FINANCIAL MODELING PPT DESCRIPTION
This is an excellent training material on developing financial models. This presentation includes the following content
1. Introduction
2. Model development process
3. Planning
4. Business logic design
5. Spreadsheet design
6. Data gathering
7. Testing and developing insight
8. Communicating
9. Managing & Coaching
10. Case excercise
11. Sample financial model (in excel)
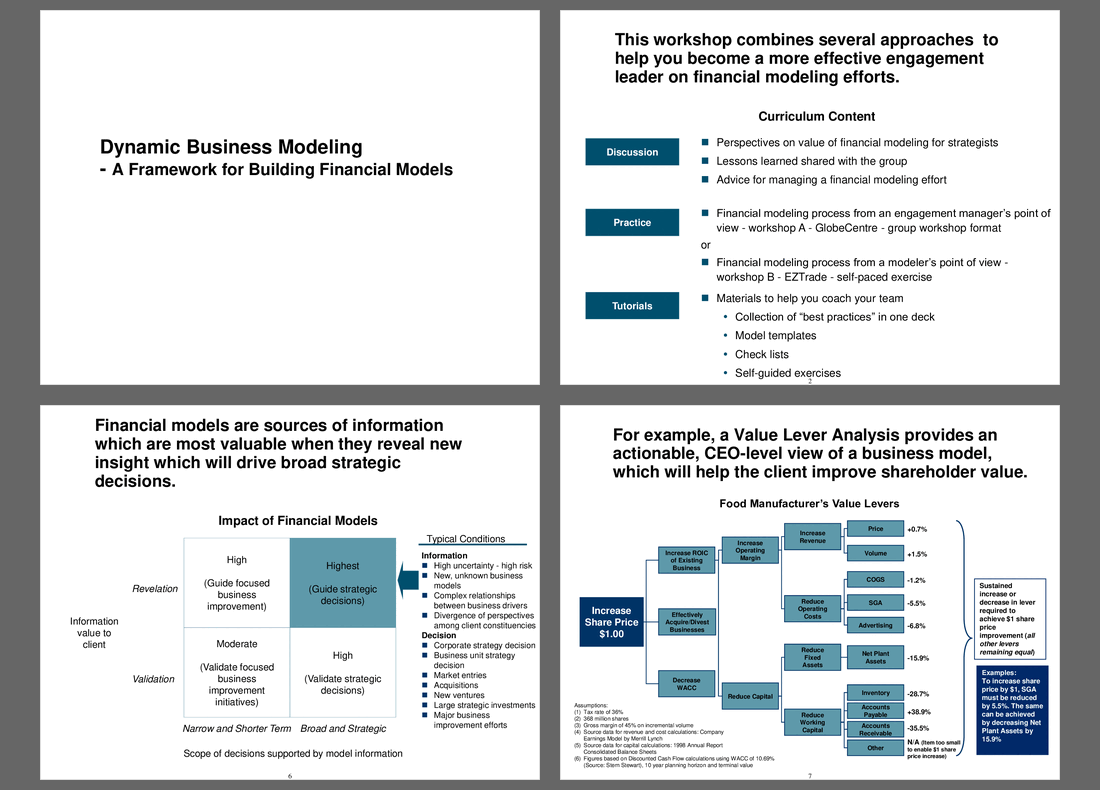
This presentation combines several approaches to help you become a more effective engagement leader on financial modeling efforts.
• Perspectives on value of financial modeling for strategists
• Lessons learned shared with the group
• Advice for managing a financial modeling effort
A Sample business model Excel attached with this material
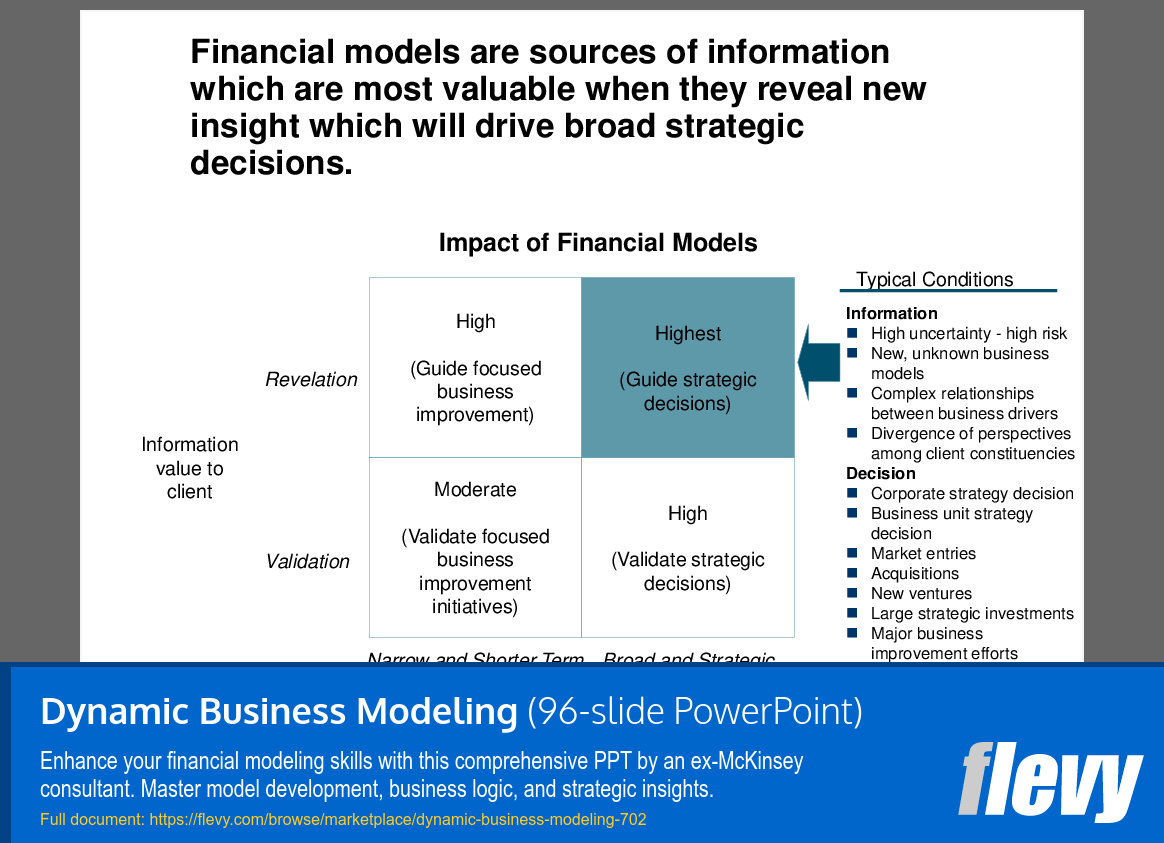
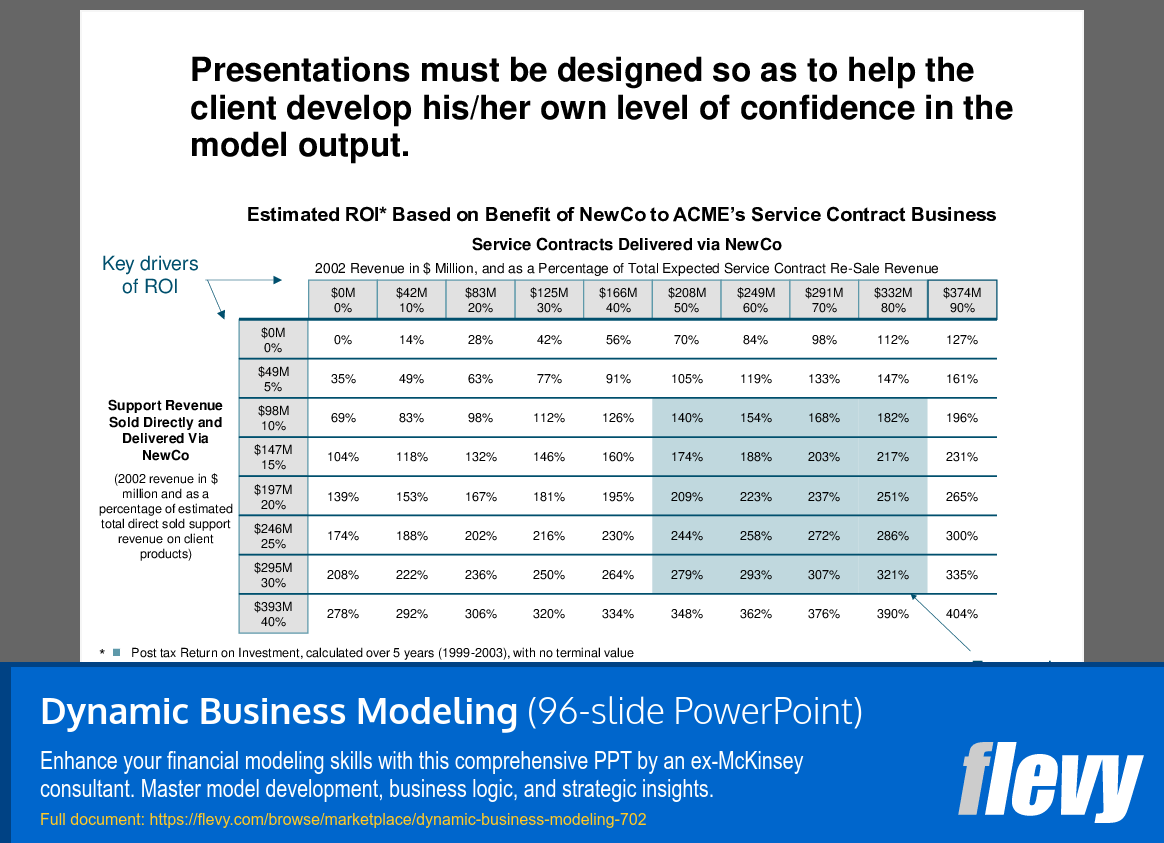
This document also delves into the critical qualities that define a well-developed financial model, emphasizing the importance of high-impact insights that drive strategic decisions. It categorizes the impact of financial models based on their ability to guide business improvements and strategic decisions, highlighting the conditions under which these models are most valuable. This approach ensures that the models are not just tools for analysis, but pivotal in shaping broad strategic directions.
The presentation outlines a comprehensive seven-step process for financial model development, starting from planning and analysis to managing and coaching. Each step is meticulously detailed, providing a clear roadmap for developing robust financial models. It stresses the importance of integrating business logic design and spreadsheet design with data gathering and testing, ensuring that the models are both accurate and insightful. This structured approach facilitates a thorough understanding of the business drivers and enhances decision-making capabilities.
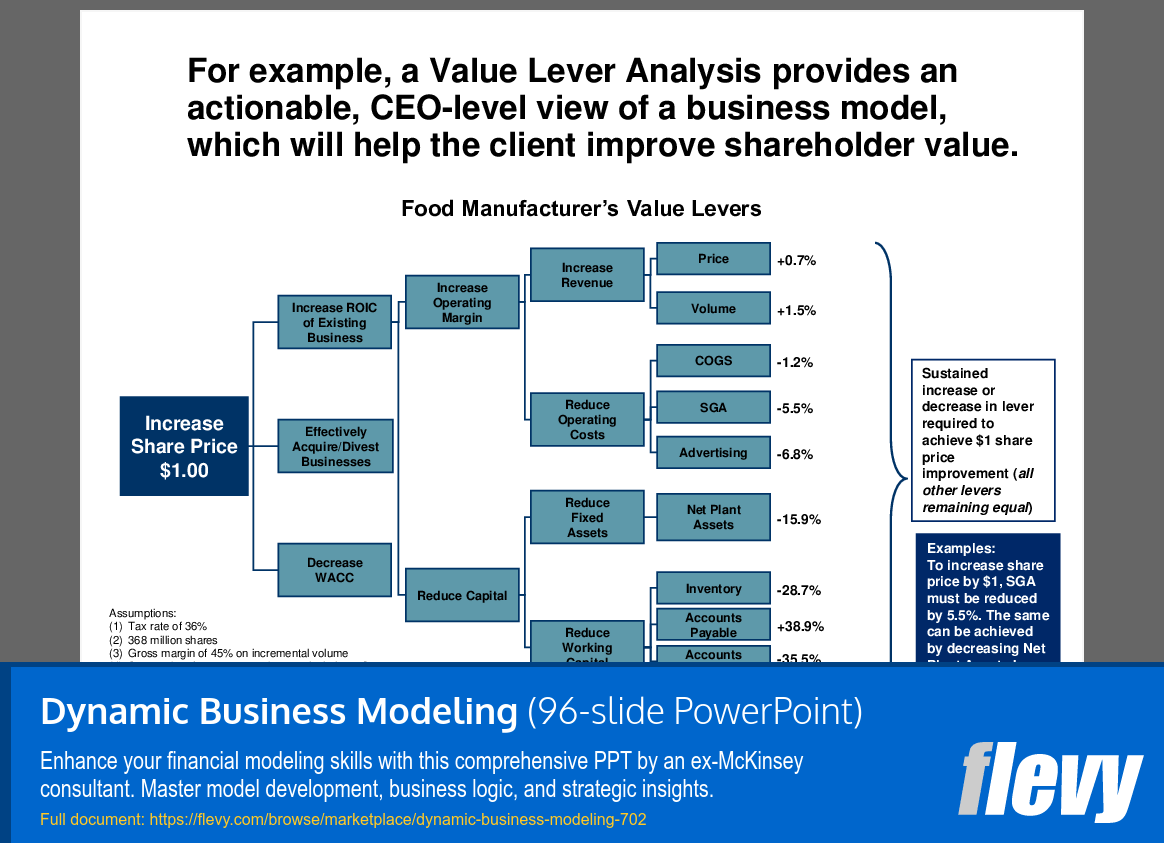
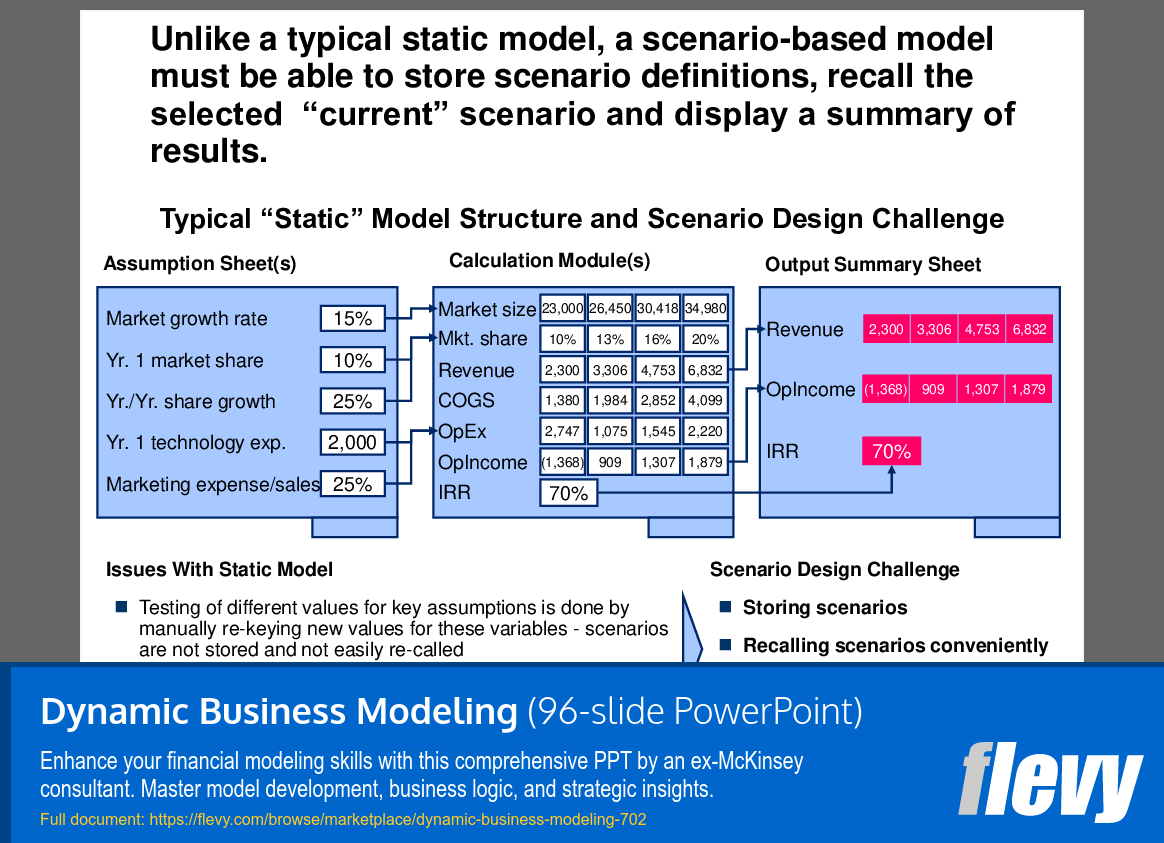
Moreover, the document addresses common challenges in financial modeling, such as the difficulty in "selling" the need for models and the frequent oversight of their potential benefits. It offers practical advice on how to coach clients to recognize the value of financial models, thereby improving communication and decision-making. The inclusion of scenario-based models and sensitivity testing techniques, like tornado charts, further enriches the toolkit for financial analysts, making this presentation an indispensable resource for those aiming to excel in financial modeling.
Got a question about the product? Email us at support@flevy.com or ask the author directly by using the "Ask the Author a Question" form. If you cannot view the preview above this document description, go here to view the large preview instead.
MARCUS OVERVIEW
This synopsis was written by Marcus [?] based on the analysis of the full 96-slide presentation.
Executive Summary
The "Dynamic Business Modeling" presentation is designed to elevate financial modeling capabilities, offering a structured approach akin to McKinsey, Bain, or BCG-quality methodologies (consulting-grade; not affiliated). This comprehensive framework guides users through the intricacies of financial model development, emphasizing data gathering, business logic design, and effective communication. Participants will learn to create credible, insightful, and flexible models that support strategic decision-making and enhance engagement leadership in financial modeling efforts.
Who This Is For and When to Use
• Corporate executives needing to understand financial modeling for strategic decisions
• Engagement leaders managing financial modeling projects
• Financial analysts looking to improve their modeling skills
• Consultants advising clients on financial strategies
• Teams involved in business strategy and financial planning
Best-fit moments to use this deck:
• During the planning phase of a financial modeling project
• When introducing new financial modeling methodologies to teams
• In workshops focused on enhancing financial modeling skills
• For coaching sessions aimed at improving team capabilities in financial modeling
Learning Objectives
• Define the essential components of a robust financial model
• Build a financial model that incorporates business logic and data insights
• Establish a structured process for effective financial modeling
• Communicate model results clearly to stakeholders
• Test and validate assumptions within financial models
• Manage and coach teams through the financial modeling process
Table of Contents
• Introduction (page 1)
• Data Gathering (page 11)
• Business Logic Design (page 19)
• Spreadsheet Design (page 25)
• Model Development Process (page 33)
• Testing and Developing Insight (page 39)
• Communicating (page 45)
• Managing and Coaching (page 49)
Primary Topics Covered
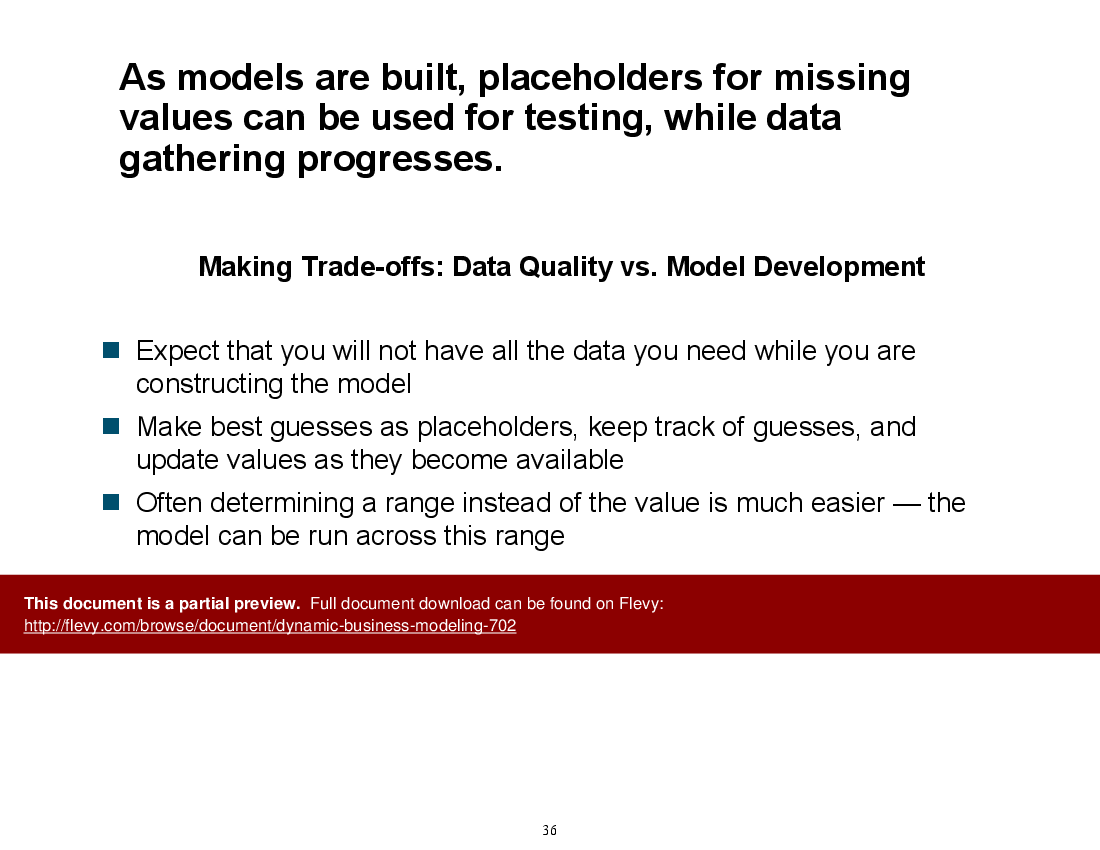
• Data Gathering - Techniques for collecting relevant data from various sources to inform financial models.
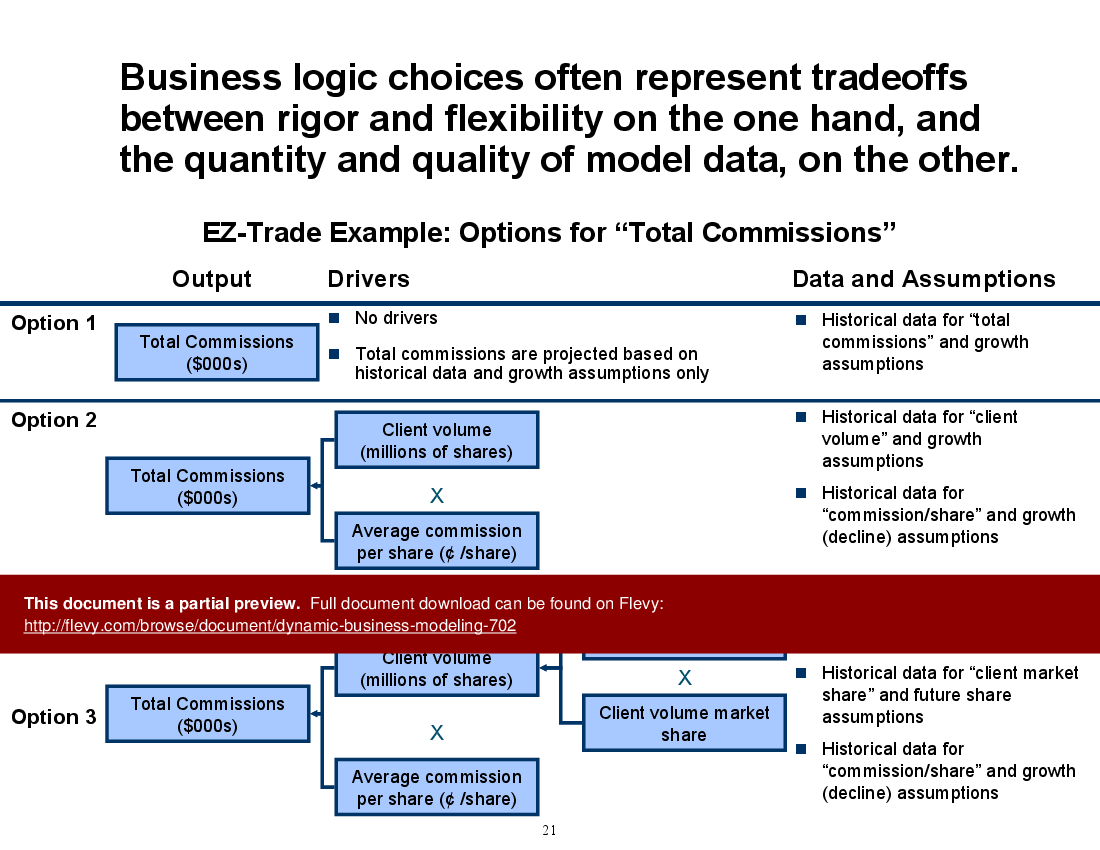
• Business Logic Design - Framework for establishing relationships between inputs and outputs in a financial model.
• Spreadsheet Design - Best practices for structuring spreadsheets to enhance clarity and usability.
• Model Development Process - A step-by-step guide to developing financial models efficiently.
• Testing and Developing Insight - Methods for validating model assumptions and generating actionable insights.
• Communicating Results - Strategies for effectively presenting model findings to stakeholders.
Deliverables, Templates, and Tools
• Financial model templates for various business scenarios
• Best practices checklist for financial modeling
• Data gathering checklists to ensure comprehensive input collection
• Business logic schematics for visualizing model relationships
• Scenario analysis tools for testing different business conditions
• Coaching materials to guide team members in financial modeling
Slide Highlights
• Overview of the financial modeling process and its importance in strategic decision-making
• Key qualities of a well-developed financial model, emphasizing credibility and flexibility
• Examples of effective data gathering techniques and sources
• Visual representations of business logic and its impact on model outputs
• Case studies demonstrating the application of financial models in real-world scenarios
Potential Workshop Agenda
Introduction to Financial Modeling (60 minutes)
• Overview of financial modeling importance
• Discussion of common pitfalls in modeling efforts
• Introduction to the seven-step model development process
Hands-On Data Gathering Session (90 minutes)
• Techniques for effective data collection
• Group exercise on identifying data sources
• Sharing best practices for gathering insights
Business Logic Design Workshop (60 minutes)
• Collaborative creation of business logic schematics
• Group discussions on model relationships
• Presentation of team-designed business logic
Customization Guidance
• Tailor the data gathering checklist to align with specific project needs
• Adjust business logic schematics to reflect unique organizational structures
• Incorporate company-specific metrics and terminology into financial models
• Modify templates to fit the specific context of the financial modeling project
Secondary Topics Covered
• Importance of flexibility in financial models
• Strategies for effective team management during modeling efforts
• Techniques for validating model assumptions and outputs
• Insights into common errors in financial modeling and how to avoid them
Topic FAQ
What are the core phases of a financial model development process?
A robust financial model development process typically moves from planning and analysis into discrete phases: data gathering, business logic design, spreadsheet design, model development, testing and insight generation, communicating results, and managing/coaching. The documentation for this approach outlines a formal seven-step process for model development.How should I structure data gathering for a financial model?
Structure data gathering by identifying relevant sources, documenting assumptions, and using standardized checklists to ensure completeness and traceability. Collect historicals, market inputs, and business drivers, and record provenance for each input. The Dynamic Business Modeling material includes a dedicated data gathering checklist to guide the process.What is business logic design and why does it matter in modeling?
Business logic design defines the relationships between inputs and outputs so the model reflects underlying commercial dynamics. Clear schematics make assumptions transparent, enable sensitivity testing, and reduce errors during development. The product provides business logic schematics to visualize these relationships.Which spreadsheet design practices improve a model’s credibility?
Credible spreadsheet design emphasizes clear structure, consistent naming, separation of inputs/calculations/outputs, and built-in error checks to aid validation and review. Visual organization supports stakeholder understanding and reduces mistakes. The presentation lists spreadsheet design best practices to implement these principles.What should I look for when buying a financial modeling toolkit for team training?
Prioritize toolkits that include training agendas, sample models, templates, checklists, and coaching materials so you can run workshops and onboard teams. Look for example exercises and a sample Excel model to practice end-to-end development. Dynamic Business Modeling includes a sample financial model in Excel.How much time should I plan for a hands-on financial modeling workshop?
A practical workshop can be structured with short modules: a 60-minute introduction, a 90-minute hands-on data gathering session, and a 60-minute business logic design workshop, among other activities. The sample agenda in the material totals at least 210 minutes for those 3 sessions.What methods should I use to validate assumptions in a model?
Common validation methods include sensitivity analysis, scenario analysis, peer review, and back-testing against historical data to check reasonableness. Visualization tools like tornado charts can highlight key drivers and risks. The resources describe sensitivity and scenario techniques including tornado charts for validation.How can engagement leaders coach teams to improve modeling quality?
Coaching combines clear objectives, role assignments, review cycles, and practical exercises to build skills. Use structured agendas, share lessons learned, and provide coaching materials and templates to standardize work. The Dynamic Business Modeling pack includes coaching materials and guidance for managing modeling efforts.Document FAQ
These are questions addressed within this presentation.
What is the purpose of financial modeling?
Financial modeling serves to provide insights that inform strategic decisions and validate business initiatives through quantitative analysis.
How do I ensure my financial model is credible?
A credible model is built on realistic assumptions, quality data sources, and thorough validation processes to ensure accuracy and reliability.
What are common pitfalls in financial modeling?
Common pitfalls include inadequate planning, poor data gathering, and insufficient testing of assumptions, which can lead to flawed models.
How can I effectively communicate model results?
Communicate results by simplifying complex data, focusing on key insights, and ensuring stakeholders understand the underlying assumptions and implications.
What tools can assist in financial modeling?
Tools such as Excel for spreadsheet design, scenario analysis software, and data visualization tools can enhance the modeling process.
How do I manage a financial modeling team?
Effective management involves clear communication of objectives, assigning roles based on expertise, and fostering collaboration throughout the modeling process.
What is the significance of business logic in financial modeling?
Business logic provides a structured framework that defines the relationships between inputs and outputs, ensuring the model accurately reflects business dynamics.
How can I validate my financial model?
Validation can be achieved through sensitivity analysis, peer reviews, and comparing model outputs against historical data to ensure consistency and reasonableness.
Glossary
• Financial Model - A quantitative representation of a business's financial performance.
• Business Logic - The framework that defines the relationships between inputs and outputs in a model.
• Data Gathering - The process of collecting relevant information to inform model assumptions.
• Spreadsheet Design - The organization and structure of data within a spreadsheet for clarity and usability.
• Sensitivity Analysis - A technique used to determine how different values of an input affect the output of a model.
• Scenario Analysis - The process of analyzing the effects of different scenarios on model outcomes.
• Validation - The process of ensuring that a model accurately reflects the business and its assumptions.
• Assumptions - The foundational inputs that drive the calculations within a financial model.
• Output - The results generated by a financial model based on the input data and assumptions.
• Stakeholders - Individuals or groups with an interest in the outcomes of the financial model.
• Model Development Process - A structured approach to creating a financial model, typically involving multiple steps.
• Error Checking - The process of reviewing a model to identify and correct mistakes.
• Engagement Leader - A person responsible for managing a financial modeling project and ensuring its success.
• Credibility - The degree to which a model is considered trustworthy and reliable.
• Flexibility - The ability of a model to adapt to changes in assumptions or inputs.
• Insight - The understanding gained from analyzing model outputs and their implications.
• Coaching - The process of guiding team members to improve their financial modeling skills.
• Templates - Pre-designed models or frameworks that can be customized for specific projects.
• Best Practices - Established methods that are recognized as the most effective in achieving desired outcomes in financial modeling.
• Communication - The process of conveying model results and insights to stakeholders in an understandable manner.
FINANCIAL MODELING PPT SLIDES
Source: Best Practices in Financial Modeling PowerPoint Slides: Dynamic Business Modeling PowerPoint (PPT) Presentation Slide Deck, Documents & Files