Degrees of Leverage and Breakeven Point (Excel XLSX)
Excel (XLSX)
BENEFITS OF THIS EXCEL DOCUMENT
- Managers must make decisions about sales volume, pricing and costs and are concerned about the impact of their decisions on profit. Therefore, they need to understand the relations among revenues, costs, volume, and profit.
- The break-even point can be defined as the level of activity at which a business makes neither a profit nor loss.
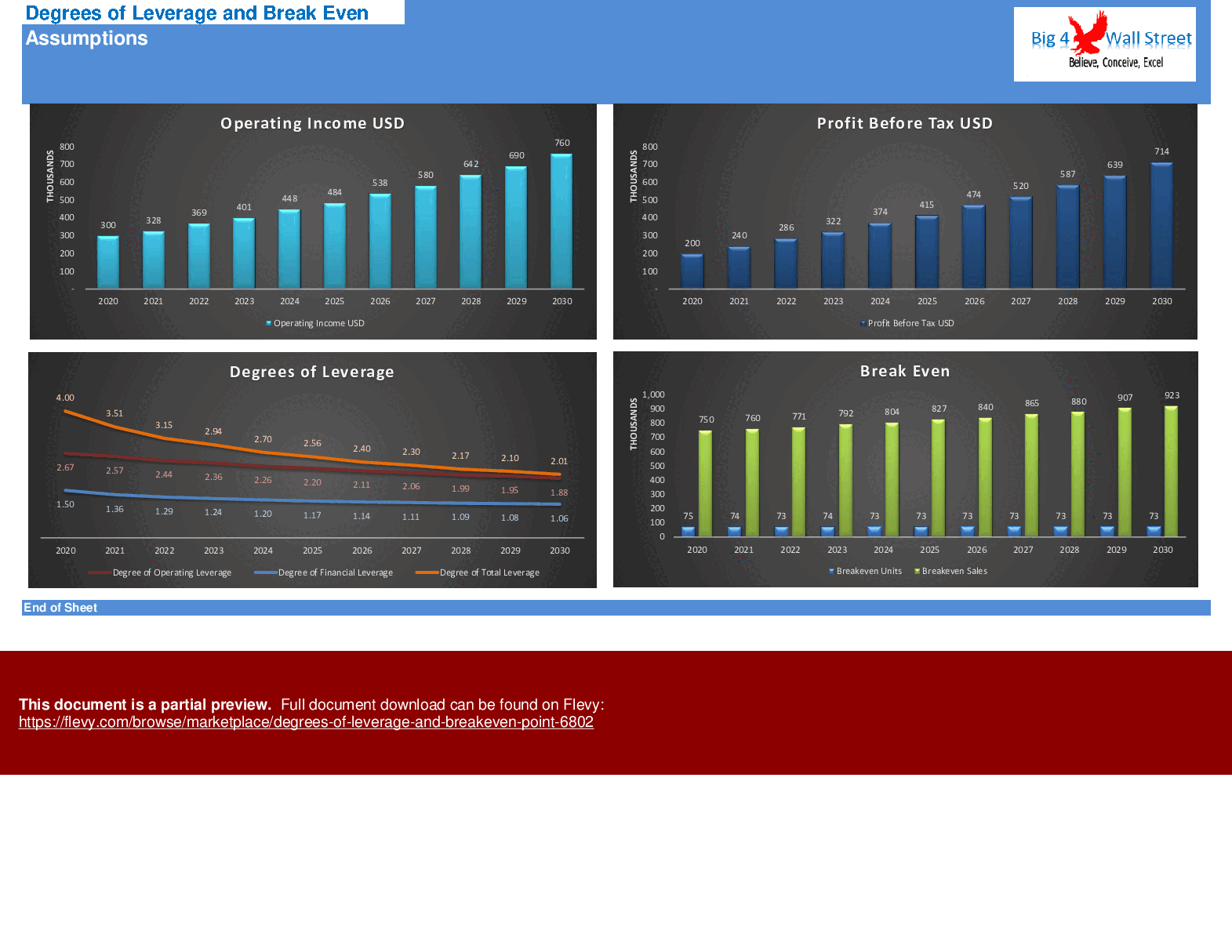
- The breakeven point is calculated based on the assumptions you have set, and then a series of sensitivities is performed along with the relevant graphs.
BREAK EVEN ANALYSIS EXCEL DESCRIPTION
Degrees of leverage and breakeven point model consists of an Excel model which presents various degrees of leverage, such as operating, financial, and total leverage, and how this is related to the breakeven point.
So, a quick overview of the model, in the contents tab you can see the structure of the model and by clicking on any of the headlines to be redirected to the relevant worksheet.
On the manual tab, you can feed the general information for the model such as: model name, responsible, timeline of the model, and date & currency conventions.
Additionally, there is a description of the color-coding of the model in the same tab. Inputs are always depicted with a yellow fill and blue letters, call up (that is direct links from other cells) are filled in light blue with blue letters while calculations are depicted with white fill and black characters. Grey cells are restricted cells which you must not change.
There is also color-coding for the various tabs of the model. Yellow tabs are mostly assumptions tabs, grey tabs are calculations tabs, blue tabs are outputs tabs (that is effectively results or graphs) and finally, light blue tabs are admin tabs (for example: the cover page, and contents).
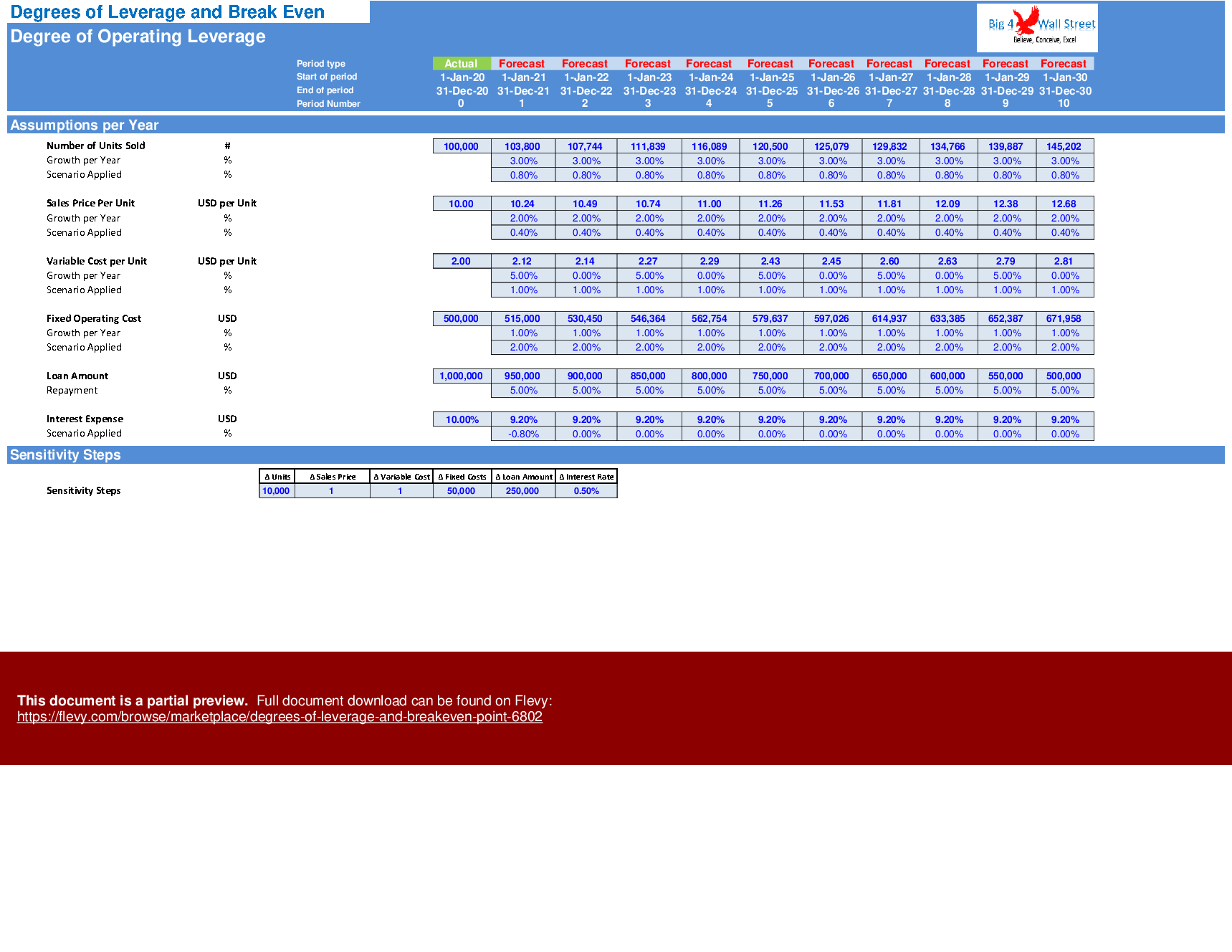
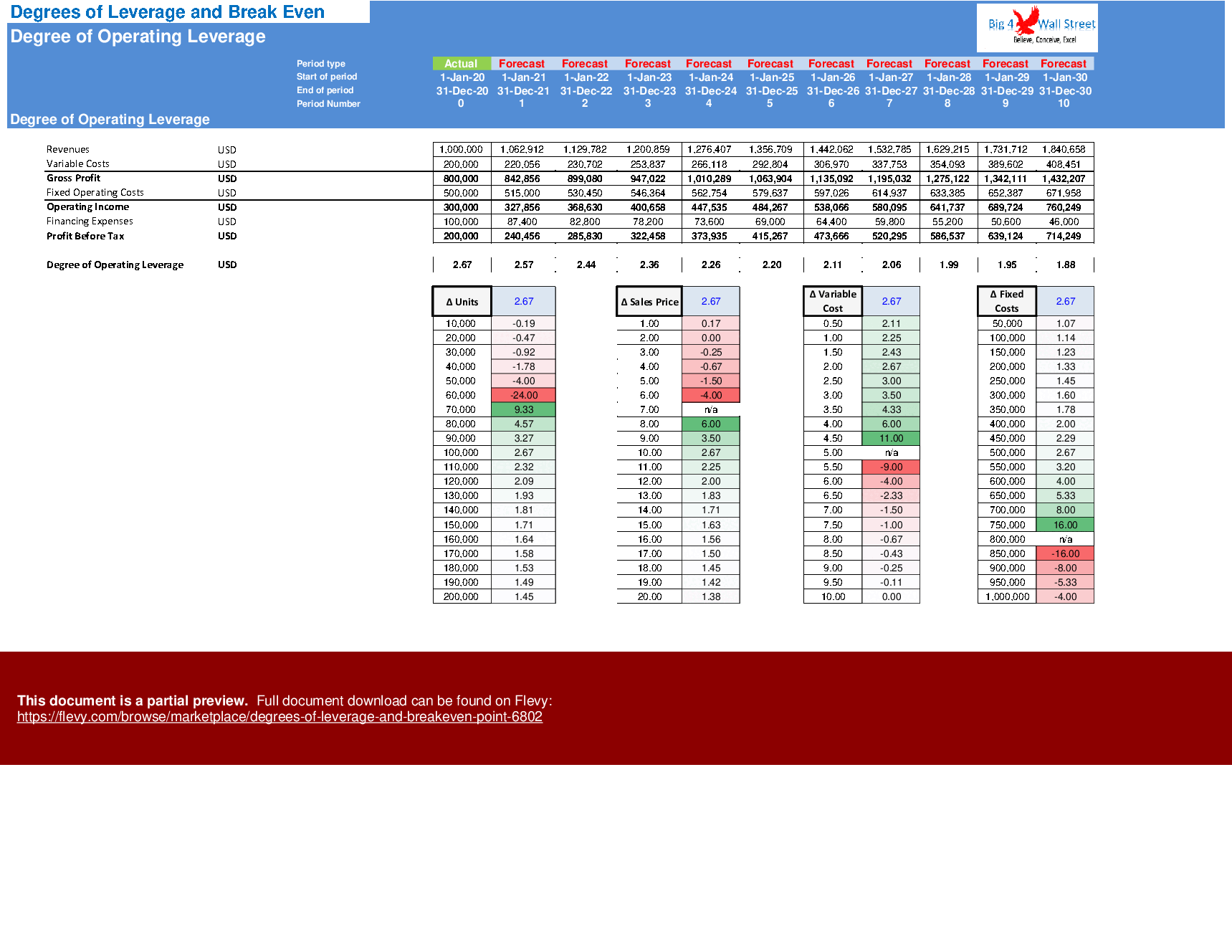
The degree of operating leverage is a measure of how much the operating income of a company changes with a change in sales. Companies with a large proportion of fixed costs per unit to variable costs per unit have higher levels of operating leverage. A high operating leverage means that an increase in sales results in significant changes in profits (both positive and negative). A low operating leverage means that a lower profit is earned on each sale but can cover its fixed costs easier.
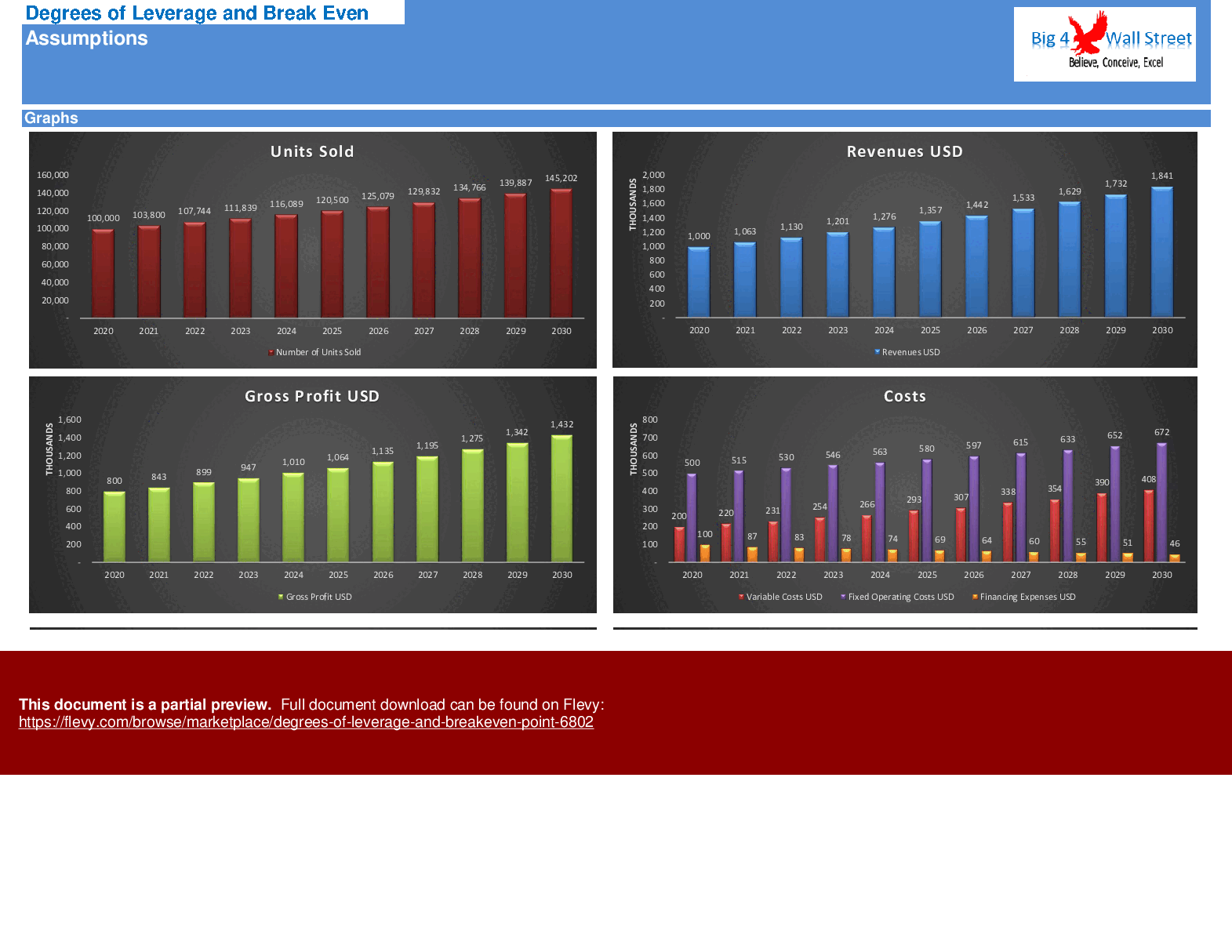
On this tab, the degree of operating leverage is calculated based on the assumptions you have set, and then a series of sensitivities is performed versus the units sold, sales price, variable cost, and fixed costs. The sensitivities are presented with a series of relevant graphs.
The degree of financial leverage measures the sensitivity of a company's profit to changes in operating income. The degree of financial leverage incorporates the impact of a change in the capital structure of the company and its impact on profits.
On this tab, the degree of financial leverage is calculated based on the assumptions you have set, and then a series of sensitivities is performed versus the units sold, sales price, variable cost, fixed costs, loan amount, and interest. The sensitivities are presented with a series of graphs.
The degree of total leverage measures the rate of change in profits to the rate of change from sales. The degree of total leverage combines the effects of operating and financial leverage. On this tab the degree of total leverage is calculated based on the assumptions you have set, and then a series of sensitivities is performed versus the units sold, sales price, variable cost, fixed costs, loan amount, and interest. The sensitivities are presented with a series of graphs.
Managers must make decisions about sales volume, pricing and costs and are concerned about the impact of their decisions on profit. Therefore, they need to understand the relations among revenues, costs, volume, and profit. The break-even point can be defined as the level of activity at which a business makes neither a profit nor loss.
On this tab the breakeven point is calculated based on the assumptions you have set, and then a series of sensitivities is performed along with the relevant graphs.
Got a question about the product? Email us at support@flevy.com or ask the author directly by using the "Ask the Author a Question" form. If you cannot view the preview above this document description, go here to view the large preview instead.
Source: Best Practices in Break Even Analysis Excel: Degrees of Leverage and Breakeven Point Excel (XLSX) Spreadsheet, Big4WallStreet