052_Introduction to Hypothesis Testing (PowerPoint PPT)
PowerPoint (PPT) + Excel (XLSX) 36 Slides
DESCRIPTION
This product (052_Introduction to Hypothesis Testing) is a 36-slide PPT PowerPoint presentation (PPT) with a supplemental Excel document, which you can download immediately upon purchase.
?Why is statistics used in Process Improvement?? Is statistics really necessary or is it a way of keeping the masses confused about something that is mostly smoke and mirrors but is touted as a panacea? Are the training programs that downplay statistics . . . bad? These are great questions. In my training sessions I always ask ?who has previously taken a stats course?? With hands still in the air, I then ask, ?how many people liked the course?? Occasionally a few hands remain up, but often they are all down. The mere mention of stats usually sends students running for the door. Well not literally . . . but looks of disdain are all too common. In any case, most process improvement professionals do not look forward to the stats part of training. And I can understand why . . . the collective academic establishment doesn?t do a good job of making stats a valued analytical tool. Stats courses are relegated to rote learning about obscure concepts with little real life application. But it doesn?t have to be that way. With appropriately designed content, a competent and passionate teacher, stats can be fun . . . engaging even. So back to the original question, ?Why is statistics used in Process Improvement?? The answer I believe is . . . to manage risk.
In any sort of data analysis where statistics are used (Mean, Range, Min, Max, etc.) we are not only summarizing the data and their attributes, but also building models to better understand the data. Take for example the mean. Perhaps the simplest of all statistics, the mean is also the simplest of models. It is, as we know, a representation of the central tendency of the data, but may not represent any of the actual data points. It serves a useful purpose but comes with risk.
At the other end of the model spectrum you might find, Regression, DOE or MANOVA, etc. These models are relatively sophisticated and are capable of telling us much about our data and processes. Their sophistication doesn?t, however, eliminate the possibility of drawing the wrong conclusions. They too come with risk . . . but it can be managed.
And this is the more general point of statistics and statistical models in process improvement ? they allow us to manage and quantify the risks associated with incomplete information, and incomplete information is often the norm. So while it isn?t a perfect solution, it certainly has proven itself as a valuable, cost effective analysis tool.
In some respects, statistics is like the peep hole in your front door. It gives you a limited view to the other side, but the view is usually sufficient to make a decision (e.g. open the door). There are risks associated with this limited view, but in most cases, good decisions are possible and the alternatives are not very attractive.
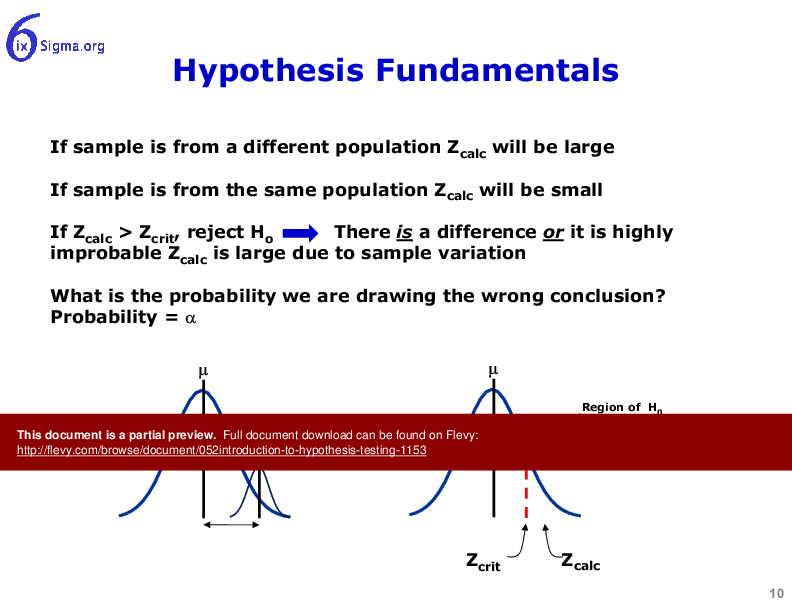
The objectives of this module are to: understand why hypothesis testing is used, understand the general concept of comparing a test statistic vs. an acceptable risk value, understand the role p-value takes in the decision process, understand how hypothesis testing relates to practical problems and solutions and understand alpha and beta risks as they relate to hypothesis testing.
This material is suitable for independent study or formal classroom training and includes a list of tools and quiz questions.
Got a question about the product? Email us at support@flevy.com or ask the author directly by using the "Ask the Author a Question" form. If you cannot view the preview above this document description, go here to view the large preview instead.
Source: 052_Introduction to Hypothesis Testing PowerPoint (PPT) Presentation, mjcarter