Managing Corporate Performance with Balanced Scorecard (PowerPoint PPTX Slide Deck)
PowerPoint (PPTX) 45 Slides
BENEFITS OF THIS POWERPOINT DOCUMENT
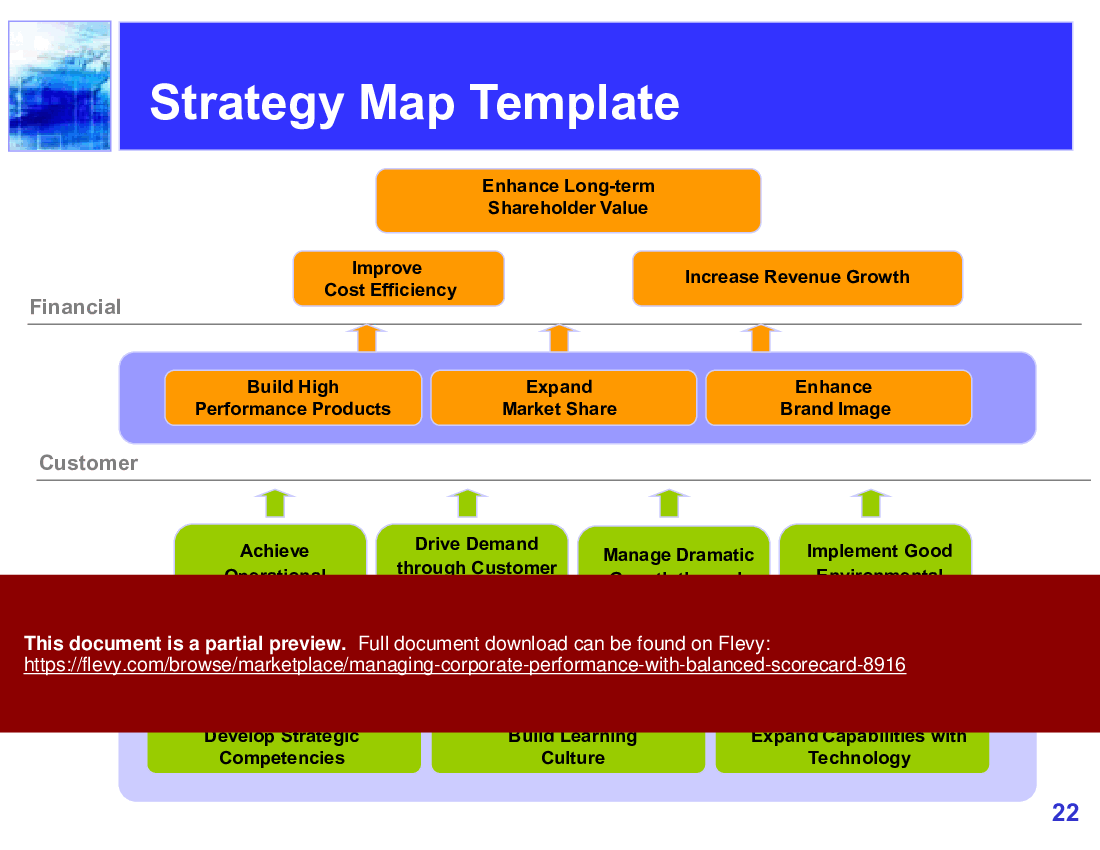
- Provides a Strategy Map Framework for Balanced Scorecard
- Provides a Strategy Map in Corporate Functions (HR, IT, Finance and Marketing)
- Provides a Corporate Performance Scorecard
BALANCED SCORECARD PPT DESCRIPTION
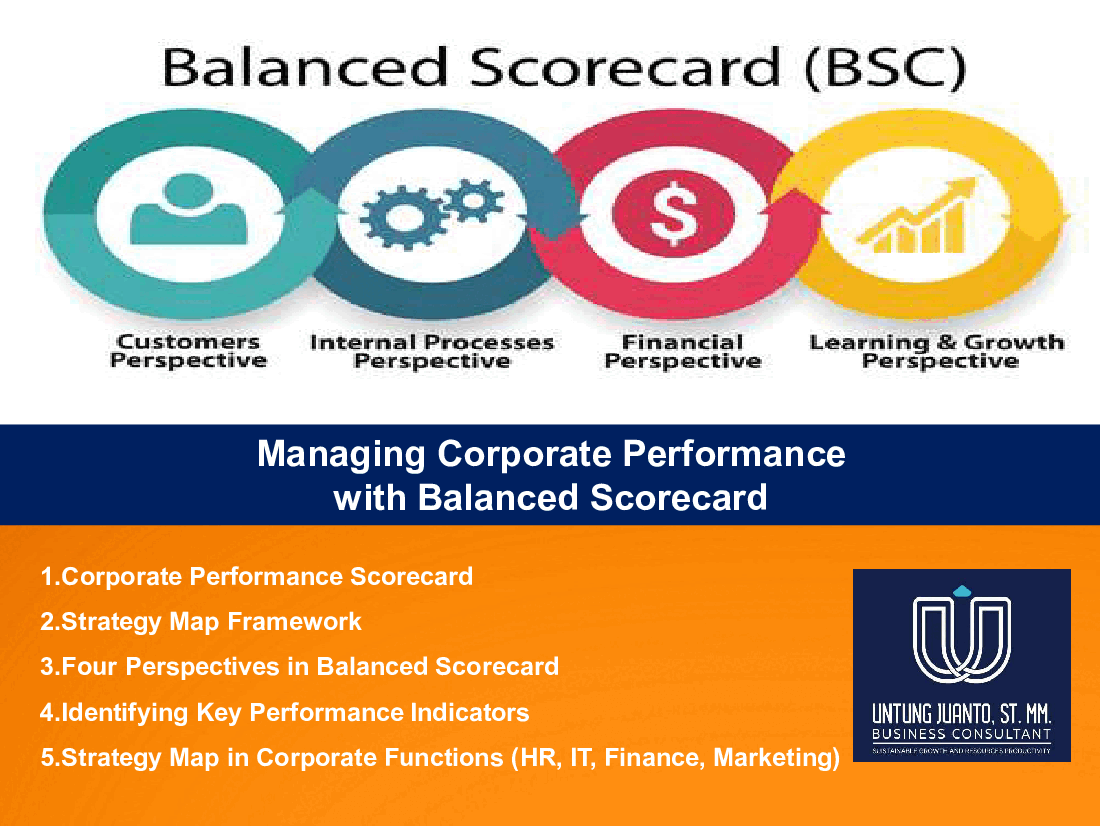
Managing Corporate Performance with Balanced Scorecard
Contents:
1. Corporate Performance Scorecard
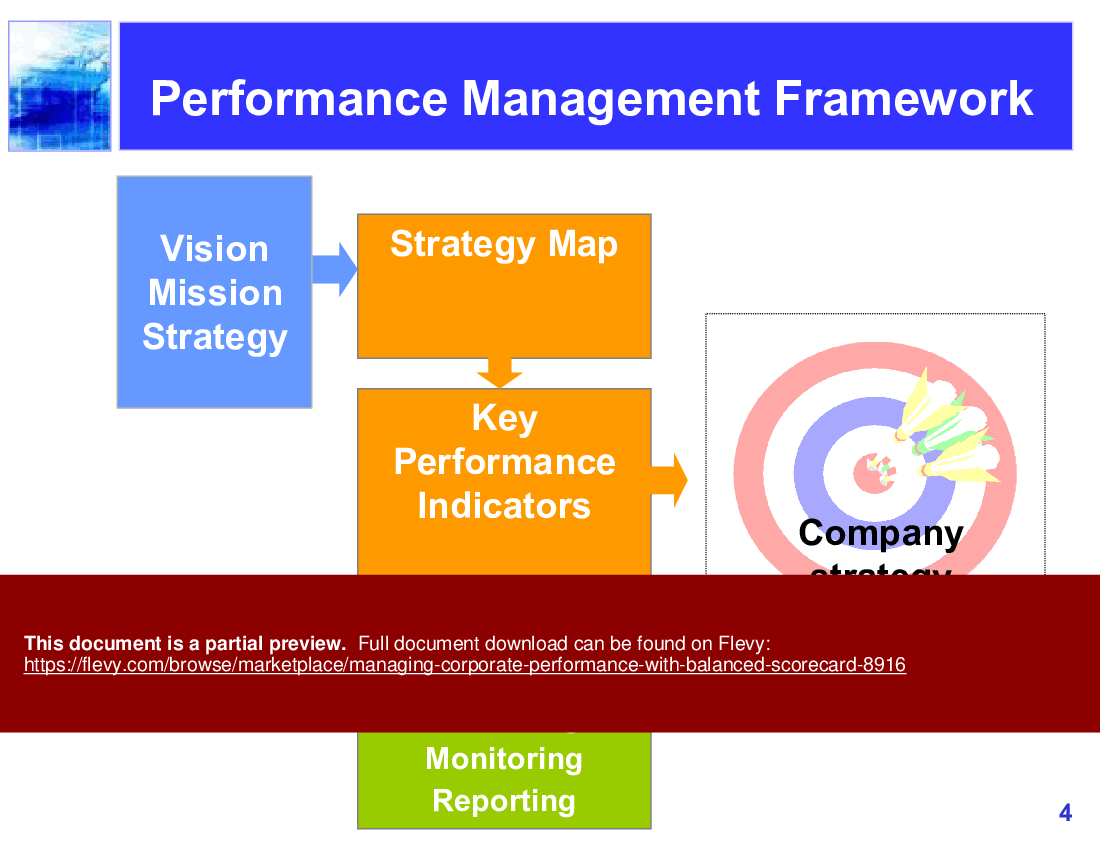
2. Strategy Map Framework
3. Four Perspectives in Balanced Scorecard
4. Identifying Key Performance Indicators
5. Strategy Map in Corporate Functions (HR, IT, Finance and Marketing)
A balanced scorecard is a strategic management performance metric that helps companies identify and improve their internal operations to help their external outcomes. It measures past performance data and provides organizations with feedback on how to make better decisions in the future.
The term balanced scorecard (BSC) refers to a strategic management performance metric used to identify and improve various internal business functions and their resulting external outcomes. Used to measure and provide feedback to organizations, balanced scorecards are common among companies in the United States, the United Kingdom, Japan, and Europe. Data collection is crucial to providing quantitative results as managers and executives gather and interpret the information. Company personnel can use this information to make better decisions for the future of their organizations.
Key Takeaways:
1. A balanced scorecard is a performance metric used to identify, improve, and control a business's various functions and resulting outcomes.
2. The concept of BSCs was first introduced in 1992 by David Norton and Robert Kaplan, who took previous metric performance measures and adapted them to include nonfinancial information.
3. BSCs were originally developed for for-profit companies but were later adapted for use by nonprofits and government agencies.
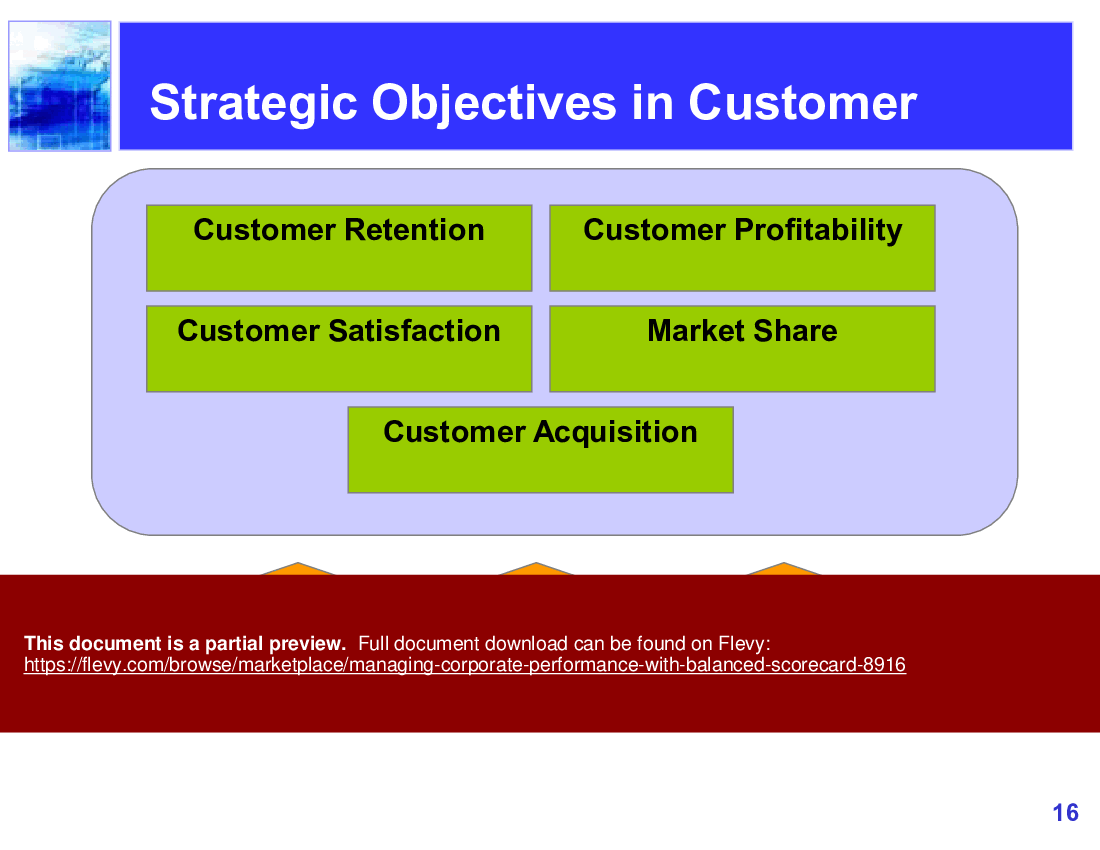
4. The balanced scorecard involves measuring four main aspects of a business: Learning and growth, business processes, customers, and finance.
5. BSCs allow companies to pool information in a single report, to provide information on service and quality in addition to financial performance, and to help improve efficiencies.
Accounting academic Dr. Robert Kaplan and business executive and theorist Dr. David Norton first introduced the balanced scorecard. The Harvard Business Review first published it in the 1992 article "The Balanced Scorecard—Measures That Drive Performance." Both Kaplan and Norton worked on a year-long project involving 12 top-performing companies. Their study took previous performance measures and adapted them to include nonfinancial information.
BSCs were originally meant for for-profit companies but were later adapted for nonprofit organizations and government agencies. The performance metric is meant to measure the intellectual capital of a company, such as training, skills, knowledge, and any other proprietary information that gives it a competitive advantage in the market. The balanced scorecard model reinforces good behavior in an organization by isolating four separate areas that need to be analyzed. These four areas, also called legs, involve:
1. Learning and growth
2. Business processes
3. Customers
4. Finance
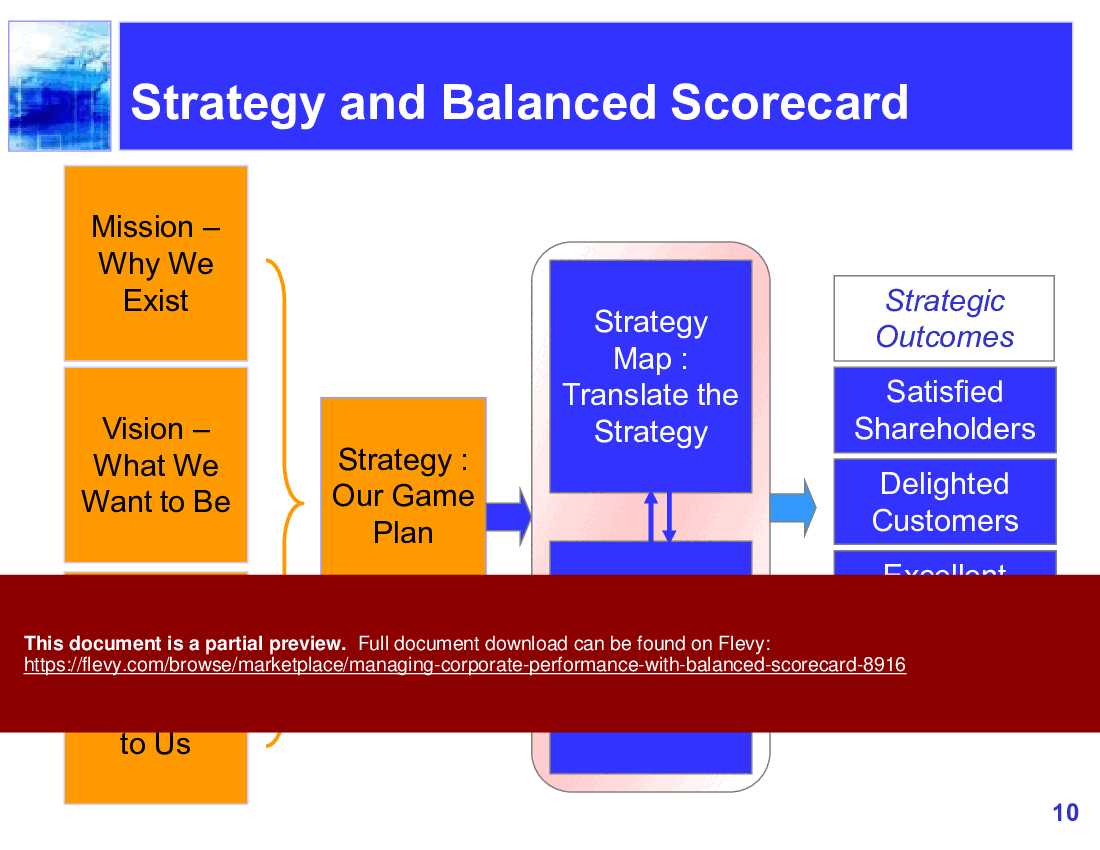
The BSC is used to gather important information, such as objectives, measurements, initiatives, and goals, that result from these four primary functions of a business. Companies can easily identify factors that hinder business performance and outline strategic changes tracked by future scorecards. The scorecard can provide information about the firm as a whole when viewing company objectives. An organization may use the balanced scorecard model to implement strategy mapping to see where value is added within an organization. A company may also use a BSC to develop strategic initiatives and strategic objectives. This can be done by assigning tasks and projects to different areas of the company in order to boost financial and operational efficiencies, thus improving the company's bottom line.
Best Regards,
UJ Consulting
Got a question about the product? Email us at support@flevy.com or ask the author directly by using the "Ask the Author a Question" form. If you cannot view the preview above this document description, go here to view the large preview instead.
Source: Best Practices in Balanced Scorecard PowerPoint Slides: Managing Corporate Performance with Balanced Scorecard PowerPoint (PPTX) Presentation Slide Deck, UJ Consulting