Root Cause Analysis (RCA) (PowerPoint PPTX Slide Deck)
PowerPoint (PPTX) 36 Slides
DESCRIPTION
Root Cause Analysis (RCA)
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) is a structured approach used to identify the underlying causes of problems or incidents to prevent recurrence. This presentation aims to provide an in-depth understanding of RCA, its methodologies, and its application in various industries.
Introduction to RCA
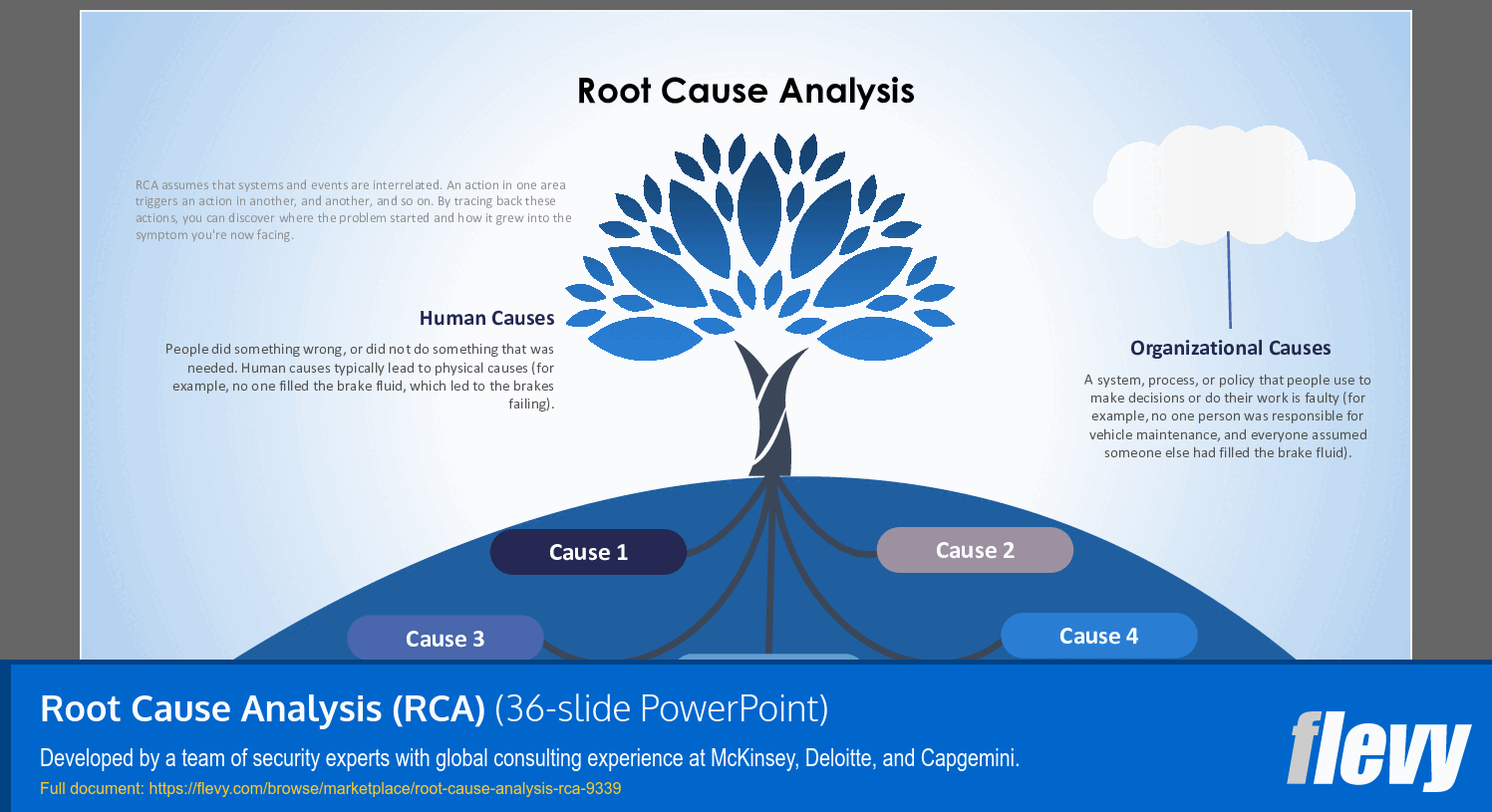
RCA is a systematic process for identifying the true source of a problem rather than just addressing its symptoms. It helps organizations enhance efficiency, improve quality, and mitigate risks by implementing long-term solutions.
Key Objectives
• Understand the RCA process
• Learn different RCA techniques
• Identify ways to implement RCA effectively
• Apply RCA in real-world scenarios
The RCA Process
The RCA process generally follows five key steps:
1. Define the Problem: Clearly describe the issue, including its impact, scope, and affected areas.
2. Gather Data: Collect relevant information, including timelines, events, and contributing factors.
3. Identify Root Causes: Use analytical techniques to pinpoint the primary causes of the problem.
4. Develop Solutions: Propose corrective actions that address root causes and prevent recurrence.
5. Implement and Monitor: Execute solutions and track their effectiveness over time.
Popular RCA Techniques
Several methodologies help in conducting an effective RCA:
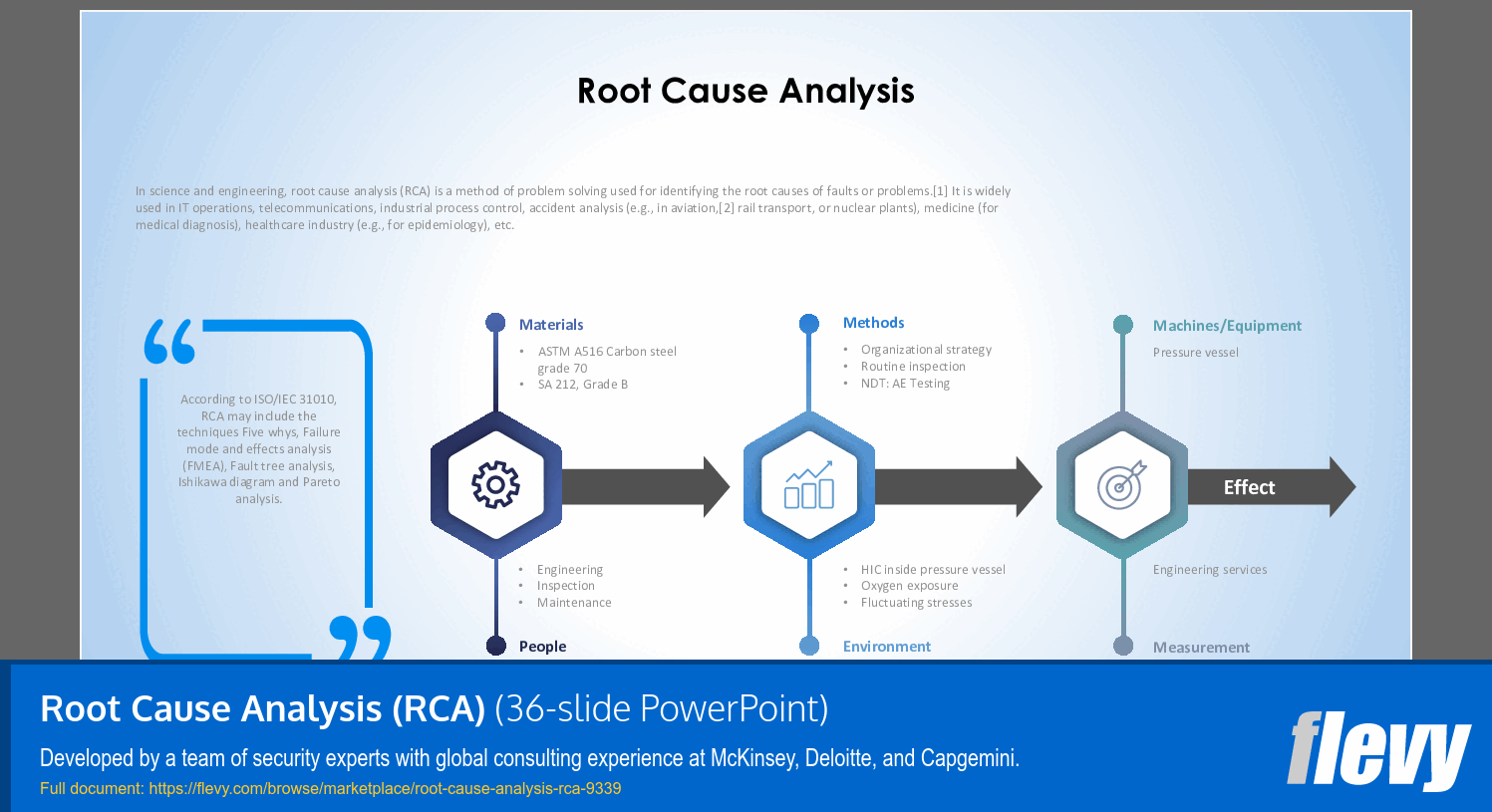
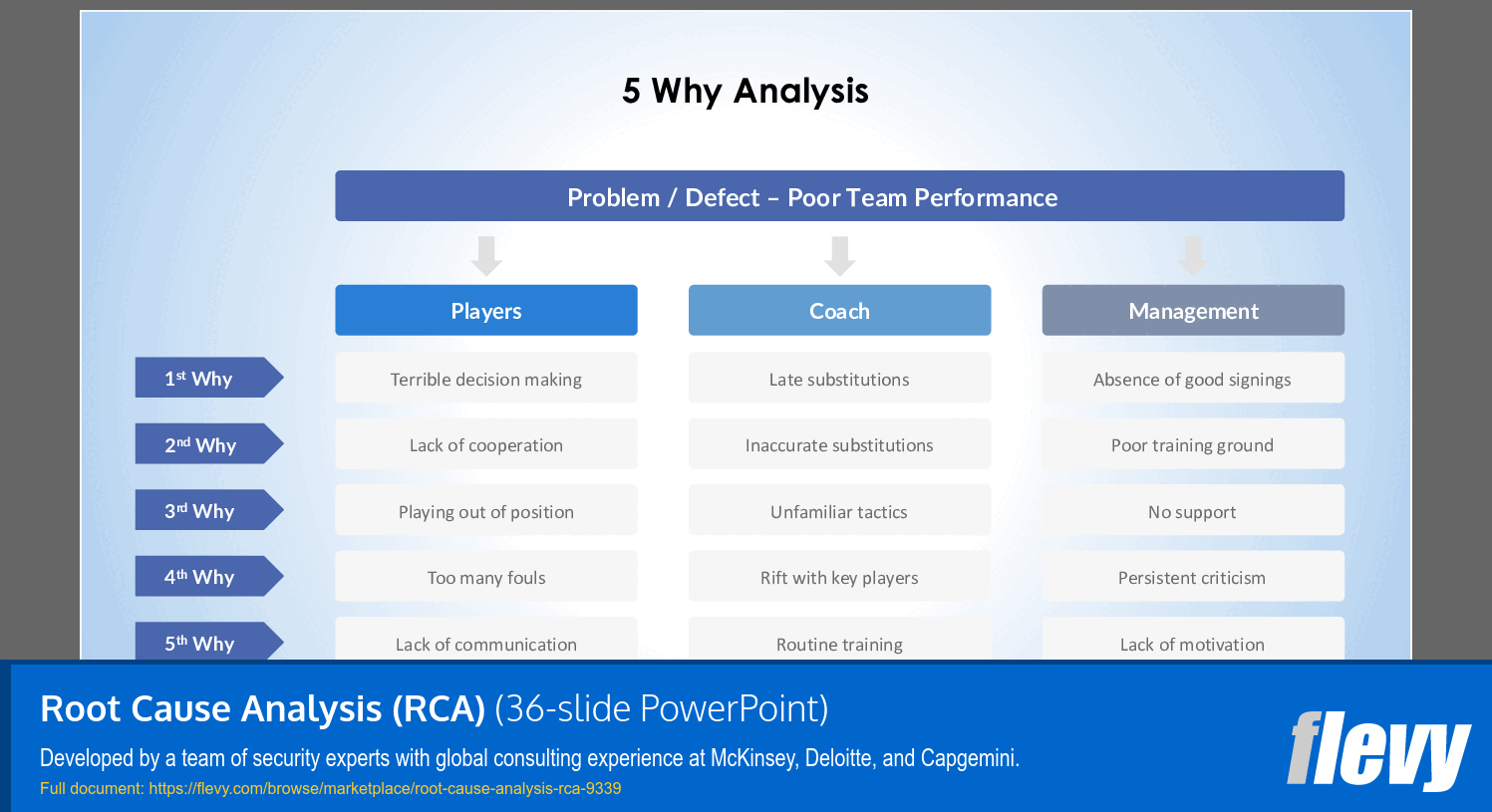
• 5 Whys Analysis: A simple method where the question "Why?" is asked repeatedly until the root cause is identified.
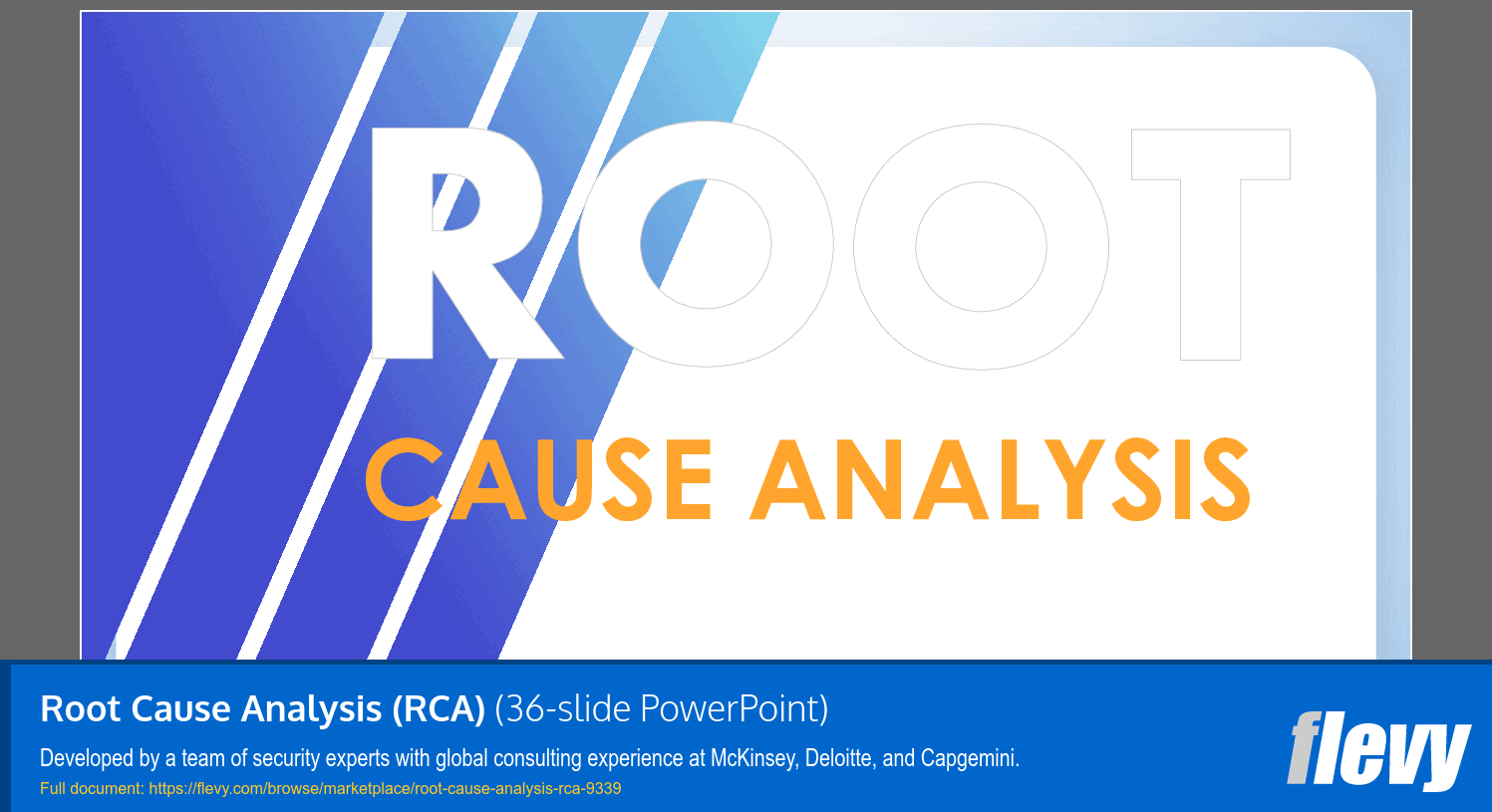
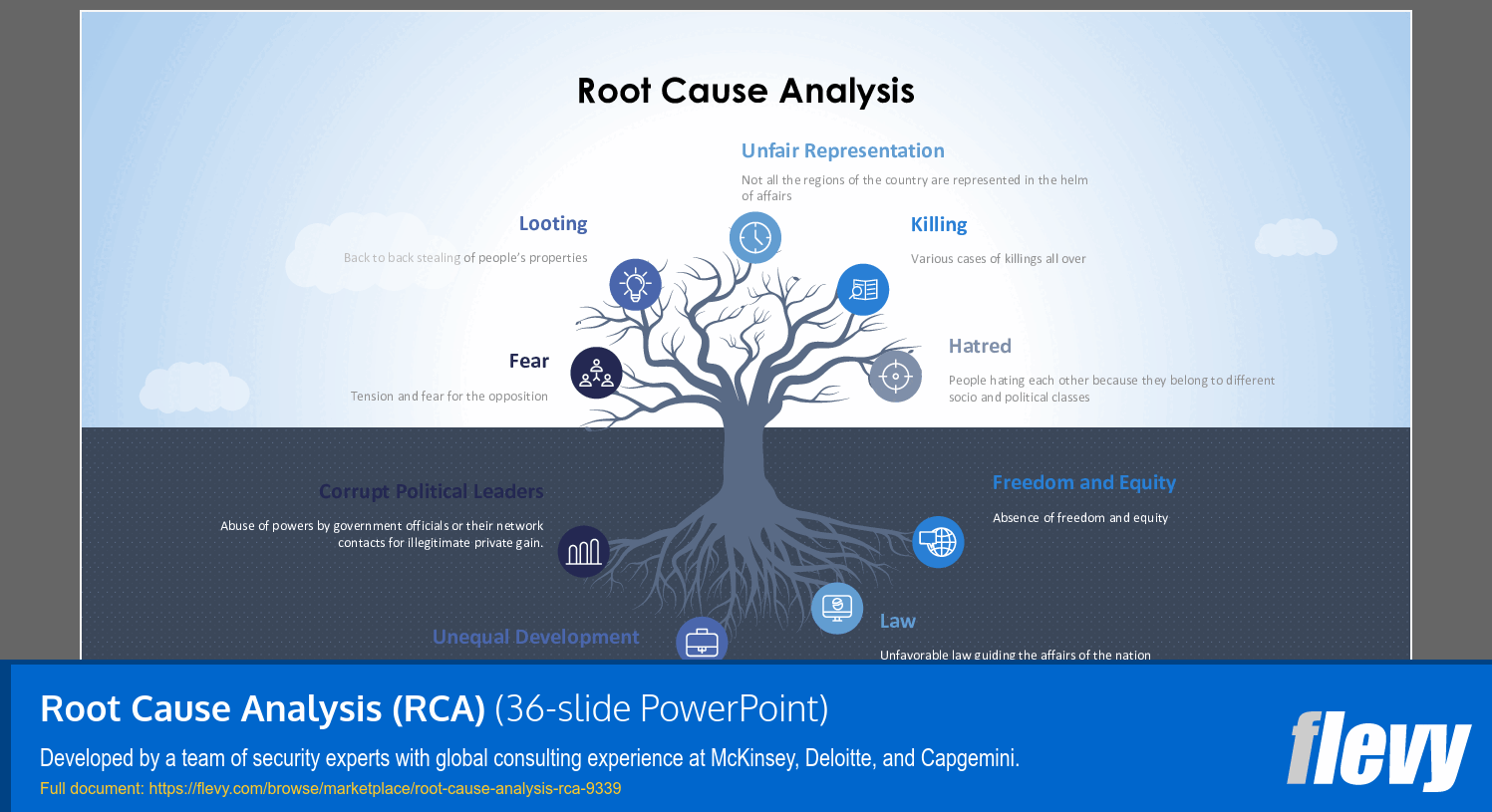
• Fishbone Diagram (Ishikawa): A visual tool that categorizes potential causes into major groups like People, Process, Equipment, and Environment.
• Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA): A proactive approach used to assess potential failures and their impact.
• Pareto Analysis: A statistical method that helps identify the most significant factors contributing to a problem.
• Fault Tree Analysis (FTA): A top-down approach used to analyze the logical relationship between various contributing factors.
Applications of RCA
RCA is widely used across industries:
• Healthcare: To improve patient safety by analyzing medical errors.
• Manufacturing: To reduce defects and enhance product quality.
• IT and Cybersecurity: To investigate system failures and security breaches.
• Aviation and Transportation: To prevent accidents and improve operational safety.
Conclusion
Root Cause Analysis is an essential tool for problem-solving and continuous improvement. By understanding and applying RCA methodologies, organizations can drive sustainable change, enhance performance, and prevent recurring issues.
Got a question about the product? Email us at support@flevy.com or ask the author directly by using the "Ask the Author a Question" form. If you cannot view the preview above this document description, go here to view the large preview instead.
Source: Best Practices in RCA, Specialized PowerPoint Templates, Specialized PowerPoint Diagrams, Root Cause Analysis PowerPoint Slides: Root Cause Analysis (RCA) PowerPoint (PPTX) Presentation Slide Deck, RadVector Consulting