Buy versus Lease Financial Model (Excel XLSX)
Excel (XLSX) + supplemental PDF
BENEFITS OF THIS EXCEL DOCUMENT
- A professional financial model to compare buy and lease scenarios for production or consumer assets
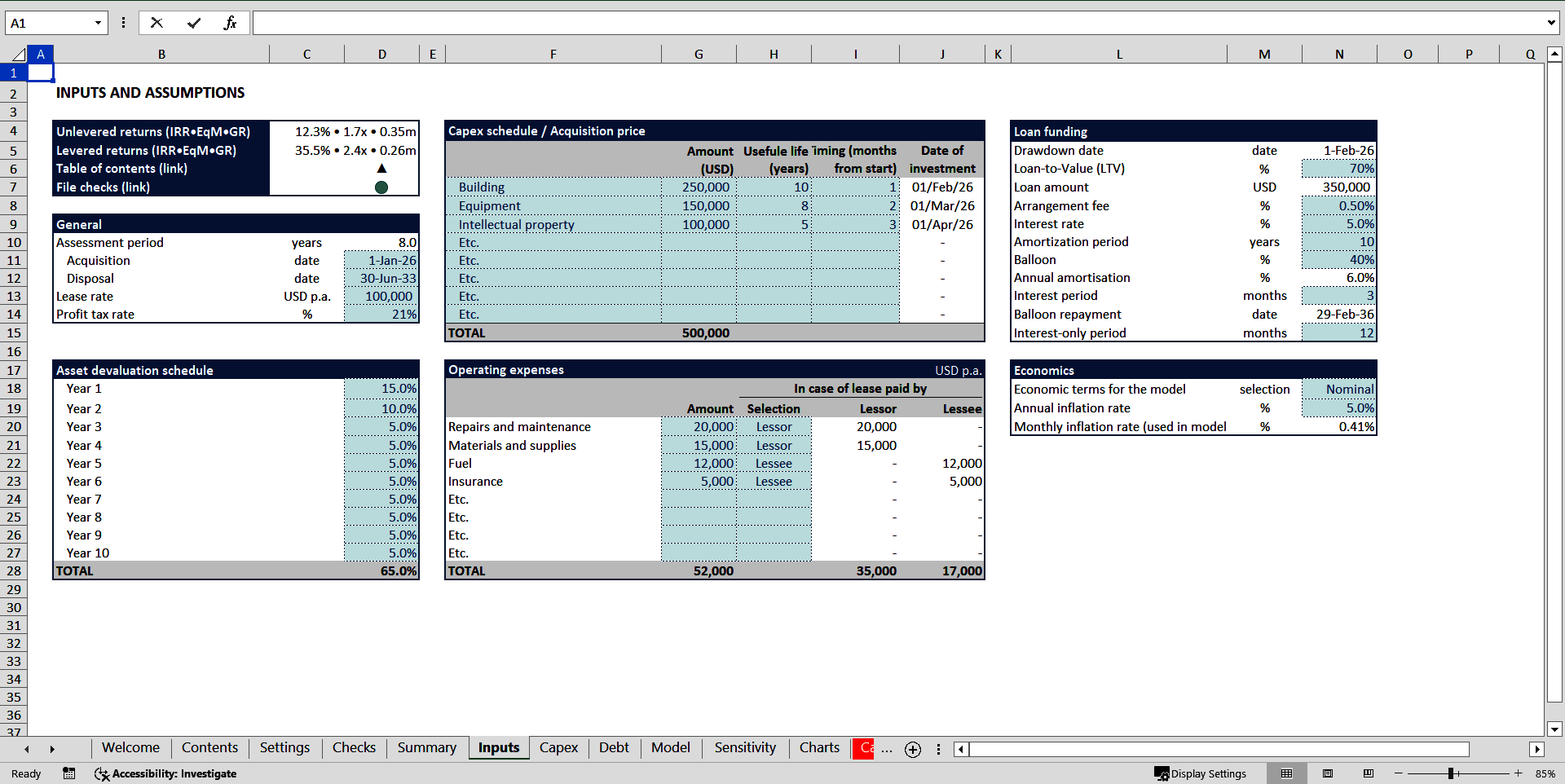
- Incorporates granular inputs
- Produces detailed reports, calculations and charts
REAL ESTATE EXCEL DESCRIPTION
This is a comprehensive and professional yet user-friendly financial model aimed at making a right decision on buying versus leasing of production and consumer-use assets. I have developed this model with those beginning entrepreneurs in mind who are not familiar with sophisticated financial concepts but need an industry grade investment banking quality financial model for their analysis.
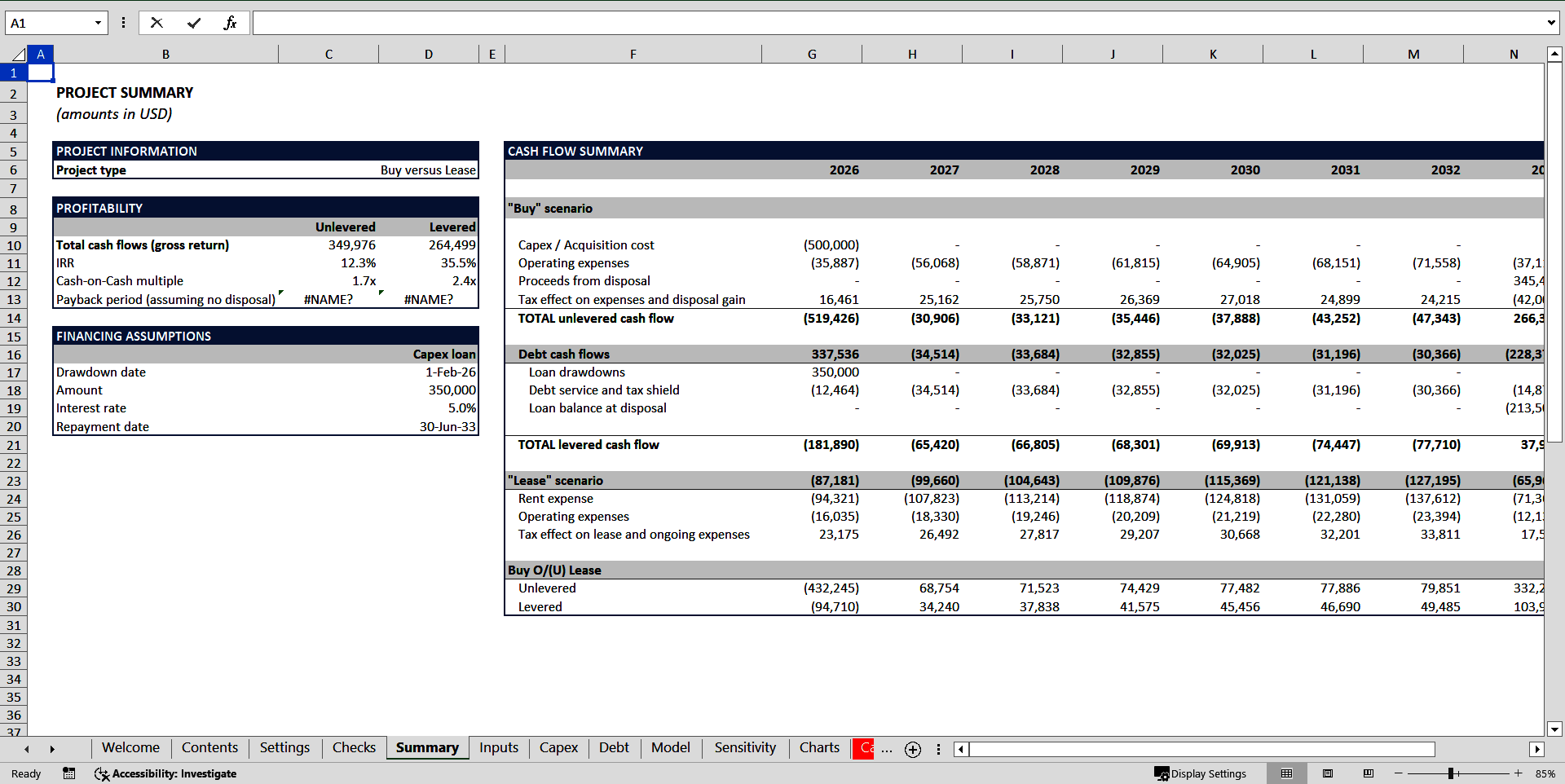
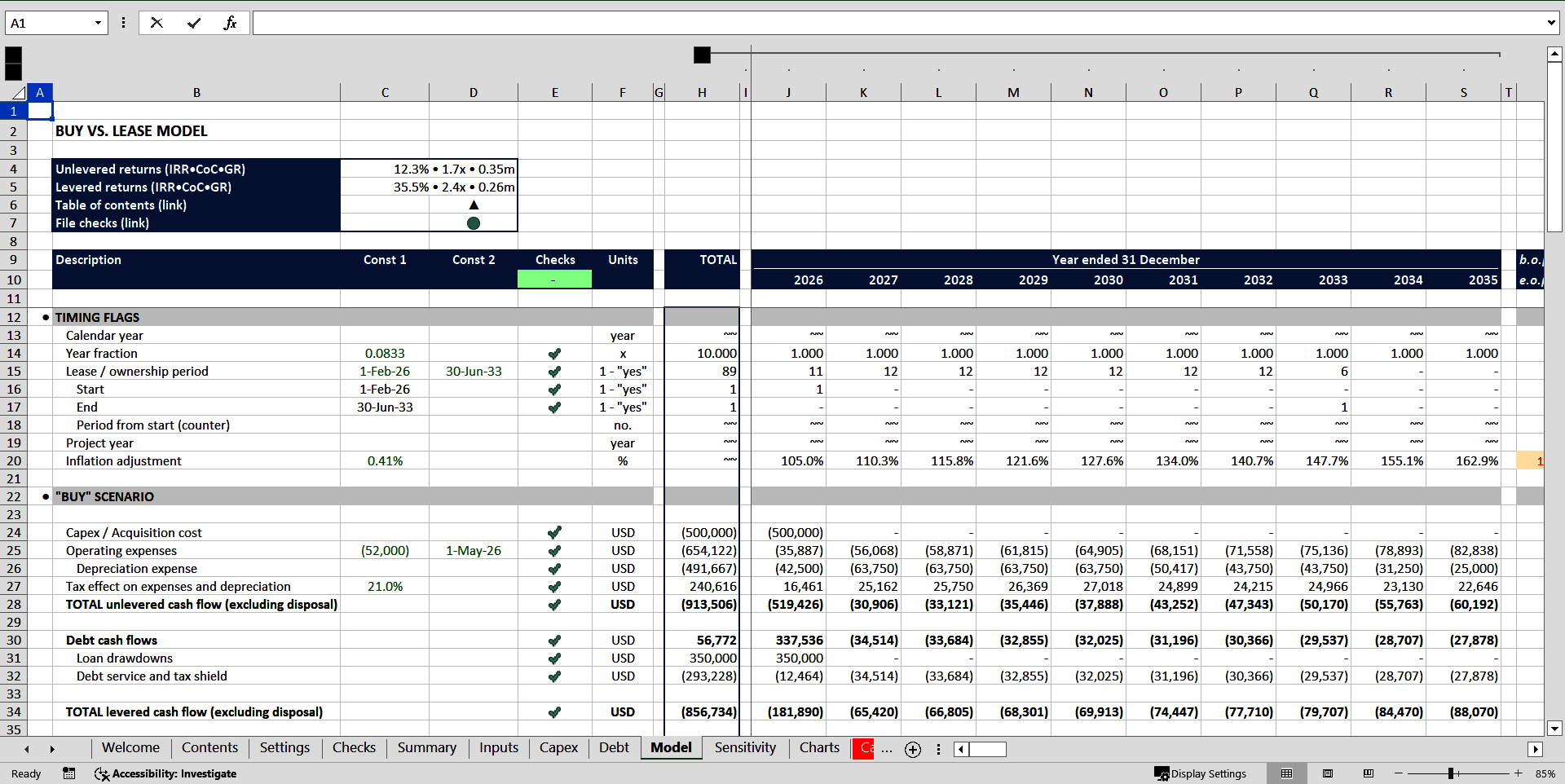
The model calculates and compares the cash flow for buying and leasing strategies.
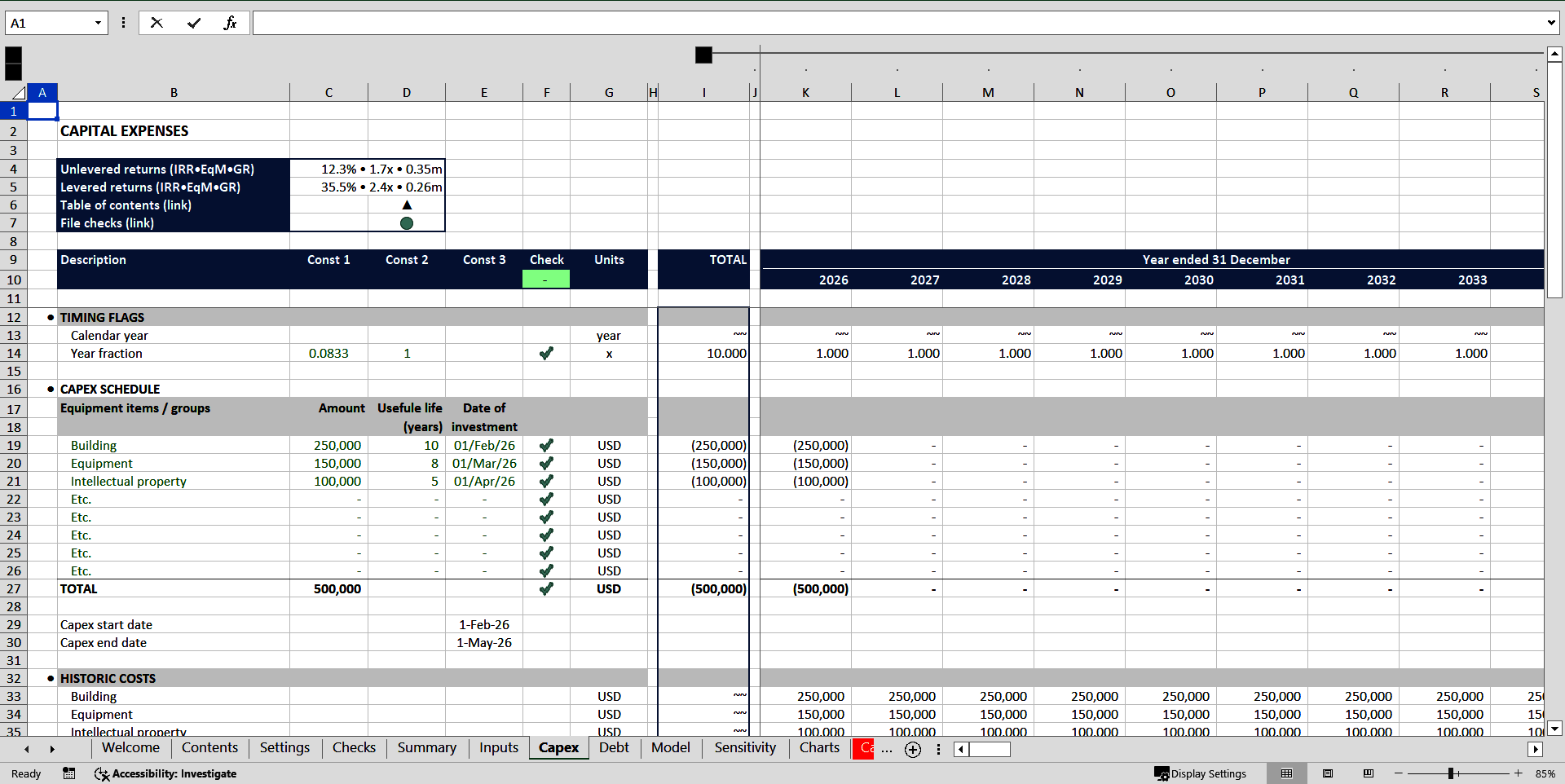
Buying an asset can take a form of a simple acquisition (in case the needed asset is available on the market) or a construction of an asset in line with user's requirements. The construction can include several phases of a capex program.
Once the asset is purchased or constructed, we start using it and incurring operating expenses related to that asset. These can be repairs and maintenance, materials and supplies, fuel, insurance and many else. If we buy an asset, all those expenses are on us; if we lease it, it is subject to an agreement between lessor and lessee on who pays which expenses.
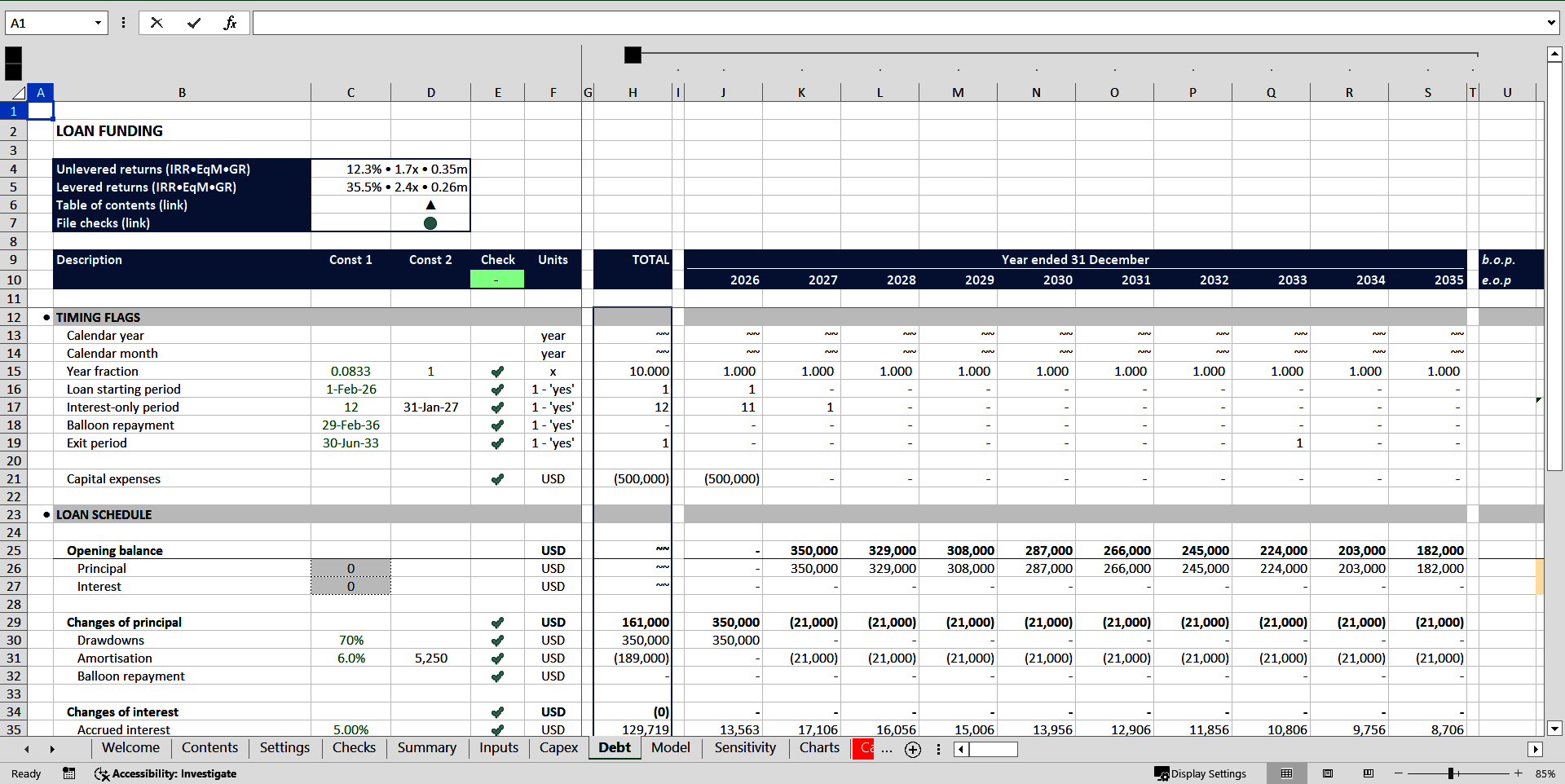
Acquisition can be partly financed by debt. Drawing debt at right terms provides leverage and increases returns significantly. In this model you can assume the debt is used to finance the acquisition and choose the LTV ratio and other loan conditions.
Operating expenses, depreciation and interest expenses create a tax shield, which means they reduce the owner's taxable profit, entailing smaller amounts of profit tax.
The final stage of the analysis is calculating exit proceed (or terminal value). This is needed for proper valuation and profitability assessment, even if the asset owners are not planning to dispose it at that point of time.
Lease scenario assumes rental payments, payments of expenses as agreed with the owner of the asset and a tax shield on lease payments and operating expenses.
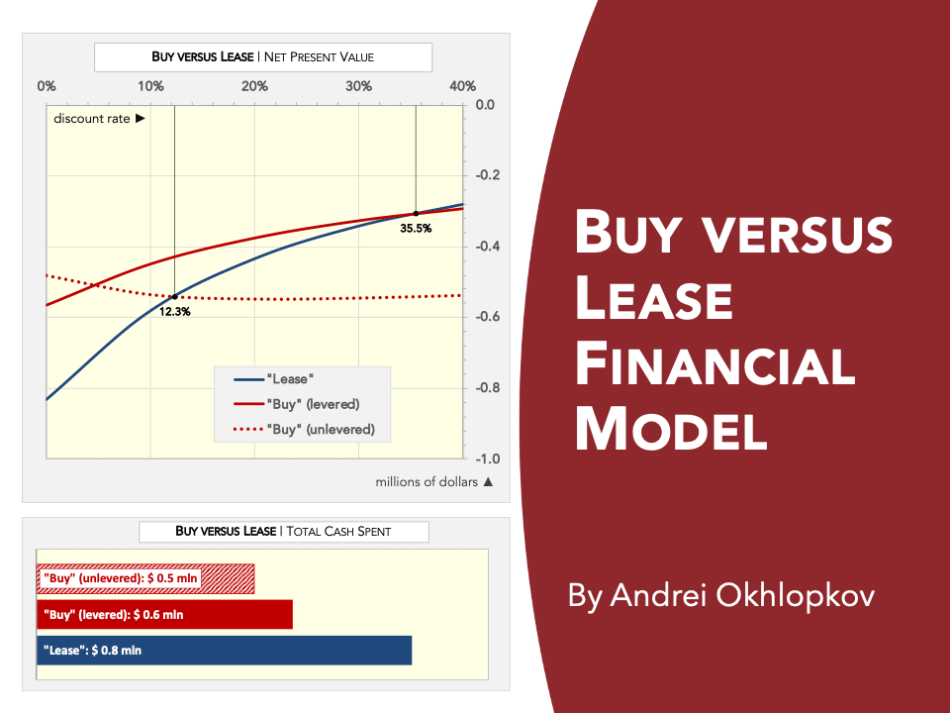
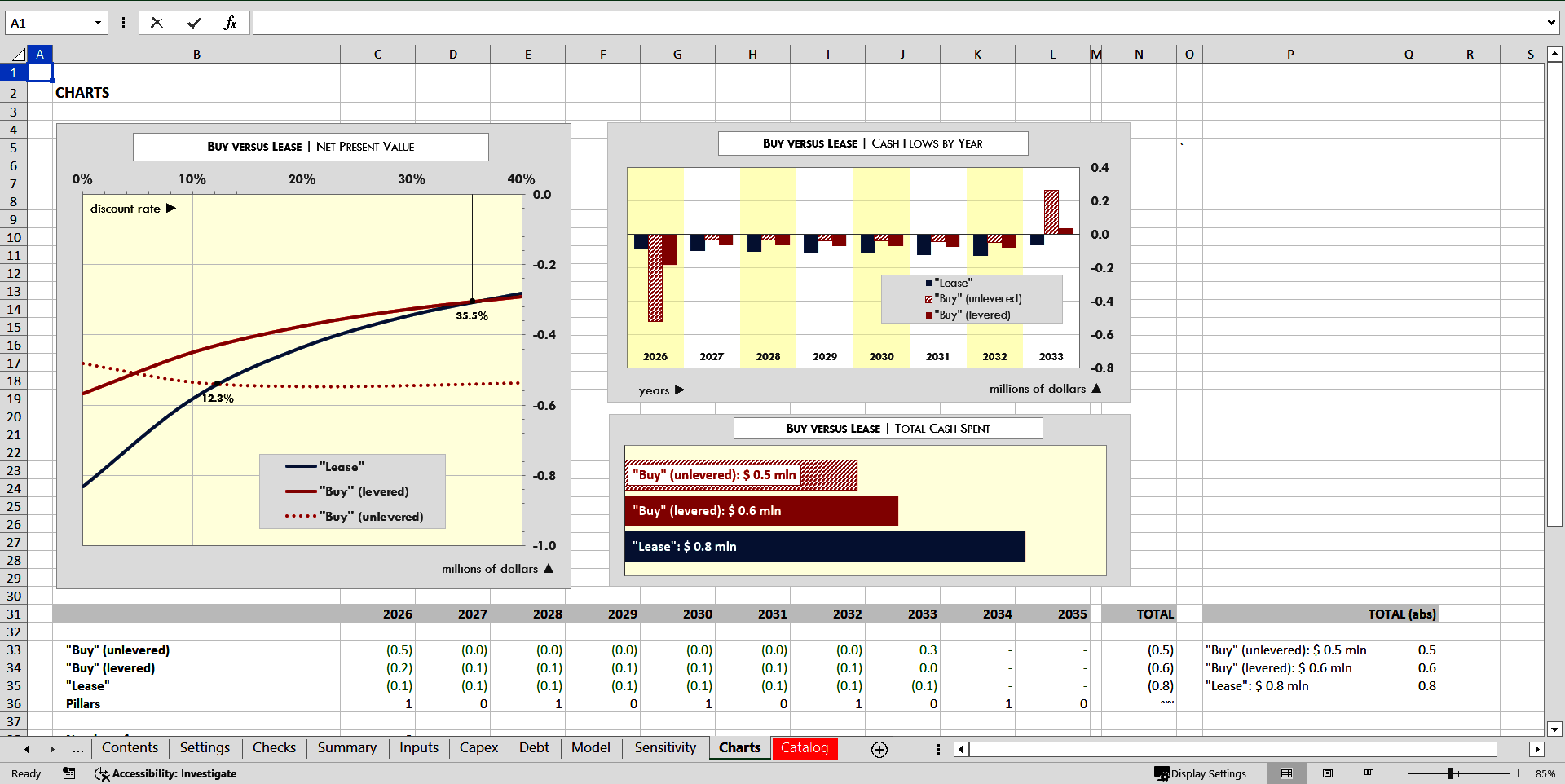
Teamed up together in the model, these assumptions and schedules are used to calculate which option is more beneficial, calculate the pay-back period, internal rate of return (IRR), cash-on-cash (CoC) multiple, break-even points of buying (levered and unlevered) versus leasing scenarios and other KPIs.
You can run the model with and without economic assumptions (inflation).
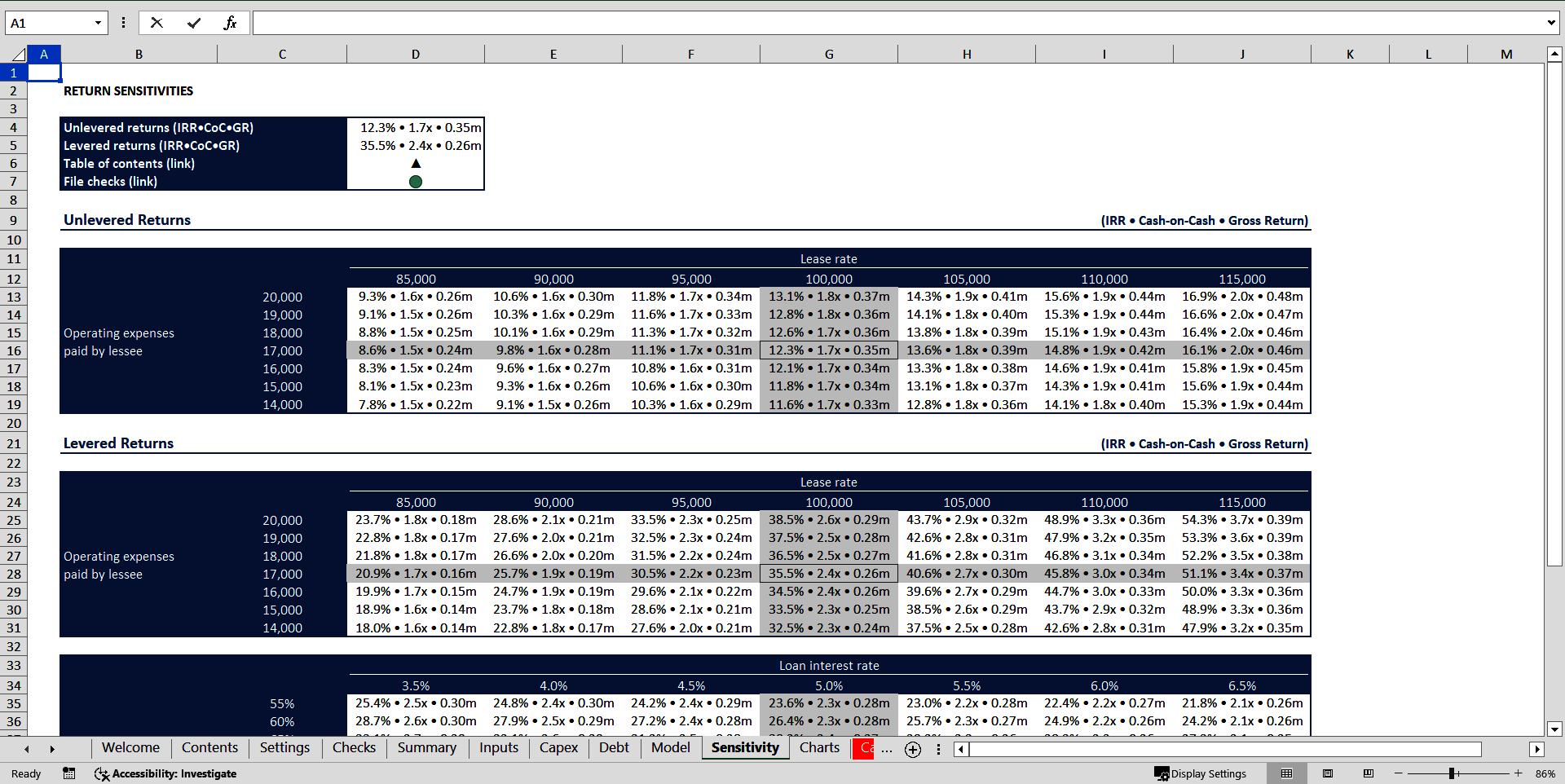
The model also calculates the sensitivity of output parameters to changes in lease rates, operating expenses paid by the lessee, loan-to-value ratio and interest rate on debt.
The model is illustrated by professionally designed magazine-quality charts.
Got a question about the product? Email us at support@flevy.com or ask the author directly by using the "Ask the Author a Question" form. If you cannot view the preview above this document description, go here to view the large preview instead.
Source: Best Practices in Real Estate Excel: Buy versus Lease Financial Model Excel (XLSX) Spreadsheet, Andrei Okhlopkov