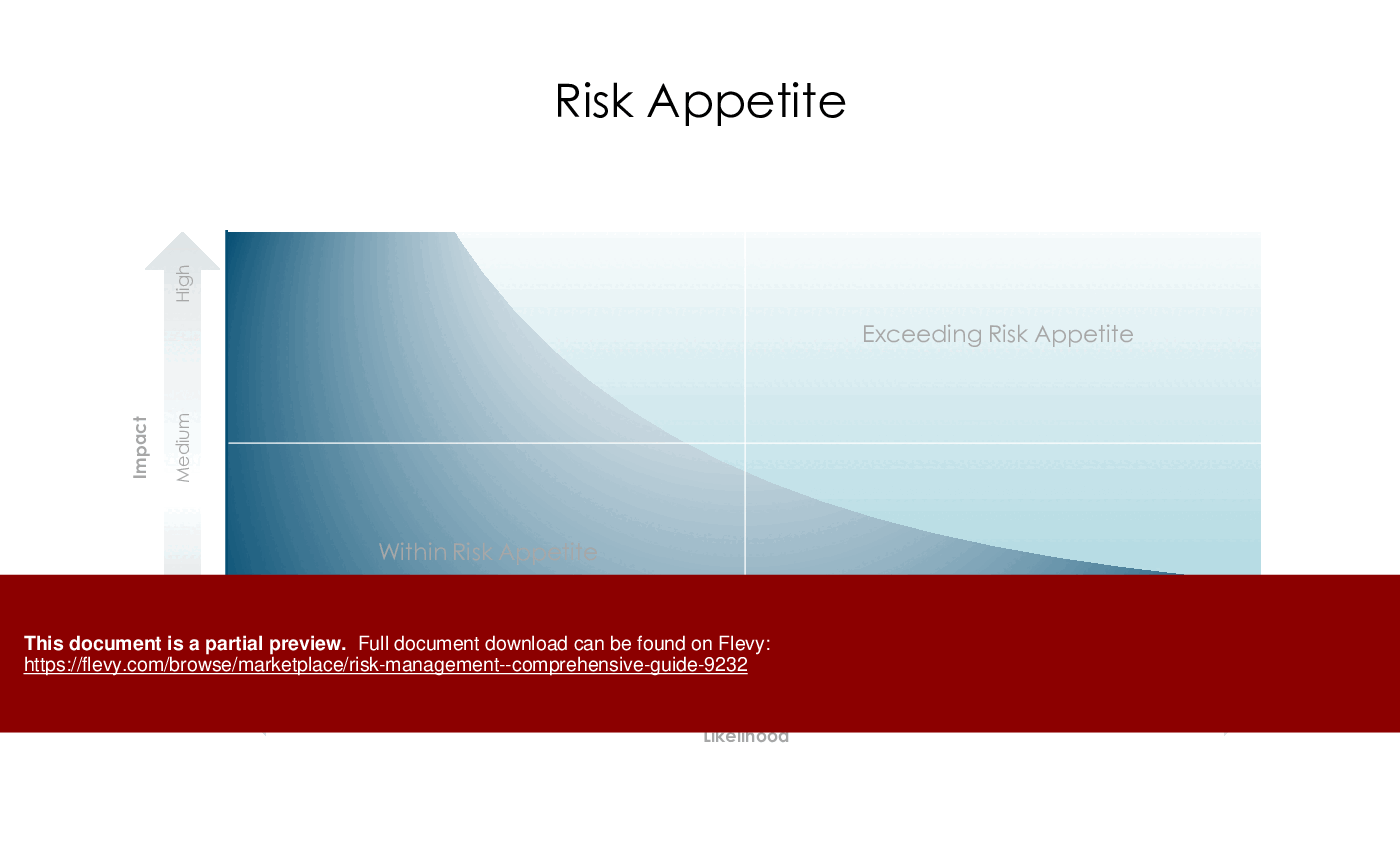
Risk Appetite and Tolerance
Risk appetite defines the level of risk an organization is willing to accept, while tolerance specifies limits for specific risks, guiding decision-making.
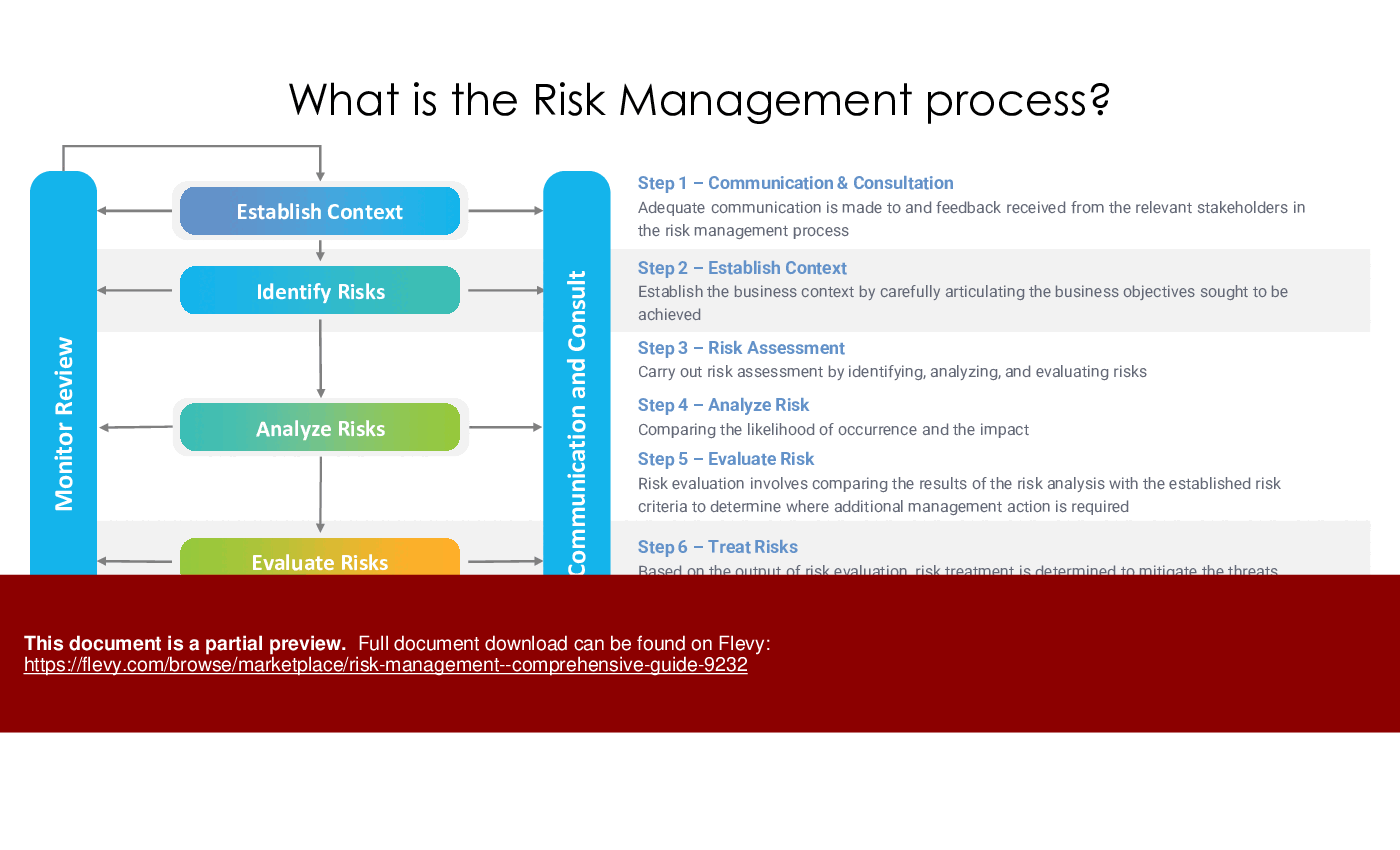
Risk Management Procedure
This iterative process includes risk planning, identification, assessment, monitoring, and tracking. It ensures a dynamic response to evolving risks.
Risk Planning
Developing a risk management plan outlines objectives, roles, responsibilities, and resources required to address risks effectively.
Risk Assessment
Assessing risks involves evaluating their impact and probability, employing tools like qualitative and quantitative analyses.
Risk Monitoring and Tracking
Regular monitoring ensures risks remain within tolerance levels, while tracking enables continuous oversight and adjustment.
Tools and Practices
Techniques such as SWOT analysis, root cause analysis, and scenario planning enhance risk identification and mitigation.
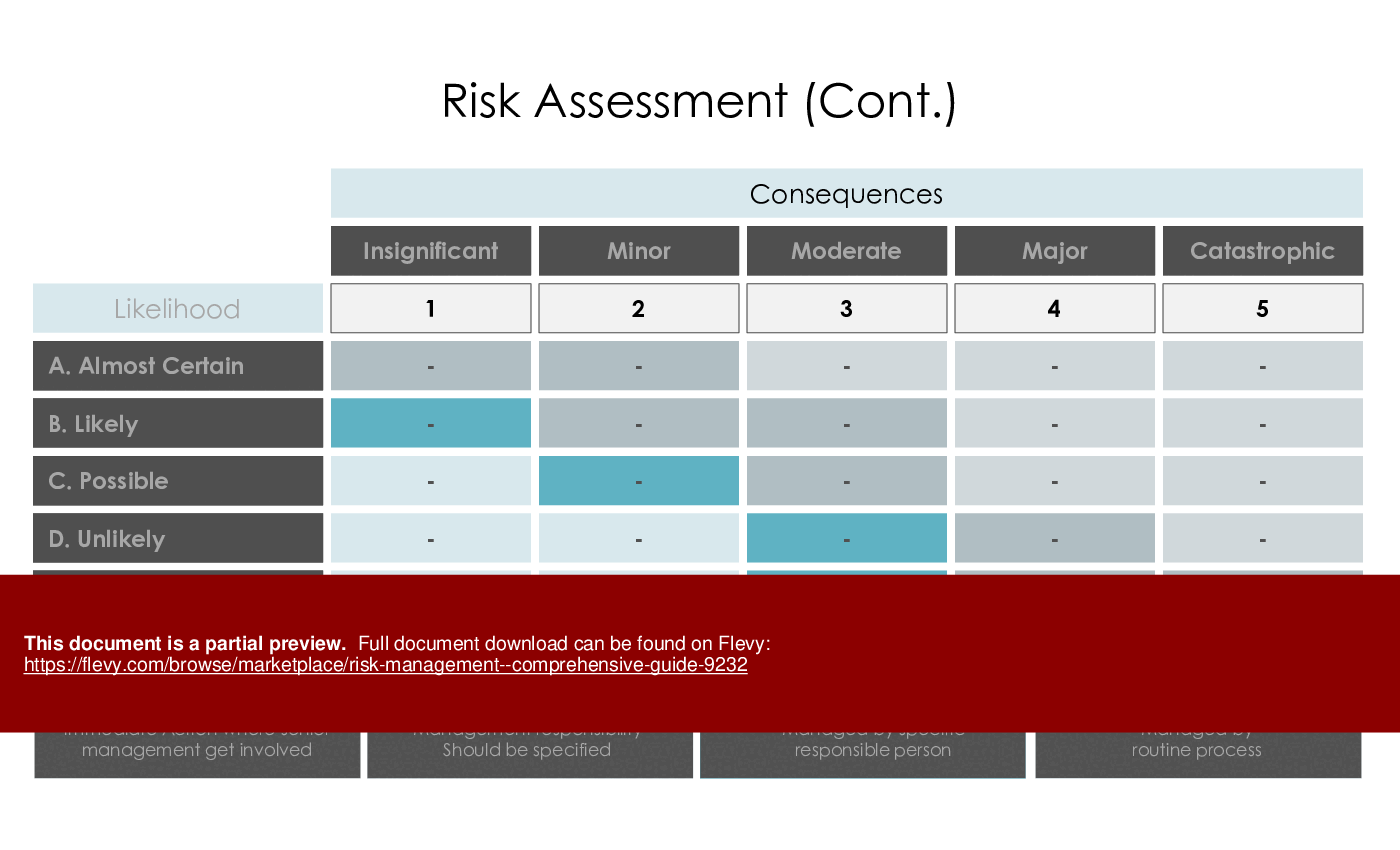
Impact & Probability Analysis
Mapping risks based on likelihood and consequences aids in prioritizing mitigation efforts.
Risk Mitigation Strategies
Strategies include avoidance, reduction, sharing, or acceptance, aligned with organizational goals and resources.
By integrating these components into an organization's framework, risk management transforms uncertainty into opportunity, ensuring sustainable growth and stability.
Got a question about the product? Email us at support@flevy.com or ask the author directly by using the "Ask the Author a Question" form. If you cannot view the preview above this document description, go here to view the large preview instead.
MARCUS OVERVIEW
This synopsis was written by Marcus [?] based on the analysis of the full 56-slide presentation.
Executive Summary
The Risk Management Comprehensive Guide is a meticulously crafted presentation designed to equip corporate executives and consultants with essential frameworks for effective risk management. Developed by a team of seasoned professionals with experience from top consulting firms, this guide covers critical aspects such as risk identification, assessment, and mitigation strategies. Users will learn to implement tools like SWOT analysis and impact probability analysis to enhance decision-making processes. This presentation serves as a vital resource for organizations aiming to navigate uncertainties and achieve their objectives.
Who This Is For and When to Use
• Corporate executives overseeing risk management initiatives
• Project managers responsible for identifying and mitigating risks
• Compliance officers ensuring adherence to regulatory standards
• Consultants advising clients on risk management strategies
Best-fit moments to use this deck:
• During strategic planning sessions to identify potential risks
• In project kick-off meetings to establish risk management protocols
• When conducting risk assessments for new initiatives or projects
Learning Objectives
• Define risk in the context of organizational objectives
• Identify various types of risks and their categories
• Assess and evaluate risks using qualitative and quantitative methods
• Develop effective risk mitigation strategies tailored to organizational needs
• Establish a risk management framework that aligns with ISO 31000 standards
• Monitor and review risk management processes for continuous improvement
Table of Contents
• Introduction (page 1)
• Types of Risk (page 2)
• Risk Categories (page 3)
• Risk Identification (page 4)
• Risk Assessment (page 5)
• Risk Planning (page 6)
• Risk Monitoring (page 7)
• Risk Tracking (page 8)
• Risk Appetite (page 9)
• Risk Tolerance (page 10)
• Impact & Probability Analysis (page 11)
• Risk Mitigation Strategies (page 12)
• Qualitative Analysis (page 13)
• Quantitative Analysis (page 14)
Primary Topics Covered
• Types of Risk - Understanding various risk types including strategic, operational, financial, and hazard risks is crucial for effective management.
• Risk Categories - Categorizing risks into internal and external types helps organizations prioritize their risk management efforts.
• Risk Identification - Identifying potential risks is the first step in the risk management process, enabling proactive measures.
• Risk Assessment - This involves analyzing and evaluating identified risks to determine their potential impact on objectives.
• Risk Appetite - Establishing a clear understanding of acceptable risk levels helps guide decision-making processes.
• Risk Mitigation Strategies - Developing tailored strategies to reduce or eliminate risks enhances organizational resilience.
Deliverables, Templates, and Tools
• Risk assessment templates for identifying and evaluating risks
• Risk register for tracking identified risks and their statuses
• Mitigation strategy frameworks for addressing various risk types
• Communication plans for stakeholder engagement during risk management processes
• Monitoring and review checklists to ensure compliance with established risk management protocols
• Impact and probability analysis tools for quantifying risks
Slide Highlights
• Overview of risk types and categories, providing a foundational understanding of risk management
• Visual representation of the risk appetite and tolerance framework, aiding in stakeholder discussions
• Detailed risk assessment matrix to facilitate risk evaluation and prioritization
• Comprehensive risk mitigation strategy outline, illustrating various approaches to managing risks
• Dashboard visuals showcasing risk tracking and monitoring metrics for real-time insights
Potential Workshop Agenda
Risk Identification Workshop (90 minutes)
• Discuss the importance of risk identification in project planning
• Engage participants in identifying potential risks relevant to their projects
• Develop a preliminary risk register based on identified risks
Risk Assessment and Mitigation Session (120 minutes)
• Review risk assessment methodologies and tools
• Analyze identified risks using qualitative and quantitative approaches
• Collaborate on developing tailored mitigation strategies for key risks
Customization Guidance
• Tailor risk assessment templates to reflect specific organizational contexts and objectives
• Adjust risk appetite and tolerance metrics based on stakeholder input and organizational goals
• Incorporate industry-specific risks into the risk register for more relevant assessments
Secondary Topics Covered
• Governance structures for effective risk management
• Stakeholder engagement strategies in risk management processes
• The role of technology in enhancing risk identification and monitoring
• Compliance considerations in risk management frameworks
• Best practices for continuous improvement in risk management
Topic FAQ
What are the typical phases of a corporate risk management process?
A common corporate risk management process follows an iterative sequence of activities: risk planning, risk identification, risk assessment, risk monitoring, and risk tracking. These phases structure how organizations define objectives, find potential threats, evaluate likelihood and impact, and continuously review controls across 5 phases.How do qualitative and quantitative risk assessments differ in practice?
Qualitative assessments rely on subjective judgment, expert input, and categorization to evaluate risk severity, while quantitative assessments use numerical data and statistical methods to estimate likelihood and impact. Both approaches are used together in many programs to balance judgment with measurable analysis using qualitative and quantitative analysis.What is impact and probability analysis and how does it help prioritize risks?
Impact and probability analysis maps identified risks according to their likelihood of occurrence and potential consequences, enabling prioritization and resource allocation. Organizations use these mappings alongside a risk assessment matrix or dashboard visuals; Flevy's Risk Management - Comprehensive Guide includes impact & probability analysis tools.What should I look for when buying a risk management template set for my organization?
Look for templates that support the full lifecycle: risk assessment templates, a risk register for tracking, mitigation strategy frameworks, communication plans, and monitoring/review checklists, plus alignment to recognized standards such as ISO 31000; these elements are listed as deliverables in the guide.How much time and team involvement are typical when running initial risk workshops?
Initial workshops often run as focused sessions: a risk identification workshop can be about 90 minutes, while a combined risk assessment and mitigation session can be around 120 minutes. These sessions typically involve cross-functional stakeholders and use templates to produce a preliminary risk register in 90–120 minutes.After an acquisition, what immediate risk management steps should integration teams take?
Integration teams should begin with systematic risk identification, populate a risk register, perform impact and probability analysis to prioritize critical risks, and define mitigation strategies and monitoring routines to track post-close issues. These steps follow the planning, identification, assessment, monitoring, and tracking sequence.How can compliance officers align their risk framework with ISO 31000 requirements?
Compliance officers should structure a risk management framework around the effect of uncertainty on objectives, document risk appetite and tolerance, use monitoring and review checklists, and ensure processes cover identification, assessment, and mitigation consistent with ISO 31000 alignment and monitoring practices.Are off-the-shelf risk templates useful for both small and large organizations?
Scalable templates that cover identification, assessment, mitigation, and monitoring can be adapted across organization sizes; modular risk registers and checklists allow tailoring to context. Flevy's Risk Management - Comprehensive Guide is presented as applicable to organizations of all sizes with scalable frameworks and tools.Document FAQ
These are questions addressed within this presentation.
What is the primary focus of this guide?
The guide focuses on equipping organizations with the frameworks and tools necessary for effective risk management, emphasizing risk identification, assessment, and mitigation.
How can this guide help in strategic planning?
By providing a structured approach to identifying and assessing risks, the guide enables organizations to incorporate risk management into their strategic planning processes.
What methodologies are covered for risk assessment?
The guide covers both qualitative and quantitative methodologies for assessing risks, allowing users to choose the most appropriate approach for their needs.
Can this presentation be customized for specific industries?
Yes, the presentation can be tailored to reflect industry-specific risks and regulatory requirements, enhancing its relevance for various sectors.
What tools are included for monitoring risks?
The guide includes templates and dashboards for tracking identified risks, facilitating ongoing monitoring and review processes.
How does this guide align with ISO 31000 standards?
The guide incorporates principles from ISO 31000, focusing on the effect of uncertainty on objectives and providing a structured risk management framework.
What are the expected outcomes after using this guide?
Users can expect to develop a comprehensive understanding of risk management processes, improve their risk identification and assessment capabilities, and implement effective mitigation strategies.
Is this guide suitable for both small and large organizations?
Yes, the guide is designed to be applicable to organizations of all sizes, providing scalable frameworks and tools for effective risk management.
Glossary
• Risk - The effect of uncertainty on objectives.
• Risk Appetite - The amount of risk an organization is willing to accept.
• Risk Tolerance - The acceptable level of variation in performance related to objectives.
• Risk Assessment - The process of identifying, analyzing, and evaluating risks.
• Risk Mitigation - Strategies to reduce or eliminate risks.
• Qualitative Analysis - Assessment based on subjective judgment rather than numerical data.
• Quantitative Analysis - Assessment based on numerical data and statistical methods.
• Stakeholders - Individuals or groups with an interest in the outcome of a project or initiative.
• ISO 31000 - An international standard for risk management principles and guidelines.
• Impact Analysis - Evaluation of the potential effects of identified risks on objectives.
• Probability Analysis - Assessment of the likelihood of identified risks occurring.
• Risk Register - A tool used to document identified risks and their statuses.
• Risk Management Framework - A structured approach to managing risks within an organization.
• Governance - The framework of rules and practices by which an organization is directed and controlled.
• Compliance - Adherence to laws, regulations, and organizational policies.
• Continuous Improvement - Ongoing efforts to enhance products, services, or processes.
• Dashboard - A visual representation of key metrics and data for monitoring performance.
• Mitigation Strategy - A plan for addressing and managing identified risks.
• Stakeholder Engagement - The process of involving individuals or groups in decision-making.
• Monitoring - The ongoing process of tracking risks and their management.
• Review - The evaluation of risk management processes and outcomes for effectiveness.
Source: Best Practices in Risk Management PowerPoint Slides: Risk Management - Comprehensive Guide PowerPoint (PPTX) Presentation Slide Deck, RadVector Consulting