Supply Chain Information Transparency Strategy (PowerPoint PPTX Slide Deck)
PowerPoint (PPTX) 25 Slides FlevyPro Document
SUPPLY CHAIN ANALYSIS PPT DESCRIPTION
Supply Chains across industries have become way too complicated and globalized today. Organizations are getting under pressure to disclose their Supply Chain information publicly, as external stakeholders are eager to know more about an organization's Supply Chain practices than what it is typically required to disclose legally.
Executives are finding it hard to deal with this situation. A majority of them have a limited understanding of the salient features and capabilities of their Supply Chains, lack the expertise to gather and report Supply Chain data, and fail to develop a Supply Chain Information Disclosure Strategy.
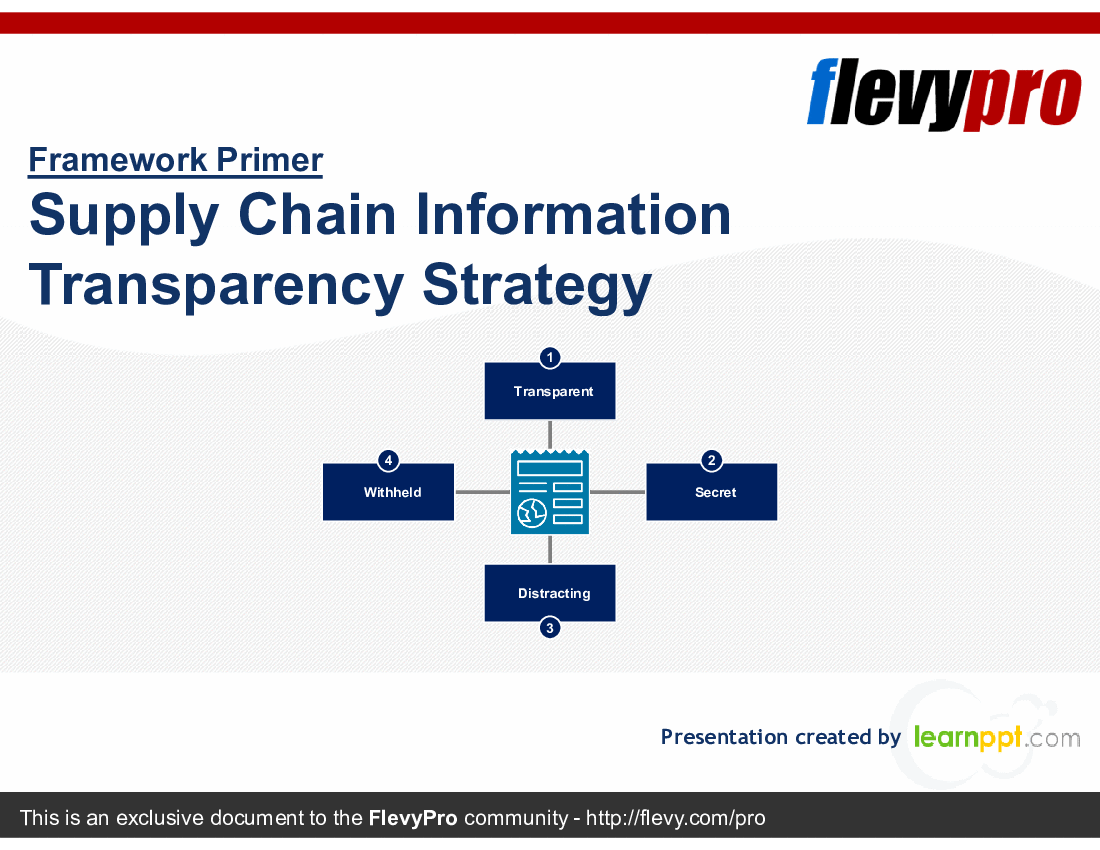
This presentation deliberates on the 4 Supply Chain Information Disclosure Strategies for the organizations to select a viable information sharing option, based on their current approach and future disclosure needs:
1. Transparent
2. Secret
3. Distracting
4. Withheld
These Information Transparency Strategies are beneficial for the executives to clarify their current approach to data disclosure and integrate it with their core business strategy. The presentation also provides an overview of the 4 categories of Supply Chain Information—that organizations can publicly disclose—and the Information Transparency Matrix.
The slide deck also includes some slide templates for you to use in your own business presentations.
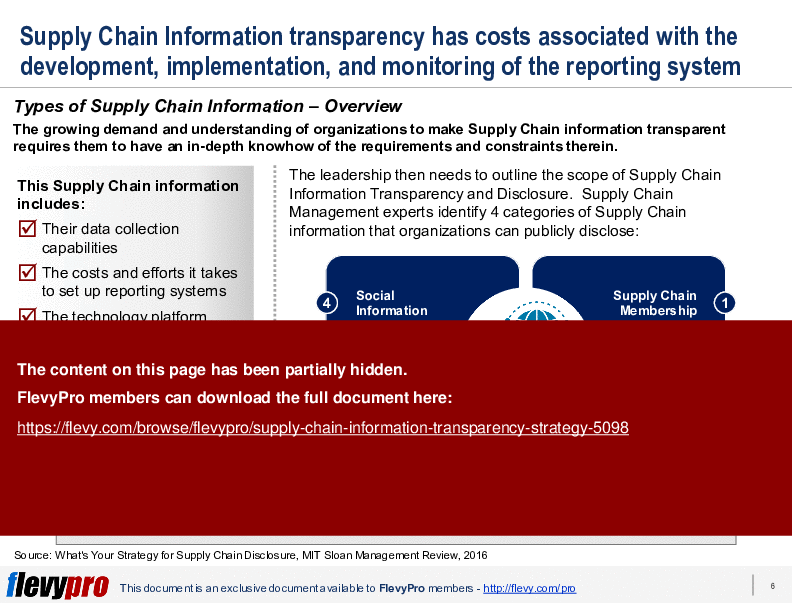
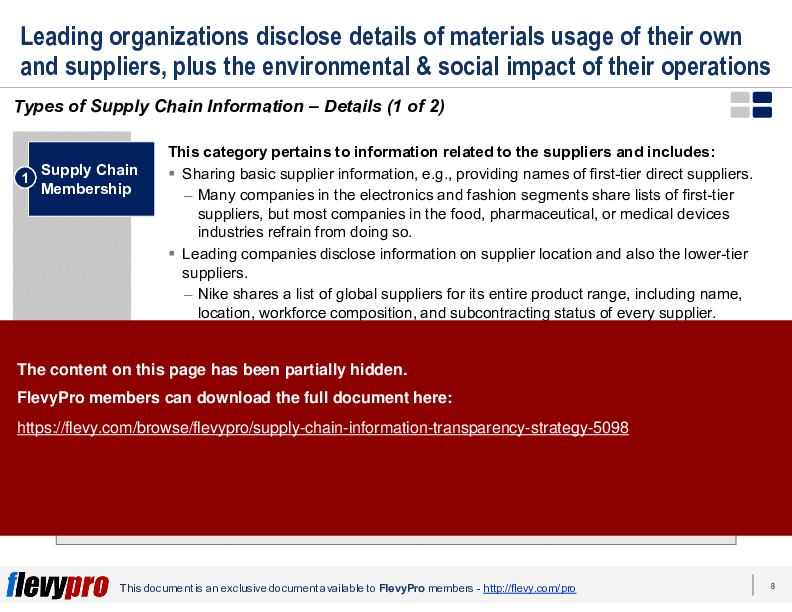
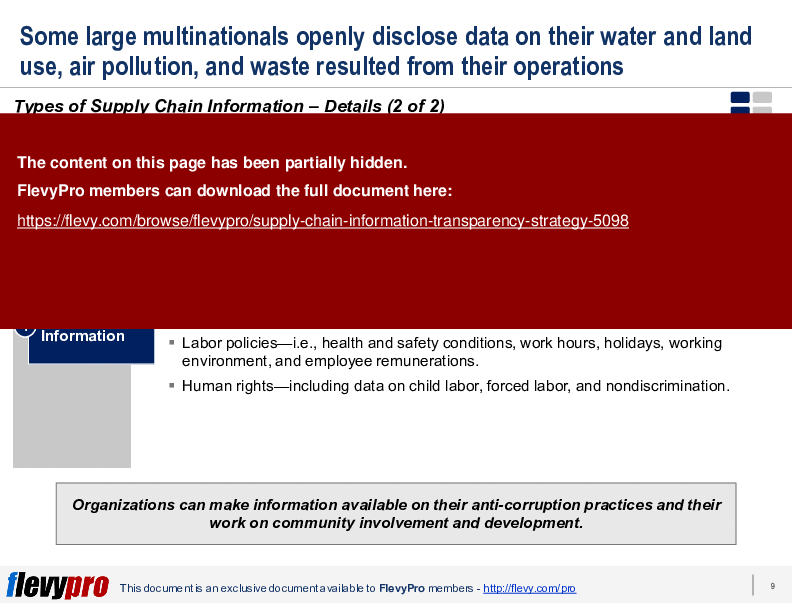
The PPT also delves into the complexities of implementing Supply Chain Information Transparency, highlighting the associated costs and efforts required for data collection, system setup, and technology platforms. Executives will gain insights into the four main categories of Supply Chain Information: Supply Chain Membership, Provenance, Environmental Information, and Social Information. These categories are essential for understanding what information can be disclosed and how it impacts stakeholder perception.
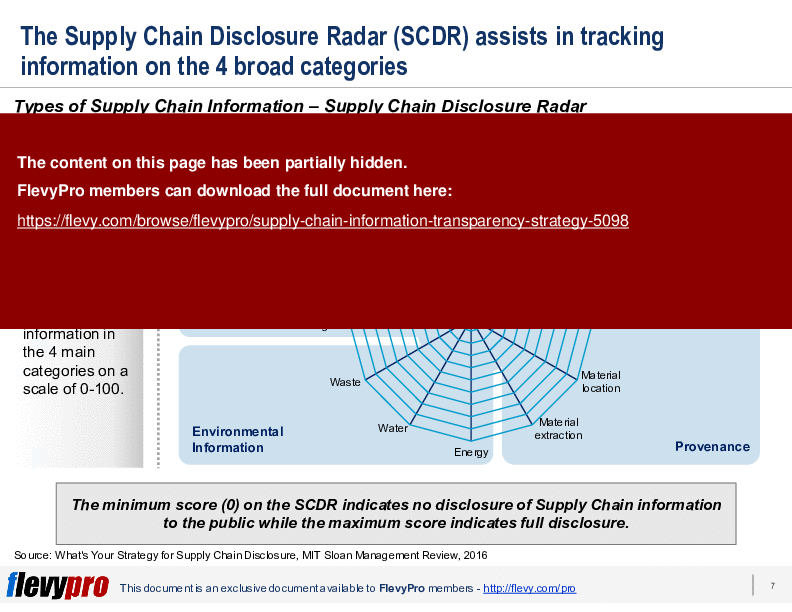
The presentation includes practical tools like the Supply Chain Disclosure Radar (SCDR) to help track and evaluate the extent of information disclosure across these categories. It also provides real-world examples of companies employing different transparency strategies, offering a comprehensive view of the advantages and pitfalls of each approach. This resource is invaluable for C-level executives aiming to refine their Supply Chain Information Transparency Strategy and align it with broader business objectives.
Got a question about this document? Email us at flevypro@flevy.com.
SUPPLY CHAIN ANALYSIS PPT SLIDES
Source: Best Practices in Supply Chain Management, Business Ethics, Transparency PowerPoint Slides: Supply Chain Information Transparency Strategy PowerPoint (PPTX) Presentation Slide Deck, LearnPPT Consulting
Did you need more documents?
Consider a FlevyPro subscription from $39/month. View plans here.
For $10.00 more, you can download this document plus 2 more FlevyPro documents. That's just $13 each.