Mastering Operational Risk Training - Workshop Day 2 (PowerPoint PPTX Slide Deck)
PowerPoint (PPTX) + Zip archive file (ZIP) 116 Slides
RISK MANAGEMENT PPT DESCRIPTION
Operational Risk is the risk of loss resulting from inadequate or failed internal processes, people, and systems or from external events. It is perhaps the most significant risk organizations face. Virtually every major loss that has taken place during the past 30 years, from Enron, Worldcom and Baring's Bank to the unauthorized trading incident at Société Générale and the subprime credit crisis, has been driven by operational failures.
Many financial institutions have spent millions of dollars trying to develop a robust framework for measuring and managing Operational Risk. Yet, in spite of this huge investment, for many organizations, developing a viable Operational Risk Management (ORM) program remains an elusive goal.
ORM involves the systematic assessment of potential operational risks, the implementation of controls to mitigate or eliminate those risks, and the continuous monitoring of the effectiveness of those controls. ORM is an important part of overall Risk Management and helps organizations to identify, evaluate, and prioritize risks in order to make informed decisions about how to allocate resources and implement controls to manage those risks. ORM is applicable to a wide range of organizations and industries, including financial services, healthcare, manufacturing, and government agencies.
This 116-slide PowerPoint is the day 2 presentation taken from a 2-day workshop called "Mastering Operational Risk – Theory & Practice (ORM in Financial Institutions)." This presentation includes the following key sections:
• Business Continuity Management (BCM)
• Corporate Loss Database
• Workshop: Developing OR framework
• Workshop: Defining Key Risk Indicators (KRI)
• Measuring and Managing Operational Risk
• Workshop: Conducting RCSA
The training workshop presentation is designed for both aspiring and active Risk officers, VPs, MDs, heads of departments, CFOs, CRO, analysts, Operational and Risk Management staff from financial services industry – banks, insurance companies, pension funds, consultancies, software vendors operating in these sectors. It will be also useful for a Risk Manager operating in a nonfinancial sector, as well as for interim Risk Managers and consultants who want to get up to speed with a new or current risk assignment.
This product also includes 2 supplemental documents:
• Quiz/Self-assessment (Word document)
• Risk glossary (Word document)
Got a question about the product? Email us at support@flevy.com or ask the author directly by using the "Ask the Author a Question" form. If you cannot view the preview above this document description, go here to view the large preview instead.
MARCUS OVERVIEW
This synopsis was written by Marcus [?] based on the analysis of the full 116-slide presentation.
Executive Summary
The "Mastering Operational Risk Training - Workshop Day 2" presentation is designed for financial institutions aiming to enhance their Operational Risk Management (ORM) capabilities. Developed by Boris Agranovich, a recognized leader in risk management, this workshop builds on insights from collaborations with major organizations like Citibank and Capgemini. Participants will engage in practical workshops covering critical frameworks such as Business Continuity Management (BCM), Key Risk Indicators (KRIs), and Risk Control Self-Assessments (RCSAs). This comprehensive training equips executives and consultants with the tools to effectively measure, manage, and mitigate operational risks in alignment with regulatory standards.
Who This Is For and When to Use
• Risk Management Executives overseeing ORM frameworks in financial institutions
• Compliance Officers ensuring adherence to regulatory requirements
• Operational Risk Analysts responsible for data collection and analysis
• Business Continuity Managers focused on maintaining critical operations during disruptions
Best-fit moments to use this deck:
• During the implementation of new ORM frameworks
• When preparing for regulatory audits or assessments
• In workshops aimed at enhancing team capabilities in risk management practices
Learning Objectives
• Define operational risk and its implications for financial institutions
• Build a comprehensive ORM framework tailored to organizational needs
• Establish effective KRIs for ongoing risk monitoring
• Conduct thorough RCSAs to identify and mitigate potential risks
• Develop a BCM strategy to ensure continuity during disruptive events
• Analyze historical loss data to inform future risk management decisions
Table of Contents
• Recap of Day 1 (page 3)
• Business Continuity Management (BCM) (page 4)
• Corporate Loss Database (CLD) (page 11)
• Workshops Overview (page 3)
• Measuring and Managing Operational Risk (page 12)
• Risk Control Self-Assessment (RCSA) (page 12)
Primary Topics Covered
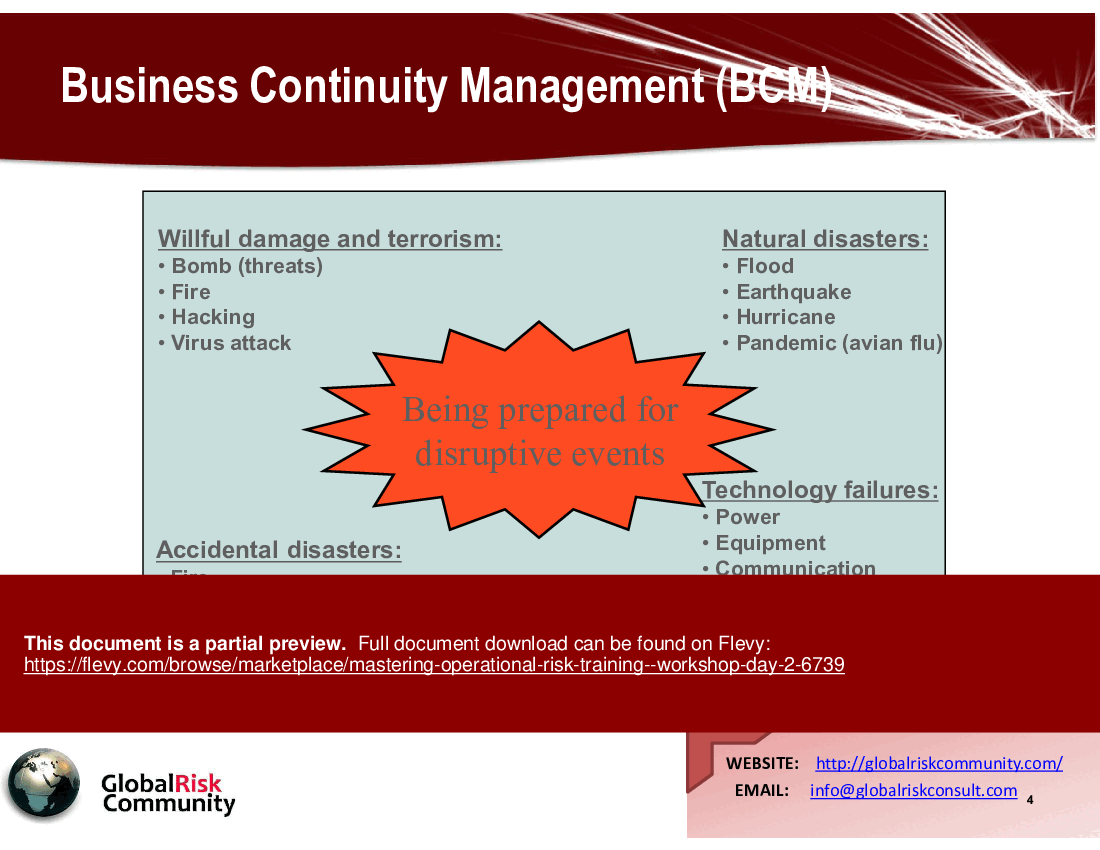
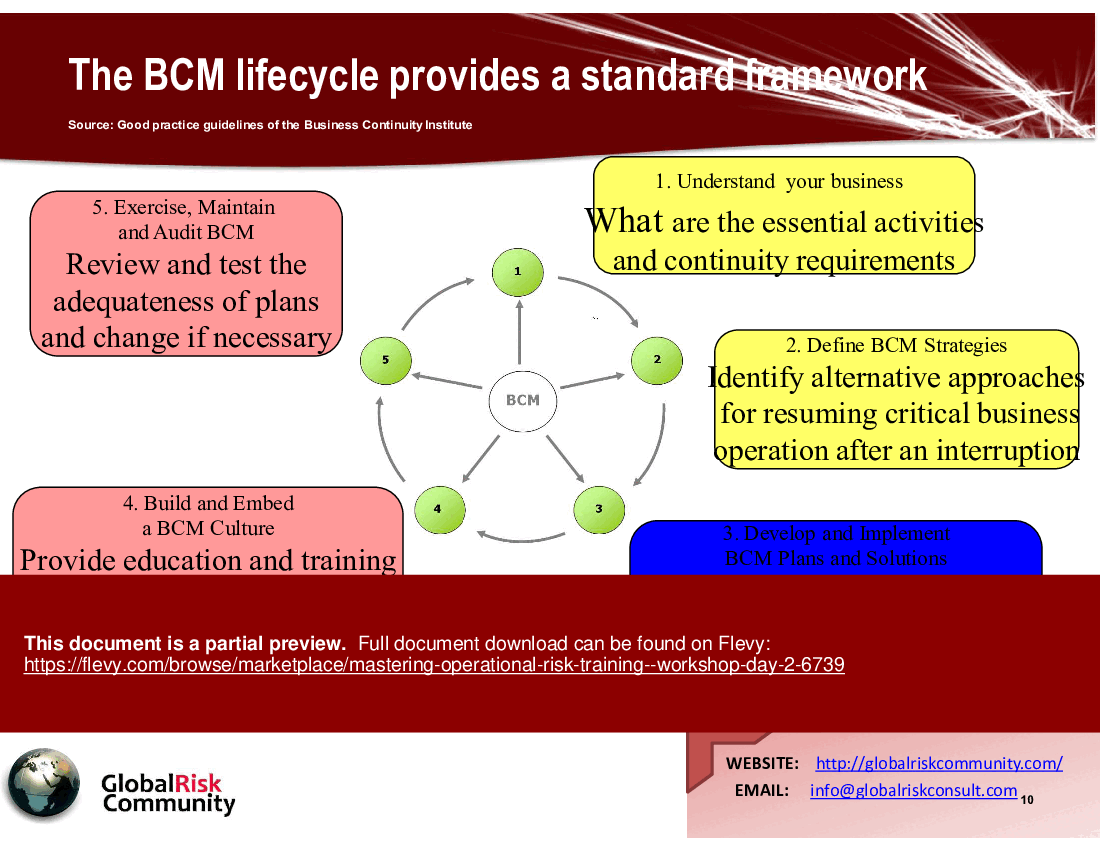
• Business Continuity Management (BCM) - Focuses on maintaining critical business operations during disruptions, addressing both natural and man-made threats.
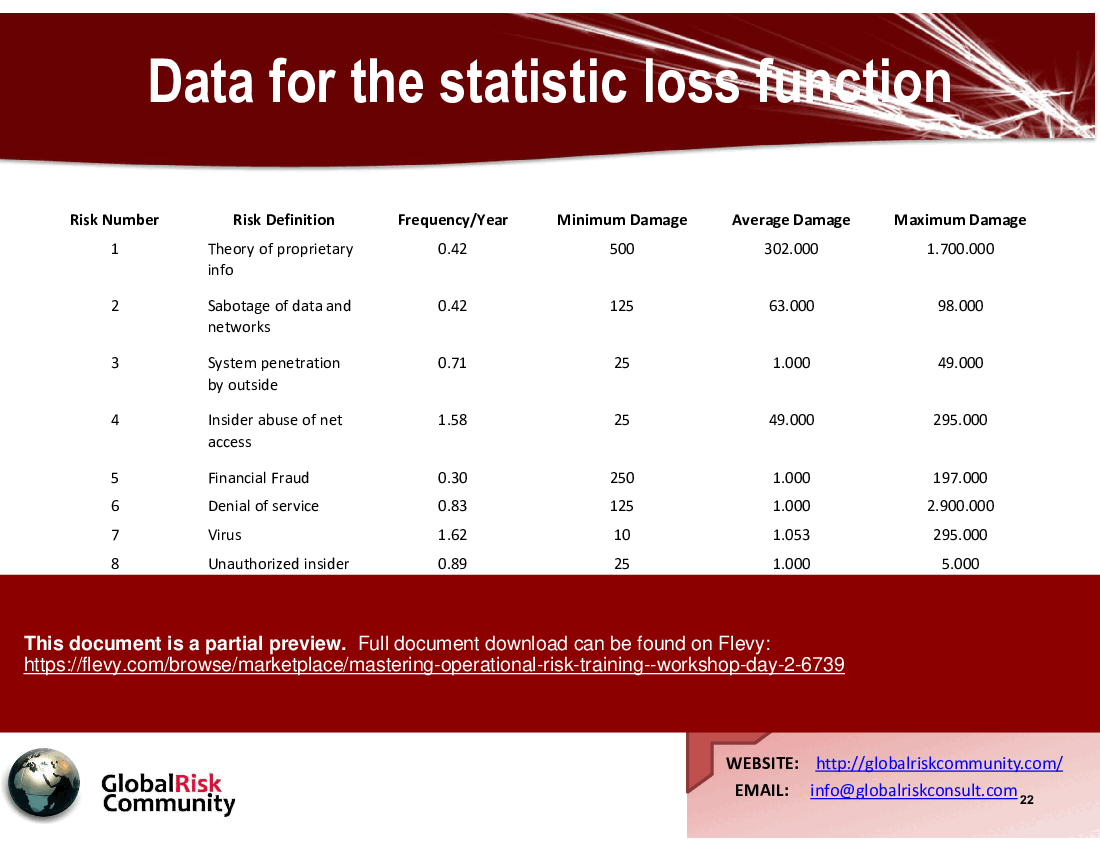
• Corporate Loss Database (CLD) - A systematic approach to capturing internal operational losses, essential for identifying and assessing operational risk.
• Key Risk Indicators (KRIs) - Metrics used to monitor risk levels and trigger alerts for potential issues.
• Risk Control Self-Assessment (RCSA) - A structured process for identifying risks and evaluating the effectiveness of controls in place.
• Operational Risk Framework - A comprehensive structure for managing operational risks, ensuring alignment with regulatory standards.
• Crisis Management Planning - Strategies for responding to crises, ensuring organizational resilience and recovery.
Deliverables, Templates, and Tools
• BCM strategy template for operational continuity planning
• CLD setup guide for capturing and analyzing loss data
• KRI dashboard template for real-time risk monitoring
• RCSA toolkit for conducting self-assessments
• Crisis management plan template for effective response strategies
• Risk reporting framework for communicating findings to stakeholders
Slide Highlights
• Overview of BCM and its importance in operational risk management
• Examples of threats that can disrupt business continuity
• Steps for setting up a Corporate Loss Database
• Key components of an effective BCM lifecycle
• Insights into quantifying operational risk through historical data analysis
Potential Workshop Agenda
BCM Overview and Best Practices (90 minutes)
• Discuss the importance of BCM in ORM
• Identify critical business processes and continuity requirements
• Develop a BCM strategy tailored to organizational needs
RCSA Workshop (60 minutes)
• Conduct a guided RCSA session to identify risks and assess controls
• Develop action plans for addressing identified risks
KRI Development Session (60 minutes)
• Define relevant KRIs for ongoing risk monitoring
• Create a KRI dashboard for real-time tracking
Customization Guidance
• Tailor the BCM strategy to reflect specific organizational processes and risks
• Modify the CLD to capture relevant loss data unique to your institution
• Adjust the KRI metrics to align with organizational risk appetite and regulatory requirements
Secondary Topics Covered
• Regulatory requirements impacting ORM
• Best practices for effective risk communication
• Techniques for conducting effective risk assessments
• The role of technology in enhancing ORM capabilities
Topic FAQ
What are the core components of an operational risk management program?
Core components include definition and governance of operational risk, Business Continuity Management (BCM), a Corporate Loss Database (CLD) for historical losses, Key Risk Indicators (KRIs) for monitoring, Risk Control Self-Assessments (RCSAs) to test controls, crisis management planning, and reporting frameworks — for example, BCM, CLD, KRIs, and RCSA.How should my team approach developing Key Risk Indicators (KRIs)?
Begin by aligning KRIs with the organization’s risk appetite and critical processes, select measurable metrics that provide early warning, and display them in a dashboard for real-time monitoring. The training includes guidance and a KRI dashboard template to define and implement relevant metrics.What is a Corporate Loss Database and how is it used in ORM?
A Corporate Loss Database (CLD) systematically captures internal loss events and related metadata to identify trends and quantify operational exposures. Organizations use CLDs to analyze historical loss drivers and inform control improvements; the workshop provides a CLD setup guide to implement this process.How do I run an effective Risk Control Self-Assessment (RCSA) workshop?
An RCSA workshop should guide participants to identify risks, map existing controls, evaluate control effectiveness, and develop action plans for gaps. The deck outlines a guided RCSA session format and supplies an RCSA toolkit to conduct assessments and record remediation actions.What should I evaluate when buying an operational risk training deck for my bank?
Look for coverage of BCM, CLD, KRIs, RCSA, crisis planning, regulatory alignment (e.g., SOX, FFIEC, ISO), audience fit for risk officers and executives, and included templates or supplemental materials. The product specifies a 116-slide presentation with templates and 2 supplemental documents.Are pre-built templates useful for smaller risk teams or interim managers?
Pre-built templates can help smaller teams and interim risk managers accelerate setup and training by providing ready formats for BCM strategies, CLD capture, KRI dashboards, and RCSA documentation; the workshop explicitly includes a BCM strategy template, CLD guide, KRI dashboard, and RCSA toolkit.Which ORM topics should a team rehearse when preparing for a regulatory audit?
Teams should rehearse Business Continuity Management planning and testing, accuracy and completeness of the Corporate Loss Database, the relevance and thresholds of KRIs, effectiveness of controls through RCSAs, and crisis response and reporting aligned with applicable standards like SOX or ISO 27001.How long should workshops be to cover BCM, RCSA, and KRI development in one session?
A practical agenda example in the training schedules a 90-minute BCM overview and strategy session, a 60-minute RCSA workshop to identify risks and actions, and a 60-minute KRI development session to define metrics and build a dashboard.Document FAQ
These are questions addressed within this presentation.
What is the purpose of a Corporate Loss Database?
A CLD captures historical loss data to identify and assess operational risks, providing a foundation for risk quantification and management.
How can we ensure our BCM strategy is effective?
An effective BCM strategy should be regularly reviewed and tested to ensure it meets the organization’s continuity requirements during disruptions.
What are Key Risk Indicators (KRIs)?
KRIs are metrics used to monitor risk levels and provide early warning signals for potential operational issues.
What is the significance of conducting RCSAs?
RCSAs help organizations identify risks and evaluate the effectiveness of controls, ensuring proactive risk management.
How often should we review our operational risk framework?
The operational risk framework should be reviewed regularly, especially in response to significant changes in the business environment or regulatory landscape.
What role does technology play in ORM?
Technology supports data collection, analysis, and reporting, enhancing the effectiveness of risk management processes.
How can we customize the training for our organization?
The training can be tailored to reflect specific organizational processes, risks, and regulatory requirements, ensuring relevance and applicability.
What are the common challenges in implementing ORM?
Common challenges include resistance to change, lack of data, and insufficient training for staff involved in risk management processes.
Glossary
• Operational Risk - The risk of loss resulting from inadequate or failed internal processes, people, systems, or external events.
• Business Continuity Management (BCM) - A framework for ensuring the continuity of critical business operations during disruptions.
• Key Risk Indicator (KRI) - A metric used to monitor risk levels and trigger alerts for potential issues.
• Risk Control Self-Assessment (RCSA) - A process for identifying risks and evaluating the effectiveness of controls in place.
• Corporate Loss Database (CLD) - A systematic database capturing internal operational losses for risk assessment.
• Crisis Management - Strategies and processes for responding to and recovering from crises.
• Risk Appetite - The level of risk an organization is willing to accept in pursuit of its objectives.
• Regulatory Compliance - Adherence to laws, regulations, and guidelines relevant to the organization’s operations.
• Data Analysis - The process of inspecting, cleansing, and modeling data to discover useful information for decision-making.
• Risk Mitigation - Strategies and actions taken to reduce the impact or likelihood of risks.
• Loss Event - An occurrence that results in a financial loss for the organization.
• Risk Management Framework - A structured approach to managing risk across an organization.
• Stakeholders - Individuals or groups with an interest in the organization’s performance and risk management practices.
• Operational Resilience - The ability of an organization to adapt to disruptions while maintaining essential functions.
• Risk Assessment - The process of identifying and analyzing potential risks that could negatively impact an organization.
• Incident Response Plan - A documented strategy for responding to and managing incidents that could disrupt operations.
• Quantitative Risk Analysis - The use of mathematical and statistical methods to assess risk.
• Qualitative Risk Analysis - The assessment of risk based on subjective judgment and experience rather than numerical data.
• Risk Tolerance - The acceptable level of risk an organization is willing to take on.
• Scenario Analysis - A process for evaluating potential future events by considering alternative possible outcomes.
Source: Best Practices in Risk Management PowerPoint Slides: Mastering Operational Risk Training - Workshop Day 2 PowerPoint (PPTX) Presentation Slide Deck, Boris Agranovich